|
Bilabial Approximant
The voiced bilabial fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is B. The official symbol is the Greek letter beta. This letter is also often used to represent the bilabial approximant, though that is more precisely written with a lowering diacritic, that is . That sound may also be transcribed as an advanced labiodental approximant , in which case the diacritic is again frequently omitted, since no contrast is likely. It has been proposed that either a turned ⟨⟩ or reversed ⟨⟩ be used as a dedicated symbol for the bilabial approximant, but despite occasional usage this has not gained general acceptance. It is extremely rare for a language to make a phonemic contrast between the voiced bilabial fricative and the bilabial approximant. The Mapos Buang language of New Guinea contains this contrast. Its bilabial approximant is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are and pronounced with the lips; and pronounced with the front of the tongue; and pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; , and , pronounced by forcing air through a narrow channel ( fricatives); and and , which have air flowing through the nose (nasals). Contrasting with consonants are vowels. Since the number of speech sounds in the world's languages is much greater than the number of letters in any one alphabet, linguists have devised systems such as the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) to assign a unique and unambiguous symbol to each attested consonant. The English alphabet has fewer consonant letters than the English language has consonant sounds, so digraphs like , , , and are used to extend the alphabet, though some letters and digraphs represent more than one consonant. For example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angor Language
Angor (Anggor) Senagi is a Senagi language of northern Papua New Guinea. It is spoken in 11 villages of Amanab Rural LLG, Sandaun Province, including Senagi village () of Bibriari ward. Dialects Dialects are Wai (Central Anggor) and Samanai (Southern Anggor). Loving and Bass (1964) list these Anggor dialects and their villages:Loving, Richard and Jack Bass. 1964. ''Languages of the Amanab Sub-District''. Port Moresby: Department of Information and Extension Services. *''Western'': Mongo *''Central west'': Amandan (), Fisi, Kwaraman (), Puramen () *''Central east'': Akrani, Baribari, Bibriari (), Merere, Nai (), Senagi (), Unupuwai, Wamu () *''Southern'': Samanai Writing system Phonology Angor has 18 consonants, which are: : Angor has 7 vowels, which are: : References External links Angor Grammar Sketch* PARADISEC The Pacific and Regional Archive for Digital Sources in Endangered Cultures (PARADISEC) is a cross-institutional project that supports work on endangere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comorian Language
Comorian (''Shikomori'', or ''Shimasiwa'', the "language of islands") is the name given to a group of four Bantu languages spoken in the Comoro Islands, an archipelago in the southwestern Indian Ocean between Mozambique and Madagascar. It is named as one of the official languages of the Union of the Comoros in the Comorian constitution. Shimaore, one of the languages, is spoken on the disputed island of Mayotte, a French department claimed by Comoros. Like Swahili, the Comorian languages are Sabaki languages, part of the Bantu language family. Each island has its own language, and the four are conventionally divided into two groups: the eastern group is composed of ''Shindzuani'' (spoken on Ndzuani) and ''Shimaore'' (Mayotte), while the western group is composed of ''Shimwali'' ( Mwali) and ''Shingazija'' ( Ngazidja). Although the languages of different groups are not usually mutually intelligible, only sharing about 80% of their lexicon, there is mutual intelligibility between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
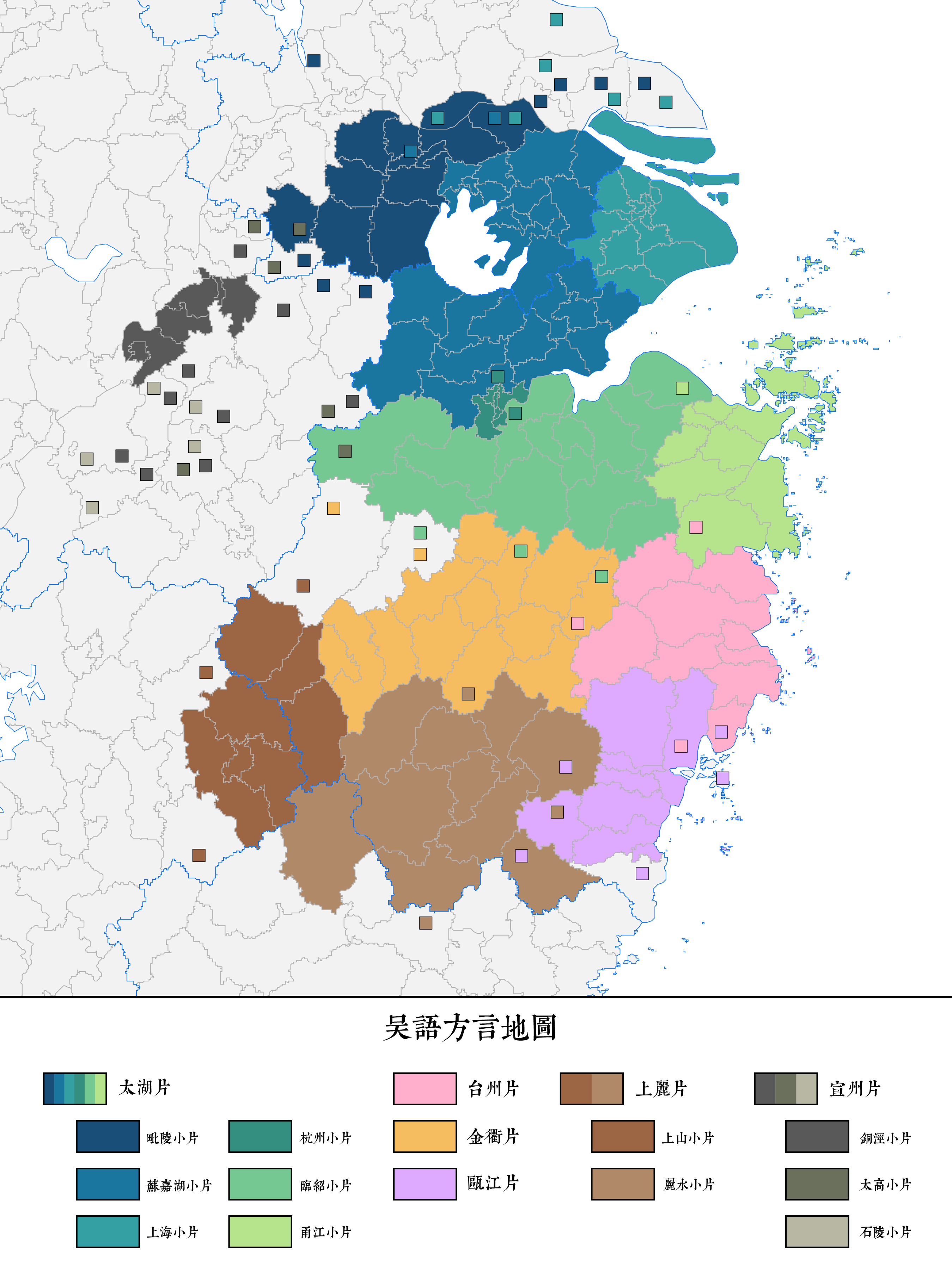
Shanghainese
The Shanghainese language, also known as the Shanghai dialect, or Hu language, is a variety of Wu Chinese spoken in the central districts of the City of Shanghai and its surrounding areas. It is classified as part of the Sino-Tibetan language family. Shanghainese, like the rest of the Wu language group, is mutually unintelligible with other varieties of Chinese, such as Mandarin. Shanghainese belongs a separate group of the Taihu Wu subgroup. With nearly 14 million speakers, Shanghainese is also the largest single form of Wu Chinese. Since the late 19th century it has served as the lingua franca of the entire Yangtze River Delta region, but in recent decades its status has declined relative to Mandarin, which most Shanghainese speakers can also speak. Like other Wu varieties, Shanghainese is rich in vowels and consonants, with around twenty unique vowel qualities, twelve of which are phonemic. Similarly, Shanghainese also has voiced obstruent initials, which is rare outsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foochow Romanized
Foochow Romanized, also known as Bàng-uâ-cê (BUC for short; ) or Hók-ciŭ-uâ Lò̤-mā-cê (), is a Latin alphabet for the Fuzhou dialect of Eastern Min adopted in the middle of the 19th century by Western missionaries. It had varied at different times, and became standardized in the 1890s. Foochow Romanized was mainly used inside of church circles, and was taught in some mission schools in Fuzhou. However, unlike its counterpart Pe̍h-ōe-jī for Hokkien, even in its prime days Foochow Romanized was by no means universally understood by Christians. R. S. Maclay, C. C. Baldwin, Samuel H. Leger: Dictionary of the Foochow Dialect, 1929 History After Fuzhou became one of the five Chinese treaty ports opened by the Treaty of Nanjing at the end of First Opium War (from 1839 to 1842), many Western missionaries arrived in the city. Faced with widespread illiteracy, they developed Latin alphabets for the Fuzhou dialect. The first attempt in romanizing the Fuzhou dial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuzhou Dialect
Fuzhou (; , Fuzhounese: Hokchew, ''Hók-ciŭ''), alternately romanized as Foochow, is the capital and one of the largest cities in Fujian province, China. Along with the many counties of Ningde, those of Fuzhou are considered to constitute the Mindong (lit. Eastern Fujian) linguistic and cultural area. Fuzhou lies on the north (left) bank of the estuary of Fujian's largest river, the Min River. All along its northern border lies Ningde, and Ningde's Gutian County lies upriver. Its population was 7,115,370 inhabitants as of the 2010 census, of whom 4,408,076 inhabitants are urban representing around 61.95%, while rural population is at 2,707,294 representing around 38.05%. As of 31 December 2018, the total population was estimated at 7,740,000 whom 4,665,000 lived in the built-up (''or metro'') area made of 5 urban districts plus Minhou County. In 2015, Fuzhou was ranked as the 10th fastest growing metropolitan area in the world by Brookings Institution. Fuzhou is liste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Dialects
Chinese, also known as Sinitic, is a branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family consisting of hundreds of local varieties, many of which are not mutually intelligible. Variation is particularly strong in the more mountainous southeast of mainland China. The varieties are typically classified into several groups: Mandarin, Wu, Min, Xiang, Gan, Hakka and Yue, though some varieties remain unclassified. These groups are neither clades nor individual languages defined by mutual intelligibility, but reflect common phonological developments from Middle Chinese. Chinese varieties differ most in their phonology, and to a lesser extent in vocabulary and syntax. Southern varieties tend to have fewer initial consonants than northern and central varieties, but more often preserve the Middle Chinese final consonants. All have phonemic tones, with northern varieties tending to have fewer distinctions than southern ones. Many have tone sandhi, with the most complex patterns in the coastal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalan Phonology
The phonology of Catalan, a Romance language, has a certain degree of dialectal variation. Although there are two standard varieties, one based on Central Eastern dialect and another one based on South-Western or Valencian dialect, this article deals with features of all or most dialects, as well as regional pronunciation differences. Various studies have focused on different Catalan varieties; for example, Wheeler and Mascaró analyze Central Eastern varieties, the former focusing on the educated speech of Barcelona and the latter focusing more on the vernacular of Barcelona, and Recasens does a careful phonetic study of Central Eastern Catalan. Catalan is characterized by final-obstruent devoicing, lenition, and voicing assimilation; a set of 7 or 8 phonemic vowels, vowel assimilations (including vowel harmony), many phonetic diphthongs, and vowel reduction, whose precise details differ between dialects. Several dialects have a dark ''l'', and all dialects have palatal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalan Orthography
The Catalan and Valencian orthographies encompass the spelling and punctuation of standard Catalan (set by the IEC) and Valencian (set by the AVL). There are also several adapted variants to the peculiarities of local dialects of Insular Catalan (Alguerese and the Balearic subdialects). History The history of the Catalan and Valencian orthographies show a singularity in regard with the other Romance languages. These have been mostly developed from Latin, adapting them to their own phonetic particularities. It had been a gradual and slow process through centuries until the creation of the Academies in the 18th century that fixed the orthography from their language dominant variety. Badia i Margarit, Antoni M. «''El procés d'unificació de l'ortografia catalana''». In the case of Catalan and Valencian, the mediaeval orthography had a noticeable homogeneity. The Royal Chancellery set a unitary written model in several fields. Thus, Ramon Muntaner expressed in his Chronicl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalan Language
Catalan (; autonym: , ), known in the Valencian Community and Carche as '' Valencian'' ( autonym: ), is a Western Romance language. It is the official language of Andorra, and an official language of three autonomous communities in eastern Spain: Catalonia, the Valencian Community, and the Balearic Islands. It also has semi-official status in the Italian comune of Alghero. It is also spoken in the Pyrénées-Orientales department of France and in two further areas in eastern Spain: the eastern strip of Aragon and the Carche area in the Region of Murcia. The Catalan-speaking territories are often called the or "Catalan Countries". The language evolved from Vulgar Latin in the Middle Ages around the eastern Pyrenees. Nineteenth-century Spain saw a Catalan literary revival, culminating in the early 1900s. Etymology and pronunciation The word ''Catalan'' is derived from the territorial name of Catalonia, itself of disputed etymology. The main theory suggests ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berta Language
Berta proper, a.k.a. ''Gebeto'', is spoken by the Berta (also ''Bertha, Barta, Burta'') in Sudan and Ethiopia. The three Berta languages, Gebeto, Fadashi and Undu, are often considered dialects of a single language. Berta proper includes the dialects Bake, Dabuso, Gebeto, Mayu, and Shuru; the dialect name ''Gebeto'' may be extended to all of Berta proper. Phonology Consonants * Voiced plosives /b, d, ɡ/ may be heard as voiceless , t, kin free variation, word-initially or word-finally. * A glottal stop �mainly occurs between vowels, and may also be heard before word-initial vowel sounds. * Nasal-stop sequences may occur morpheme-initially as b, nd, ŋɡ, ŋkʼ * /ŋ/ is heard as �when preceding a front vowel /i/ or /e/. * /kʼ/ is heard as a palatal ʼwhen before front vowels. * /ɡ/ can be heard as voiced palatal �or as a voiceless palatal when before front vowels. * /h/ in word-final position can be heard as a fricative * /s, θ/ may sometimes occur as sligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |