|
Blockade Of La Rochelle
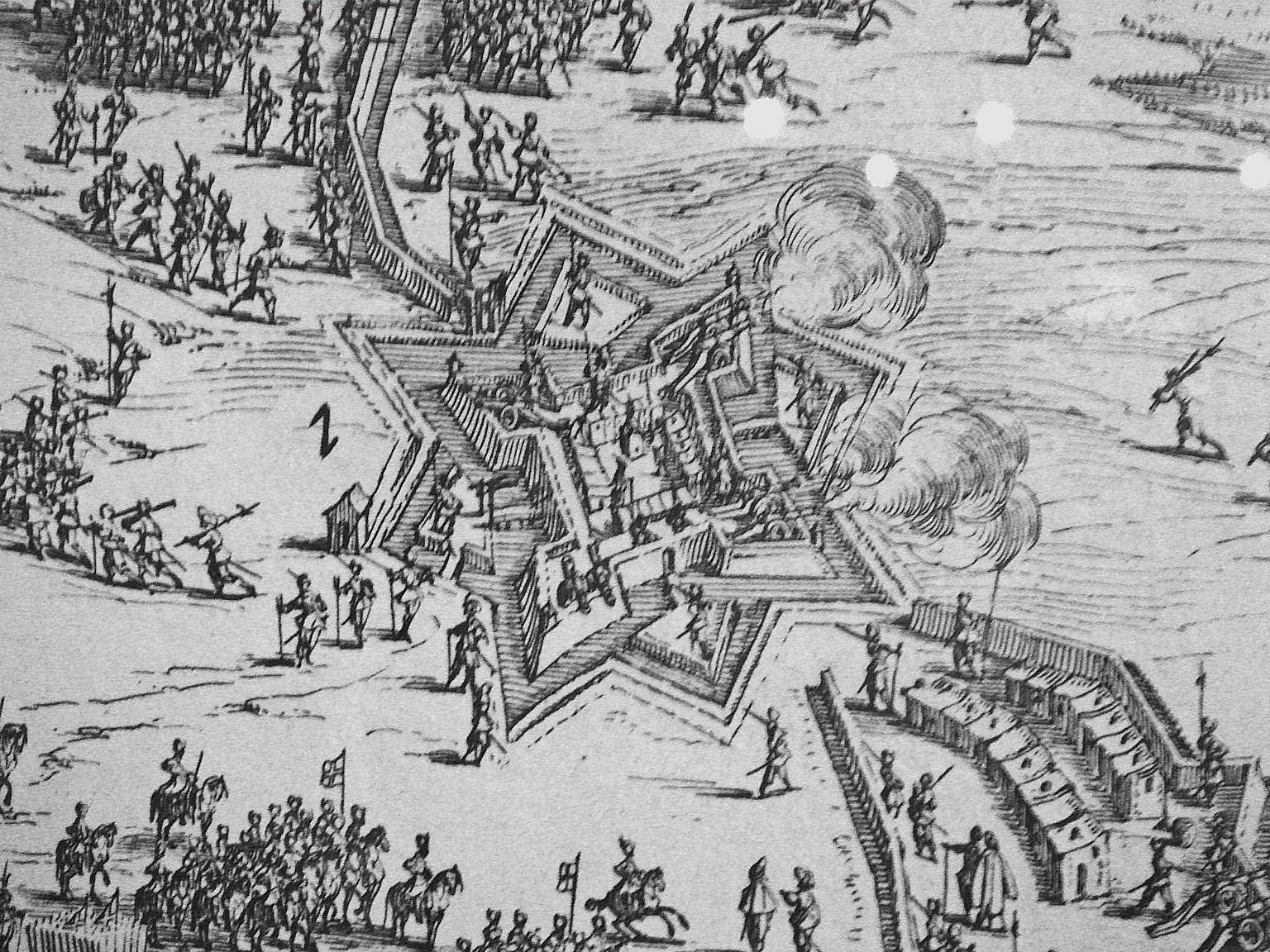
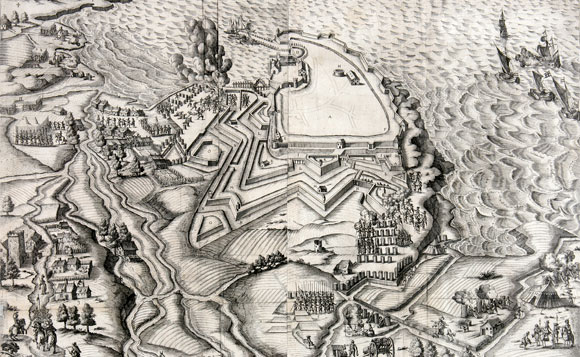
The Blockade of La Rochelle (French: ''Blocus de La Rochelle'') took place in 1621-1622 during the repression of the Huguenot rebellion by the French king Louis XIII. In June 1621, Louis XIII besieged and captured Saint-Jean d'Angély, a strategic city controlling the approaches to the Huguenot stronghold of La Rochelle. Louis XIII chose however to move south with his main force for the Siege of Montauban. The blockade Meanwhile, Louis XIII ordered the Duke of Épernon to blockade La Rochelle by sea as well as by land. On the sea, however, efforts were ineffective, as many small ships could easily go through ships of the Royal Navy and the Huguenots generally had mastery of the sea. At one point they attacked the harbour of Brouage and attempted to block it by sinking ships filled with stones at its entrance. In July 1621, d'Épernon established his headquarters on land in La Jarrie, in the vicinity of La Rochelle. In August, the shipowner Jean Guiton was named by the City Counc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
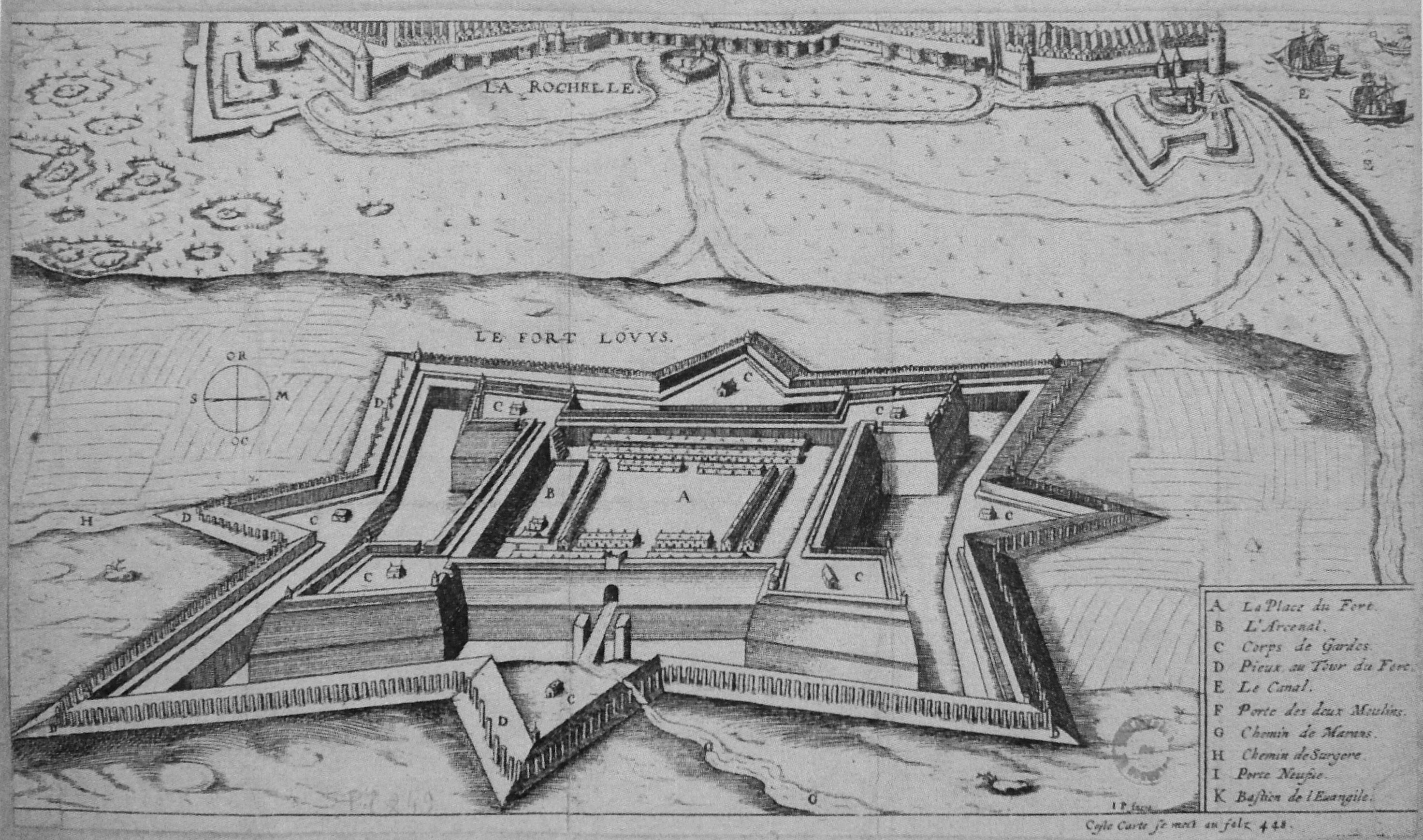
Fort Louis In La Rochelle
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large stone walls had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae (famous for the huge stone blocks of its 'cyclopean' walls). A Greek ''Towns of ancient Greece#Military settlements, phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the ancient Roman, Roman castellum or English language, English fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Guise
Count of Guise and Duke of Guise (pronounced �ɥiz were titles in the French nobility. Originally a seigneurie, in 1417 Guise was erected into a county for René, a younger son of Louis II of Anjou. While disputed by the House of Luxembourg (1425–1444), the county was ultimately retained by the House of Anjou and its descendants, passing in 1520 to the cadet branch of the ducal House of Lorraine that became known as the House of Guise, headed by Claude of Lorraine. In 1528, the county was elevated to a dukedom and peerage of France for him. The Dukes of Guise and their sons played a prominent role in the French Wars of Religion, during which they were the leaders of the ultra-Catholic faction. This dukedom became extinct in 1688, and the lands attached to it passed to the Princess Palatine Anne, a great-granddaughter of Charles of Lorraine-Guise, Duke of Mayenne – although she was not the heiress in strict primogeniture, that being the Duke of Mantua. The dukedom was rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1622 In France
Events from the year 1622 in France. Incumbents *Monarch: Louis XIII Events * April 16 – Huguenot rebellions: Blockade of La Rochelle ends in royal victory. * May – Huguenot rebellions: siege of Royan – The Huguenot city of Royan is taken by royal forces after a 6-day siege. * June 11 – Huguenot rebellions: siege of Nègrepelisse – The Huguenot city of Nègrepelisse is taken by royal forces after a short siege by royal forces; the entire population is subsequently massacred and the city burned to the ground. * July 22 – Huguenot rebellions: siege of Montpellier begins. * October 18 – Treaty of Montpellier signed, ending the siege of Montpellier and the first of the Huguenot rebellions. * October 27 – Huguenot rebellions: The inconclusive Naval battle of Saint-Martin-de-Ré is fought between the Huguenot fleet of La Rochelle, commanded by Jean Guiton, and a royal fleet under the command of Charles, Duke of Guise. * Compagnie Ordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Wars Of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the term which is used in reference to a period of civil war between French Catholic Church, Catholics and Protestantism, Protestants, commonly called Huguenots, which lasted from 1562 to 1598. According to estimates, between two and four million people died from violence, famine or diseases which were directly caused by the conflict; additionally, the conflict severely damaged the power of the French monarchy. The fighting ended in 1598 when Henry of Navarre, who had converted to Catholicism in 1593, was proclaimed Henry IV of France and issued the Edict of Nantes, which granted substantial rights and freedoms to the Huguenots. However, the Catholics continued to have a hostile opinion of Protestants in general and they also continued to have a hostile opinion of him as a person, and his assassination in 1610 triggered a fresh round of Huguenot rebellions in the 1620s. Tensions between the two religions had been building since the 1530s, exacerba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of La Rochelle
The siege of La Rochelle (, or sometimes ) was a result of a war between the French royal forces of Louis XIII of France and the Huguenots of La Rochelle in 1627–28. The siege marked the height of the struggle between the Catholics and the Protestants in France, and ended with a complete victory for King Louis XIII and the Catholics. Background The 1598 Edict of Nantes that ended the French Wars of Religion granted Protestants, commonly known as Huguenots, a large degree of autonomy and self-rule. La Rochelle was the centre of Huguenot seapower, and a key point of resistance against the Catholic royal government. The assassination of Henry IV of France in 1610 led to the appointment of Marie de' Medici as regent for her nine-year-old son, Louis XIII. Her removal in 1617 caused a series of revolts by powerful regional nobles, both Catholic and Protestant, while religious tensions were heightened by the outbreak of the 1618 to 1648 Thirty Years War. In 1621, Louis re-estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capture Of Ré Island
Capture may refer to: *Asteroid capture, a phenomenon in which an asteroid enters a stable orbit around another body *Capture, a software for lighting design, documentation and visualisation *"Capture" a song by Simon Townshend *Capture (band), an Australian electronicore band previously known as Capture the Crown *Capture (chess), to remove the opponent's piece from the board by taking it with one's own piece * Capture effect, a phenomenon in which only the stronger of two signals near the same FM frequency will be demodulated *Capture fishery, a wild fishery in which the aquatic life is not controlled and needs to be captured or fished * ''Capture'' (TV series), a reality show * ''The Capture'' (TV series), UK drama series *Electron capture, a nuclear reaction * Motion capture, the process of recording movement and translating that movement onto a digital model *Neutron capture, a nuclear reaction *Regulatory capture, situations in which a government agency created to act in the pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Montpellier
The Treaty of Montpellier (or the Peace of Montpellier) was signed in Montpellier on 18 October 1622 between King Louis XIII of France and Duke Henry II of Rohan. The treaty followed the siege of Montpellier and ended hostilities between French royalists and the Huguenots. Moreover, it confirmed the tenets of the Edict of Nantes, pardoned Henry II, and allowed the Huguenots to maintain their numerous forts and garrisons. See also *List of treaties External linksLouis XIII and Religion {{Montpellier-stub 1622 in France 1622 treaties Montpellier Montpellier (, , ; oc, Montpelhièr ) is a city in southern France near the Mediterranean Sea. One of the largest urban centres in the region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania, Montpellier is the prefecture of the Departments of ... Montpellier Huguenot rebellions History of Occitania (administrative region) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Battle Of Saint-Martin-de-Ré
The Naval battle of Saint-Martin-de-Ré (French:''Bataille navale de Saint-Martin-de-Ré'') took place on 27 October 1622, between the Huguenot fleet of La Rochelle under Jean Guiton, and a Royal fleet under Charles de Guise. Under Henry IV the city had enjoyed a certain freedom and prosperity until the 1620s, but the city entered in conflict with the central authority of King Louis XIII with the Huguenot rebellion of 1622. Louis XIII sent a small army for a Blockade of La Rochelle in 1621 and 1622. A fleet from La Rochelle fought a much larger royal fleet under the Charles de Guise in front of Saint-Martin-de-Ré, and managed to fight to a standstill on 27 October 1622. The battle lasted two hours, and as many as 20,000 cannon shots were exchanged, but the encounter remained inconclusive. A peace had been signed a few days earlier on 19 October 1622, the Peace of Montpellier, which encouraged the people of La Rochelle to end hostilities. Through the Peace of Montpellier, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bataille Navale Re 1622 (1908–1993), French actress
{{surname, Bataille ...
Bataille is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *Christian Bataille (born 1946), French politician *Frédéric Bataille (1850–1946), French educator, poet and mycologist *Georges Bataille (1897–1962), French intellectual and literary figure *Henri Jules Bataille (1816–1882), French general *Henry Bataille (1872–1922), French dramatist and poet *Laetitia Bataille, French journalist and writer *Laurence Bataille (1930–1986), French psychoanalyst and writer *Matthieu Bataille (born 1978), French judoka *Nicolas Bataille (1926–2008), French comedian and director *Sylvia Bataille Sylvia Bataille (born Sylvia Maklès; 1 November 1908 – 22 December 1993) was a French actress of Romanian-Jewish descent. When she was twenty, she married the writer Georges Bataille with whom she had a daughter, the psychoanalyst Laurence Bata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Louis (La Rochelle)
Fort Louis was a Royal fort built just outside the walls of the Huguenot city in La Rochelle. The fort was a source of great tension between the Huguenots of La Rochelle and Louis XIII, and was perceived as a real threat to their survival. Marshal Lesdiguieres predicted "Either La Rochelle must take Fort Louis, or the Fort will destroy La Rochelle." The construction of the fort had been started by the Count of Soissons in 1620 during the first Huguenot rebellion. With the Treaty of Montpellier, Louis XIII had agreed to remove the fort in due time, but he and his Minister Richelieu later temporised and avoided the promised removals despite the requests by La Rochelle.''The Huguenots of La Rochelle'' by Louis Delmas p.13/ref> Fort Louis played a key role in establishing the fortifications around La Rochelle during the 1627-1628 Siege of La Rochelle The siege of La Rochelle (, or sometimes ) was a result of a war between the French royal forces of Louis XIII of France and the Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis De Bourbon, Comte De Soissons
Louis de Bourbon, Comte de Soissons (May 1604 – 6 July 1641) was the son of Charles de Bourbon, Count of Soissons and Anne de Montafié. A second cousin of Louis XIII of France he was a '' prince du Sang'', those considered part of the Royal family. Part of the faction who opposed Cardinal Richelieu and his policy of war with Spain, he was killed leading a revolt at the Battle of La Marfée in 1641. Biography Born in Paris, son of Charles, Count of Soissons and Anne de Montafié. Louis was made governor of the Dauphiné province (1612), an office inherited at the death of his father, and later governor of the Champagne province (1631). Around 1612, he was made the Grand Master of France, the head of the royal household. In 1636, Louis conspired with his cousin Gaston d'Orléans and the count of Montrésor with the intention to murder Cardinal Richelieu and depose the King, but the plot failed. The King's mother, Marie de' Medici, had tried as well on numerous occasions t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Royan
The siege of Royan (French: Siège de Royan) was a siege accomplished by the young French king Louis XIII in 1622, against the Protestant stronghold of Royan. This siege followed the siege of Montauban, in which Louis XIII had failed against the Huguenot city. The siege started at the beginning of May 1622. After 6 days, despite support from La Rochelle, the city surrendered, the defenders obtaining to withdraw to La Rochelle with weapons and luggage, although they had to leave cannons and ammunition.''A History of the Huguenots'' by William Shergold Browning, p.23/ref> See also * French Wars of Religion * Huguenot rebellions Notes {{reflist 1622 in France Royan, Siege of Royan Royan (; in the Saintongeais dialect; oc, Roian) is a commune and town in the south-west of France, in the department of Charente-Maritime in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region. Its inhabitants are known as ''Royannais'' and ''Royannaises''. Capi ... History of Charente-Maritime Conflicts in 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |