|
Bordonúa
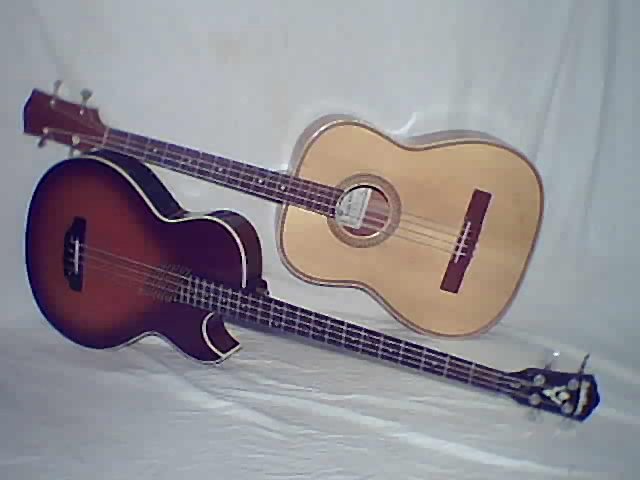
The Bordonua (Bordonúa) is a large, deep body (sound-boxes are usually deep) bass guitar which is native to Puerto Rico. They are made using several different shapes and sizes. The Bordonúa is the least common of the three stringed instruments that make up the Puerto Rican ''orquesta jibara'' (i.e., the cuatro, the tiple and the Bordonúa). The Bordonua usually has three sound holes, with a large central one and two smaller ones in the two corners of the upper bout. The usual body shape is quite slender and tapers in towards the top, however there is a wide variety of other designs also. History The original Bordonua is said to have evolved from the old 16th century Spanish Acoustic bass guitar called the ''Bajo de la Una''. There were also special melodic Bordonuas that were used during the 1920s and 1930s as accompaniment to melody instead of the bass role. These were oddly tuned like a tiple. This configuration is no longer used on the island. They are also related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bordonua Plan
The Bordonua (Bordonúa) is a large, deep body (sound-boxes are usually deep) bass guitar which is native to Puerto Rico. They are made using several different shapes and sizes. The Bordonúa is the least common of the three stringed instruments that make up the Puerto Rican ''orquesta jibara'' (i.e., the cuatro, the tiple and the Bordonúa). The Bordonua usually has three sound holes, with a large central one and two smaller ones in the two corners of the upper bout. The usual body shape is quite slender and tapers in towards the top, however there is a wide variety of other designs also. History The original Bordonua is said to have evolved from the old 16th century Spanish Acoustic bass guitar called the ''Bajo de la Una''. There were also special melodic Bordonuas that were used during the 1920s and 1930s as accompaniment to melody instead of the bass role. These were oddly tuned like a tiple. This configuration is no longer used on the island. They are also related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bordonua
The Bordonua (Bordonúa) is a large, deep body (sound-boxes are usually deep) bass guitar which is native to Puerto Rico. They are made using several different shapes and sizes. The Bordonúa is the least common of the three stringed instruments that make up the Puerto Rican ''orquesta jibara'' (i.e., the cuatro, the tiple and the Bordonúa). The Bordonua usually has three sound holes, with a large central one and two smaller ones in the two corners of the upper bout. The usual body shape is quite slender and tapers in towards the top, however there is a wide variety of other designs also. History The original Bordonua is said to have evolved from the old 16th century Spanish Acoustic bass guitar called the ''Bajo de la Una''. There were also special melodic Bordonuas that were used during the 1920s and 1930s as accompaniment to melody instead of the bass role. These were oddly tuned like a tiple. This configuration is no longer used on the island. They are also related to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuatro (Puerto Rico)
The Puerto Rican cuatro (Spanish: cuatro puertorriqueño) is the national instrument of Puerto Rico. It belongs to the lute family of string instruments, and is guitar-like in function, but with a shape closer to that of the violin. The word ''cuatro'' means "four", which was the total number of strings of the earliest Puerto Rican instrument known by the ''cuatro'' name. The current cuatro has ten strings in five courses, tuned, in fourths, from low to high B3 B2♦E4 E3♦A3 A3♦D4 D4♦G4 G4 (note that the bottom two pairs are in octaves, while the top three pairs are tuned in unison), and a scale length of 500-520 millimetres. The cuatro is the most familiar of the three instruments which make up the Puerto Rican jíbaro orchestra (the cuatro, the tiple and the bordonúa). A cuatro player is called a ''cuatrista''. This instrument has had its prominent performers like Andrés Jiménez, Edwin Colón Zayas, Yomo Toro, Iluminado Davila Medina and the maestro Maso Rivera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
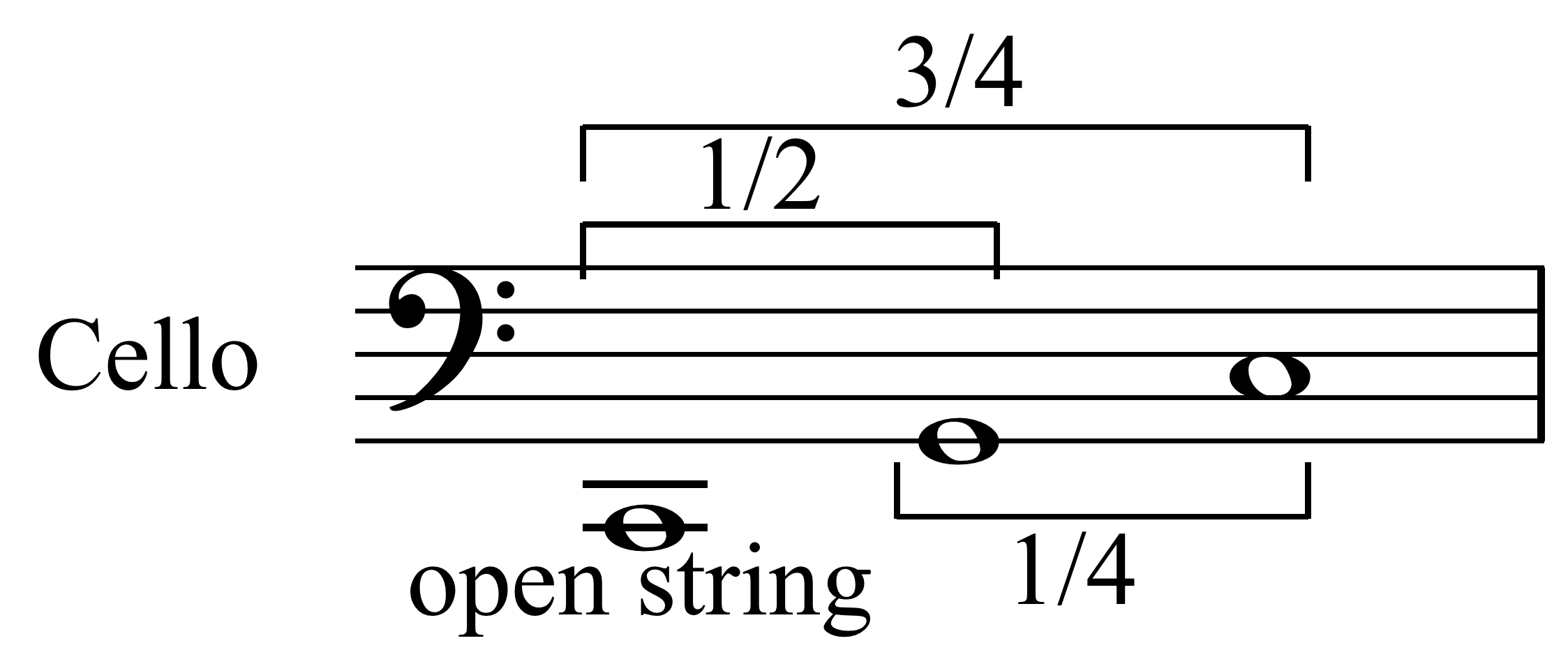
String Instrument
String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner. Musicians play some string instruments by plucking the strings with their fingers or a plectrum—and others by hitting the strings with a light wooden hammer or by rubbing the strings with a bow. In some keyboard instruments, such as the harpsichord, the musician presses a key that plucks the string. Other musical instruments generate sound by striking the string. With bowed instruments, the player pulls a rosined horsehair bow across the strings, causing them to vibrate. With a hurdy-gurdy, the musician cranks a wheel whose rosined edge touches the strings. Bowed instruments include the string section instruments of the orchestra in Western classical music (violin, viola, cello and double bass) and a number of other instruments (e.g., viols and gambas used in early music from the Baro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accompaniment
Accompaniment is the musical part which provides the rhythmic and/or harmonic support for the melody or main themes of a song or instrumental piece. There are many different styles and types of accompaniment in different genres and styles of music. In homophonic music, the main accompaniment approach used in popular music, a clear vocal melody is supported by subordinate chords. In popular music and traditional music, the accompaniment parts typically provide the "beat" for the music and outline the chord progression of the song or instrumental piece. The accompaniment for a vocal melody or instrumental solo can be played by a single musician playing an instrument such as piano, pipe organ, or guitar. While any instrument can in theory be used as an accompaniment instrument, keyboard and guitar-family instruments tend to be used if there is only a single instrument, as these instruments can play chords and basslines simultaneously (chords and a bassline are easier to pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiple
A tiple (, literally treble or soprano), is a plucked typically 12-string chordophone of the guitar family. A tiple player is called a ''tiplista''. The first mention of the tiple comes from musicologist Pablo Minguet e Irol in 1752. Although many variations of the instrument exist, the tiple is mostly associated with Colombia, and is considered the national instrument. The Puerto Rican version characteristically has fewer strings, as do variants from Cuba, Mallorca, and elsewhere among countries of Hispanic origin. Tiple family Colombian tiple The Colombian tiple (in Spanish: ''tiple'') is an instrument of the guitar family, similar in appearance although slightly smaller (about 18%) than a standard classical guitar. The typical fretboard scale is about 530 mm (just under 21 inches), and the neck joins the body at the 12th fret. There are 12 strings, grouped in four tripled courses. Traditional tuning from lowest to highest course is C E A D, although many modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandurria
The bandurria is a plucked chordophone from Spain, similar to the mandolin and bandola, primarily used in Spanish folk music, but also found in former Spanish colonies. Instrument development Prior to the 18th century, the bandurria had a round back, similar or related to the mandore. It had become a flat-backed instrument by the 18th century, with five double courses of strings, tuned in fourths. The original bandurrias of the Medieval period had three strings. During the Renaissance they gained a fourth string. During the Baroque period the bandurria had 10 strings (5 pairs). The modern bandurria has 12 strings (6 pairs). The strings are tuned in unison pairs, going up in fourths from the low G#. The lowest four strings are a major-third above those of a standard guitar and the highest two strings are a fourth above a standard guitar, i.e. G, c, f, b, e and a. File:bandurria1.jpg, Bandurria (front view) File:Bandurria2.JPG, Bandurria (back view) File:bandurria3.jpg, Bandurri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folk Music
Folk music is a music genre that includes traditional folk music and the contemporary genre that evolved from the former during the 20th-century folk revival. Some types of folk music may be called world music. Traditional folk music has been defined in several ways: as music transmitted orally, music with unknown composers, music that is played on traditional instruments, music about cultural or national identity, music that changes between generations (folk process), music associated with a people's folklore, or music performed by custom over a long period of time. It has been contrasted with commercial and classical styles. The term originated in the 19th century, but folk music extends beyond that. Starting in the mid-20th century, a new form of popular folk music evolved from traditional folk music. This process and period is called the (second) folk revival and reached a zenith in the 1960s. This form of music is sometimes called contemporary folk music or folk rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vihuela
The vihuela () is a 15th-century fretted plucked Spanish string instrument, shaped like a guitar (figure-of-eight form offering strength and portability) but tuned like a lute. It was used in 15th- and 16th-century Spain as the equivalent of the lute in Italy and has a large resultant repertory. There were usually five or six doubled strings. A bowed version, the vihuela de arco (arco meaning bow), was conceived in Spain and made in Italy from 1480. One consequence was the phrase vihuela de mano being thereafter applied to the original plucked instrument. The term ''vihuela'' became "viola" in Italian ("viole" in Fr.; "viol" in Eng.), and the bowed vihuela de arco was to serve as a prototype in the hands of the Italian craftsmen for the " da gamba" family of fretted bowed string instruments, as developed starting in 1480. Their vihuela-inherited frets made these easier to play in tune than the rebec family (precursors of the " da braccio" family), and so they became popular for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg , image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg , national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond") , national_anthem = (English: "Royal March") , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Madrid , coordinates = , largest_city = Madrid , languages_type = Official language , languages = Spanish language, Spanish , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = , ethnic_groups_ref = , religion = , religion_ref = , religion_year = 2020 , demonym = , government_type = Unitary state, Unitary Parliamentary system, parliamentary constitutional monarchy , leader_title1 = Monarchy of Spain, Monarch , leader_name1 = Felipe VI , leader_title2 = Prime Minister of Spain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustic Bass Guitar
The acoustic bass guitar (sometimes shortened to acoustic bass or initialized ABG) is a bass instrument with a hollow wooden body similar to, though usually larger than a steel-string acoustic guitar. Like the traditional electric bass guitar and the double bass, the acoustic bass guitar commonly has four strings, which are normally tuned E-A-D-G, an octave below the lowest four strings of the 6-string guitar, which is the same tuning pitch as an electric bass guitar. Because it can sometimes be difficult to hear an acoustic bass guitar without an amplifier, even in settings with other acoustic instruments, most acoustic basses have pickups, either magnetic or piezoelectric or both, so that they can be amplified with a bass amp. Traditional music of Mexico features several varieties of acoustic bass guitars, such as the guitarrón, a very large, deep-bodied Mexican 6-string acoustic bass guitar played in Mariachi bands, the león, plucked with a pick, and the bajo sexto, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordophone
String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner. Musicians play some string instruments by plucking the strings with their fingers or a plectrum—and others by hitting the strings with a light wooden hammer or by rubbing the strings with a bow. In some keyboard instruments, such as the harpsichord, the musician presses a key that plucks the string. Other musical instruments generate sound by striking the string. With bowed instruments, the player pulls a rosined horsehair bow across the strings, causing them to vibrate. With a hurdy-gurdy, the musician cranks a wheel whose rosined edge touches the strings. Bowed instruments include the string section instruments of the orchestra in Western classical music (violin, viola, cello and double bass) and a number of other instruments (e.g., viols and gambas used in early music from the Baroque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |