|
Borophene
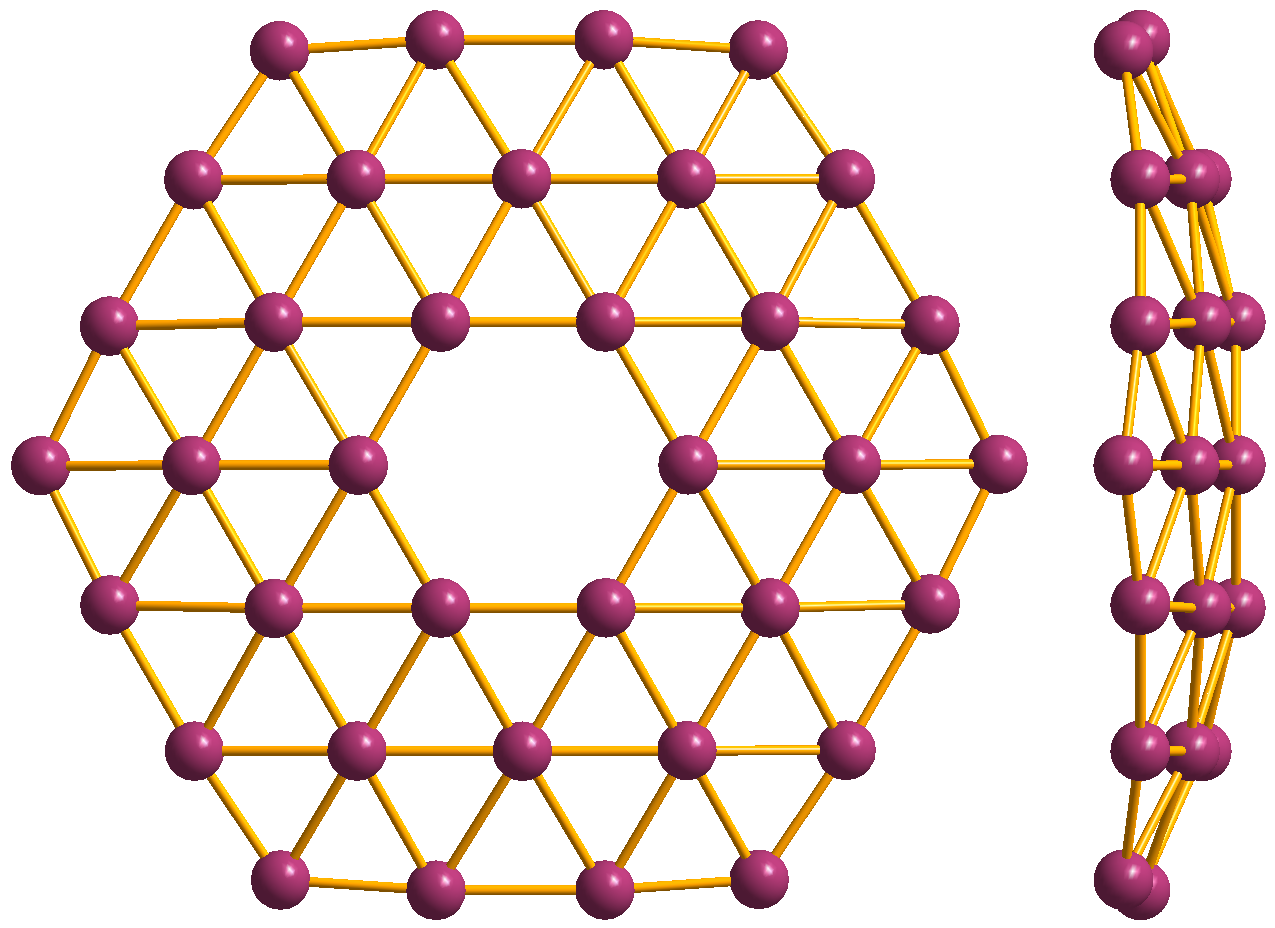
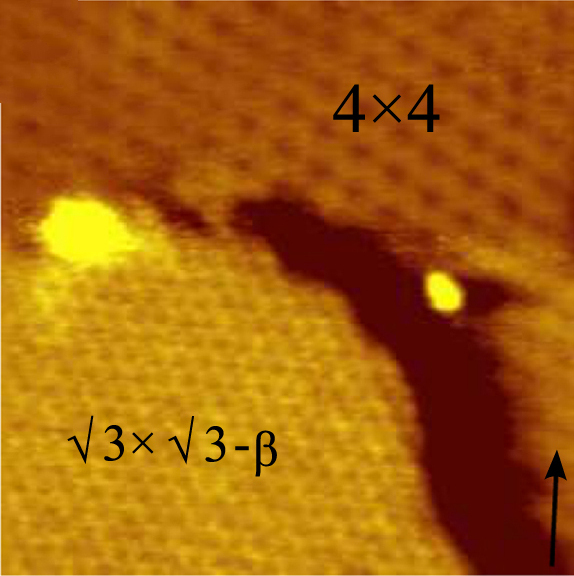
Borophene is a crystalline atomic monolayer of boron, i.e., it is a two-dimensional allotrope of boron and also known as ''boron sheet''. First predicted by theory in the mid-1990s, different borophene structures were experimentally confirmed in 2015. Properties Experimentally various atomically thin, crystalline and metallic borophenes were synthesized on clean metal surfaces under ultrahigh-vacuum conditions. Its atomic structure consists of mixed triangular and hexagonal motifs, such as shown in Figure 1. The atomic structure is a consequence of an interplay between two-center and multi-center in-plane bonding, which is typical for electron deficient elements like boron. Borophenes exhibit in-plane elasticity and ideal strength. It can be stronger than graphene, and more flexible, in some configurations. Boron nanotubes are also stiffer than graphene, with a higher 2D Young's modulus than any other known carbon and noncarbon nanostructures. Borophenes undergo novel stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borophene
Borophene is a crystalline atomic monolayer of boron, i.e., it is a two-dimensional allotrope of boron and also known as ''boron sheet''. First predicted by theory in the mid-1990s, different borophene structures were experimentally confirmed in 2015. Properties Experimentally various atomically thin, crystalline and metallic borophenes were synthesized on clean metal surfaces under ultrahigh-vacuum conditions. Its atomic structure consists of mixed triangular and hexagonal motifs, such as shown in Figure 1. The atomic structure is a consequence of an interplay between two-center and multi-center in-plane bonding, which is typical for electron deficient elements like boron. Borophenes exhibit in-plane elasticity and ideal strength. It can be stronger than graphene, and more flexible, in some configurations. Boron nanotubes are also stiffer than graphene, with a higher 2D Young's modulus than any other known carbon and noncarbon nanostructures. Borophenes undergo novel stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-dimensional Materials
In materials science, the term single-layer materials or 2D materials refers to crystalline solids consisting of a single layer of atoms. These materials are promising for some applications but remain the focus of research. Single-layer materials derived from single elements generally carry the -ene suffix in their names, e.g. graphene. Single-layer materials that are compounds of two or more elements have -ane or -ide suffixes. 2D materials can generally be categorized as either 2D allotropes of various elements or as compounds (consisting of two or more covalently bonding elements). It is predicted that there are hundreds of stable single-layer materials. The atomic structure and calculated basic properties of these and many other potentially synthesisable single-layer materials, can be found in computational databases. 2D materials can be produced using mainly two approaches: top-down exfoliation and bottom-up synthesis. The exfoliation methods include sonication, mechanical, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lai-Sheng Wang
Lai-Sheng Wang (, born 1961 in Henan, China) is an experimental physical chemist currently serving as the Chair of the Chemistry Department at Brown University. Wang is known for his work on atomic gold pyramids and planar boron clusters. Education Wang obtained a B.S. degree in Chemistry from Wuhan University in 1982, and a Ph.D. in Chemistry from the University of California, Berkeley in 1990. He completed his postdoctoral stay at Rice University before moving to Richland, WA in 1993 to accept a joint position between Washington State University and Pacific Northwest National Laboratory. In 2009 he moved to Brown University, where he teaches physical chemistry and conducts research. He was named the Jesse H. and Louisa D. Sharpe Metcalf Professor of Chemistry in 2015 and Chair of the Department in 2019. Research Throughout his career, Wang has predominately studied nanoclusters and solution-phase chemistry in the gas phase, focusing on the fundamental behaviors of nanoclust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borospherene
Borospherene (B40) is a cluster molecule containing 40 boron atoms. It is similar to buckminsterfullerene, the "spherical" carbon structure, but with a different symmetry. The discovery of borospherene was announced in July 2014, and is described in the journal ''Nature Chemistry''. Borospherene is similar to other cluster molecules, including buckminsterfullerene (C60), stannaspherene, and plumbaspherene. The molecule includes unusual heptagonal faces. Structure Borospherene has a unique axis of symmetry (a 180° rotation), so it is not really "spherical" like buckminsterfullerene (which has icosahedral symmetry). Its symmetry group is D2d (antiprismatic symmetry, like a baseball). It includes 48 boron triangles between four seven-sided rings and two six-membered rings. There are four sets of eight equivalent boron atoms, and two sets of four equivalent atoms. Each boron atom binds to four or five other boron atoms (see illustration in article from Brown University). Lai-Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allotropes Of Boron
Boron can be prepared in several crystalline and amorphous forms. Well known crystalline forms are α-rhombohedral (α-R), β-rhombohedral (β-R), and β-tetragonal (β-T). In special circumstances, boron can also be synthesized in the form of its α-tetragonal (α-T) and γ-orthorhombic (γ) allotropes. Two amorphous forms, one a finely divided powder and the other a glassy solid, are also known. Although at least 14 more allotropes have been reported, these other forms are based on tenuous evidence or have not been experimentally confirmed, or are thought to represent mixed allotropes, or boron frameworks stabilized by impurities. Whereas the β-rhombohedral phase is the most stable and the others are metastable, the transformation rate is negligible at room temperature, and thus all five phases can exist at ambient conditions. Amorphous powder boron and polycrystalline β-rhombohedral boron are the most common forms. The latter allotrope is a very hardVickers hardness comparab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphene
Graphene () is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice nanostructure. "Carbon nanostructures for electromagnetic shielding applications", Mohammed Arif Poothanari, Sabu Thomas, et al., ''Industrial Applications of Nanomaterials'', 2019. "Carbon nanostructures include various low-dimensional allotropes of carbon including carbon black (CB), carbon fiber, carbon nanotubes (CNTs), fullerene, and graphene." The name is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, reflecting the fact that the allotrope of carbon contains numerous double bonds. Each atom in a graphene sheet is connecte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicene
Silicene is a two-dimensional allotrope of silicon, with a hexagonal honeycomb structure similar to that of graphene. Contrary to graphene, silicene is not flat, but has a periodically buckled topology; the coupling between layers in silicene is much stronger than in multilayered graphene; and the oxidized form of silicene, 2D silica, has a very different chemical structure from graphene oxide. History Although theorists had speculated about the existence and possible properties of free-standing silicene, researchers first observed silicon structures that were suggestive of silicene in 2010. Using a scanning tunneling microscope they studied self-assembled silicene nanoribbons and silicene sheets deposited onto a silver crystal, Ag(110) and Ag(111), with atomic resolution. The images revealed hexagons in a honeycomb structure similar to that of graphene, which, however, were shown to originate from the silver surface mimicking the hexagons. Density functional theory (DFT) cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borospherene
Borospherene (B40) is a cluster molecule containing 40 boron atoms. It is similar to buckminsterfullerene, the "spherical" carbon structure, but with a different symmetry. The discovery of borospherene was announced in July 2014, and is described in the journal ''Nature Chemistry''. Borospherene is similar to other cluster molecules, including buckminsterfullerene (C60), stannaspherene, and plumbaspherene. The molecule includes unusual heptagonal faces. Structure Borospherene has a unique axis of symmetry (a 180° rotation), so it is not really "spherical" like buckminsterfullerene (which has icosahedral symmetry). Its symmetry group is D2d (antiprismatic symmetry, like a baseball). It includes 48 boron triangles between four seven-sided rings and two six-membered rings. There are four sets of eight equivalent boron atoms, and two sets of four equivalent atoms. Each boron atom binds to four or five other boron atoms (see illustration in article from Brown University). Lai-Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aufbau Principle
The aufbau principle , from the German ''Aufbauprinzip'' (building-up principle), also called the aufbau rule, states that in the ground state of an atom or ion, electrons fill subshells of the lowest available energy, then they fill subshells of higher energy. For example, the 1s subshell is filled before the 2s subshell is occupied. In this way, the electrons of an atom or ion form the most stable electron configuration possible. An example is the configuration for the phosphorus atom, meaning that the 1s subshell has 2 electrons, and so on. Electron behavior is elaborated by other principles of atomic physics, such as Hund's rule and the Pauli exclusion principle. Hund's rule asserts that if multiple orbitals of the same energy are available, electrons will occupy different orbitals singly and with the same spin before any are occupied doubly. If double occupation does occur, the Pauli exclusion principle requires that electrons that occupy the same orbital must have differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogenation, C=C (and other) bonds ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogenated
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic compounds. Hydrogenation typically constitutes the addition of pairs of hydrogen atoms to a molecule, often an alkene. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces double and triple bonds in hydrocarbons. Process Hydrogenation has three components, the unsaturated substrate, the hydrogen (or hydrogen source) and, invariably, a catalyst. The reduction reaction is carried out at different temperatures and pressures depending upon the substrate and the activity of the catalyst. Related or competing reactions The same catalysts and conditions that are used for hydrogenation reactions can also lead to isomerization of the alkenes from cis to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scanning Tunneling Spectroscopy
Scanning tunneling spectroscopy (STS), an extension of scanning tunneling microscopy (STM), is used to provide information about the density of electrons in a sample as a function of their energy. In scanning tunneling microscopy, a metal tip is moved over a conducting sample without making physical contact. A bias voltage applied between the sample and tip allows a current to flow between the two. This is as a result of quantum tunneling across a barrier; in this instance, the physical distance between the tip and the sample The scanning tunneling microscope is used to obtain "topographs" - topographic maps - of surfaces. The tip is rastered across a surface and (in constant current mode), a constant current is maintained between the tip and the sample by adjusting the height of the tip. A plot of the tip height at all measurement positions provides the topograph. These topographic images can obtain atomically resolved information on metallic and semi-conducting surfaces Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |