|
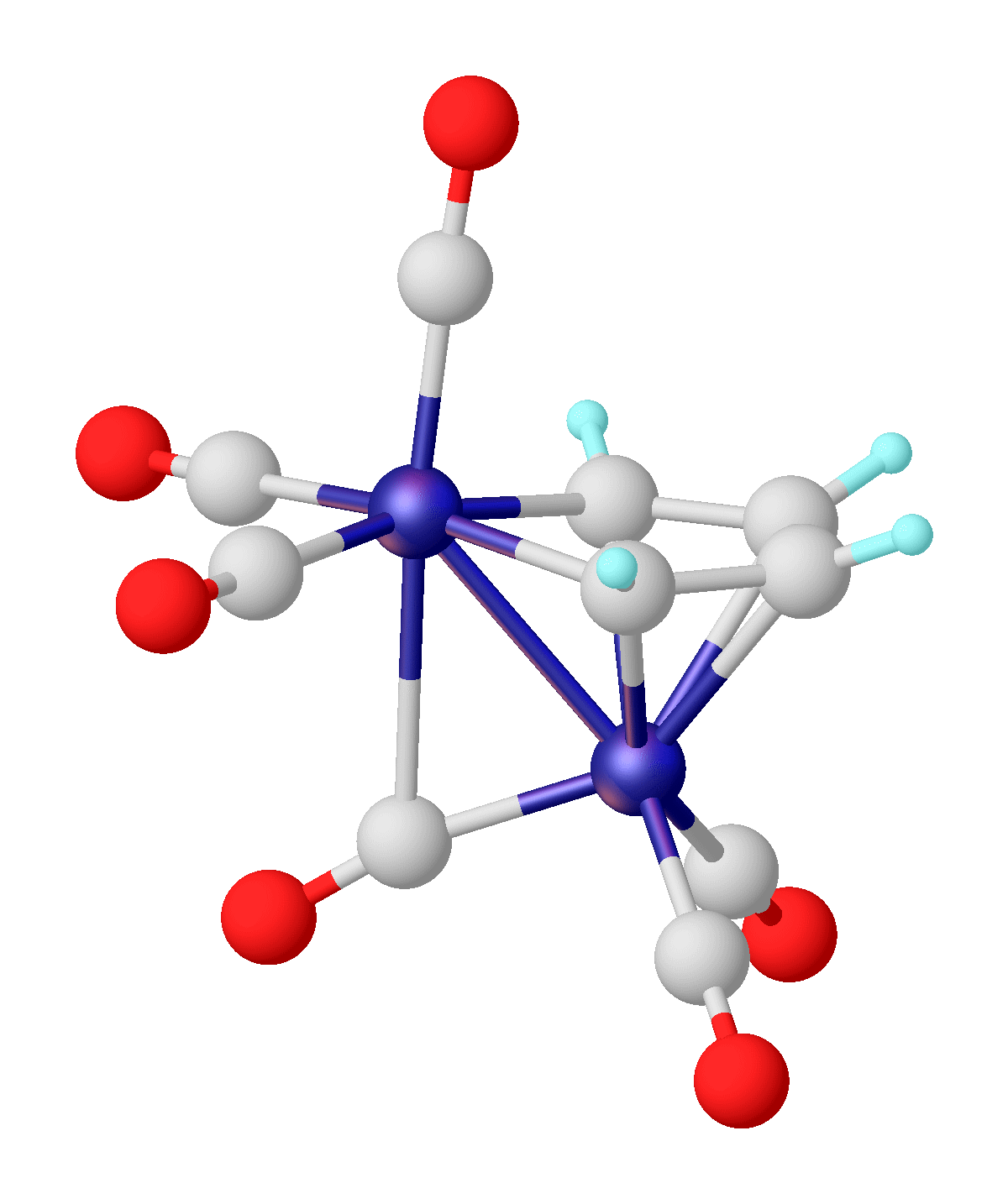
Bismole
Bismole is a theoretical heterocyclic organic compound, a five-membered ring with the formula C4 H4 BiH. It is classified as a metallole. It can be viewed as a structural analog of pyrrole, with bismuth replacing the nitrogen atom of pyrrole. The unsubstituted compound has not been isolated due to the high energy of the Bi-H bond. Substituted derivatives, which have been synthesized, are called bismoles. Reactions 2,5-Bis(trimethylsilyl)-3,4-dimethyl-1-phenyl-1''H''-bismole, for example, can be formed by the reaction of (1''Z'',3''Z'')-1,4-bis(trimethylsilyl)-1,4-diiodobuta-2,3-dimethyl-1,3-diene and diiodophenylbismuthine. Bismoles can be used to form ferrocene-like sandwich compounds. See also *Organobismuth chemistry Organobismuth chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to bismuth chemical bond. Applications are few. The main bismuth oxidation states are Bi(III) and Bi(V) as in all higher group 15 elements. The energy of a b ... Referenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metalloles
Metalloles are derivatives of cyclopentadiene in which the carbon atom at position 5, the saturated carbon, is replaced by a heteroatom. In contrast to its parent compound, the numbering of the metallole starts at the heteroatom. Some of these compounds are described as organometallic compounds, but in the list below quite a number of metalloids are present too. Many metalloles are fluorescent. Polymeric derivatives of pyrrole and thiophene are of interest in molecular electronics. Metalloles, which can also be viewed as structural analogs of pyrrole, include: * Arsole, a moderately-aromatic arsenic analog * Bismole, a bismuth analog * Borole, a boron analog * Furan (oxole), an oxygen analog * Gallole, a gallium analog * Germole, a germanium analog * Phosphole, a phosphorus analog * Pyrrole (azole), a nitrogen analog * Selenophene, a selenium analog * Silole, a silicon analog * Stannole, a tin analog * Stibole, an antimony analog * Tellurophene, a tellurium analog *Plumbole, a lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallole
Metalloles are derivatives of cyclopentadiene in which the carbon atom at position 5, the saturated carbon, is replaced by a heteroatom. In contrast to its parent compound, the numbering of the metallole starts at the heteroatom. Some of these compounds are described as organometallic compounds, but in the list below quite a number of metalloids are present too. Many metalloles are fluorescent. Polymeric derivatives of pyrrole and thiophene are of interest in molecular electronics. Metalloles, which can also be viewed as structural analogs of pyrrole, include: * Arsole, a moderately-aromatic arsenic analog * Bismole, a bismuth analog * Borole, a boron analog * Furan (oxole), an oxygen analog * Gallole, a gallium analog * Germole, a germanium analog * Phosphole, a phosphorus analog * Pyrrole (azole), a nitrogen analog * Selenophene, a selenium analog * Silole, a silicon analog * Stannole, a tin analog * Stibole, an antimony analog * Tellurophene, a tellurium analog *Plumbole, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterocyclic
A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of these heterocycles. Examples of heterocyclic compounds include all of the nucleic acids, the majority of drugs, most biomass (cellulose and related materials), and many natural and synthetic dyes. More than half of known compounds are heterocycles. 59% of US FDA-approved drugs contain nitrogen heterocycles. Classification The study of heterocyclic chemistry focuses especially on unsaturated derivatives, and the preponderance of work and applications involves unstrained 5- and 6-membered rings. Included are pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan. Another large class of heterocycles refers to those fused to benzene rings. For example, the fused benzene derivatives of pyridine, thiophene, pyrrole, and furan are quinol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arsole
Arsole, also called arsenole or arsacyclopentadiene, is an organoarsenic compound with the formula C4H4AsH. It is classified as a metallole and is isoelectronic to and related to pyrrole except that an arsenic atom is substituted for the nitrogen atom. Whereas the pyrrole molecule is planar, the arsole molecule is not, and the hydrogen atom bonded to arsenic extends out of the molecular plane. Arsole is only moderately aromatic, with about 40% the aromaticity of pyrrole. Arsole itself has not been reported in pure form, but several substituted analogs called arsoles exist. Arsoles and more complex arsole derivatives have similar structure and chemical properties to those of phosphole derivatives. When arsole is fused to a benzene ring, this molecule is called arsindole, or benzarsole. Nomenclature Arsole belongs to the series of heterocyclic pnictogen compounds. The naming of cyclic organoarsenic compounds such as arsole is based on an extension of the Hantzsch–Widman nomencla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seventh in total abundance in the Milky Way and the Solar System. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bond to form N2, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas. N2 forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere, making it the most abundant uncombined element. Nitrogen occurs in all organisms, primarily in amino acids (and thus proteins), in the nucleic acids ( DNA and RNA) and in the energy transfer molecule adenosine triphosphate. The human body contains about 3% nitrogen by mass, the fourth most abundant element in the body after oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen. The nitrogen cycle describes the movement of the element from the air, into the biosphere and organic compounds, then back into the atmosphere. Many indus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismuth Heterocycles
Bismuth is a chemical element with the symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs naturally, and its sulfide and oxide forms are important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead. It is a brittle metal with a silvery-white color when freshly produced. Surface oxidation generally gives samples of the metal a somewhat rosy cast. Further oxidation under heat can give bismuth a vividly iridescent appearance due to thin-film interference. Bismuth is both the most diamagnetic element and one of the least thermally conductive metals known. Bismuth was long considered the element with the highest atomic mass whose nuclei do not spontaneously decay. However, in 2003 it was discovered to be extremely weakly radioactive. The metal's only primordial isotope, bismuth-209, experiences alpha decay at such a minute rate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organobismuth Chemistry
Organobismuth chemistry is the chemistry of organometallic compounds containing a carbon to bismuth chemical bond. Applications are few. The main bismuth oxidation states are Bi(III) and Bi(V) as in all higher group 15 elements. The energy of a bond to carbon in this group decreases in the order P > As > Sb > Bi. The first reported use of bismuth in organic chemistry was in oxidation of alcohols by Challenger in 1934 (using Ph3Bi(OH)2). Knowledge about methylated species of bismuth in environmental and biological media is limited. Discovery Triethylbismuth, the first known organobismuth compound, is prepared in 1850 by Löwig and Schweizer from iodoethane and a potassium–bismuth alloy. As with most trialkylbismuth compounds, BiEt3 has an extremely pungent and unpleasant odor, and is spontaneously oxidized in air. The chemistry of these complexes first begin receiving significant attention when Grignard reagents and organolithium compounds become available. OrganoBi(III) compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandwich Compound
In organometallic chemistry, a sandwich compound is a chemical compound featuring a metal bound by haptic, covalent bonds to two arene (ring) ligands. The arenes have the formula , substituted derivatives (for example ) and heterocyclic derivatives (for example ). Because the metal is usually situated between the two rings, it is said to be "sandwiched". A special class of sandwich complexes are the metallocenes. The term ''sandwich compound'' was introduced in organometallic nomenclature in 1956 in a report by J. D. Dunitz, L. E. Orgel and R. A. Rich, who confirmed the structure of ferrocene by X-ray crystallography. The correct structure, in which the molecule features an iron atom ''sandwiched'' between two parallel cyclopentadienyl rings, had been proposed several years previously by Robert Burns Woodward and, separately, by Ernst Otto Fischer. The structure helped explain puzzles about ferrocene's conformers. This result further demonstrated the power o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferrocene
Ferrocene is an organometallic compound with the formula . The molecule is a complex consisting of two cyclopentadienyl rings bound to a central iron atom. It is an orange solid with a camphor-like odor, that sublimes above room temperature, and is soluble in most organic solvents. It is remarkable for its stability: it is unaffected by air, water, strong bases, and can be heated to 400 °C without decomposition. In oxidizing conditions it can reversibly react with strong acids to form the ferrocenium cation . The rapid growth of organometallic chemistry is often attributed to the excitement arising from the discovery of ferrocene and its many analogues, such as metallocenes. History Discovery Ferrocene was discovered by accident thrice. The first known synthesis may have been made in the late 1940s by unknown researchers at Union Carbide, who tried to pass hot cyclopentadiene vapor through an iron pipe. The vapor reacted with the pipe wall, creating a "yellow sludg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismuthine
Bismuthine (IUPAC name: bismuthane) is the chemical compound with the formula BiH3. As the heaviest analogue of ammonia (a pnictogen hydride), BiH3 is unstable, decomposing to bismuth metal well below 0 °C. This compound adopts the expected pyramidal structure with H–Bi–H angles of around 90°. The term ''bismuthine'' may also refer to a member of the family of organobismuth(III) species having the general formula , where R is an organic substituent. For example, Bi(CH3)3 is ''trimethylbismuthine''. Preparation and properties BiH3 is prepared by the redistribution of methylbismuthine (BiH2Me):Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. "Inorganic Chemistry" Academic Press: San Diego, 2001.. :3 BiH2Me → 2 BiH3 + BiMe3 The required BiH2Me, which is also thermally unstable, is generated by reduction of methylbismuth dichloride, BiCl2Me with LiAlH4. As suggested by the behavior of SbH3, BiH3 is unstable and decomposes to its constituent elements according to the following equatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elsevier
Elsevier () is a Dutch academic publishing company specializing in scientific, technical, and medical content. Its products include journals such as ''The Lancet'', ''Cell'', the ScienceDirect collection of electronic journals, '' Trends'', the '' Current Opinion'' series, the online citation database Scopus, the SciVal tool for measuring research performance, the ClinicalKey search engine for clinicians, and the ClinicalPath evidence-based cancer care service. Elsevier's products and services also include digital tools for data management, instruction, research analytics and assessment. Elsevier is part of the RELX Group (known until 2015 as Reed Elsevier), a publicly traded company. According to RELX reports, in 2021 Elsevier published more than 600,000 articles annually in over 2,700 journals; as of 2018 its archives contained over 17 million documents and 40,000 e-books, with over one billion annual downloads. Researchers have criticized Elsevier for its high profit marg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Analog
A structural analog (analogue in modern traditional English; Commonwealth English), also known as a chemical analog or simply an analog, is a compound having a structure similar to that of another compound, but differing from it in respect to a certain component. It can differ in one or more atoms, functional groups, or substructures, which are replaced with other atoms, groups, or substructures. A structural analog can be imagined to be formed, at least theoretically, from the other compound. Structural analogs are often isoelectronic. Despite a high chemical similarity, structural analogs are not necessarily functional analogs and can have very different physical, chemical, biochemical, or pharmacological properties. In drug discovery, either a large series of structural analogs of an initial lead compound are created and tested as part of a structure–activity relationship study or a database is screened for structural analogs of a lead compound. Chemical analogues of il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
