|
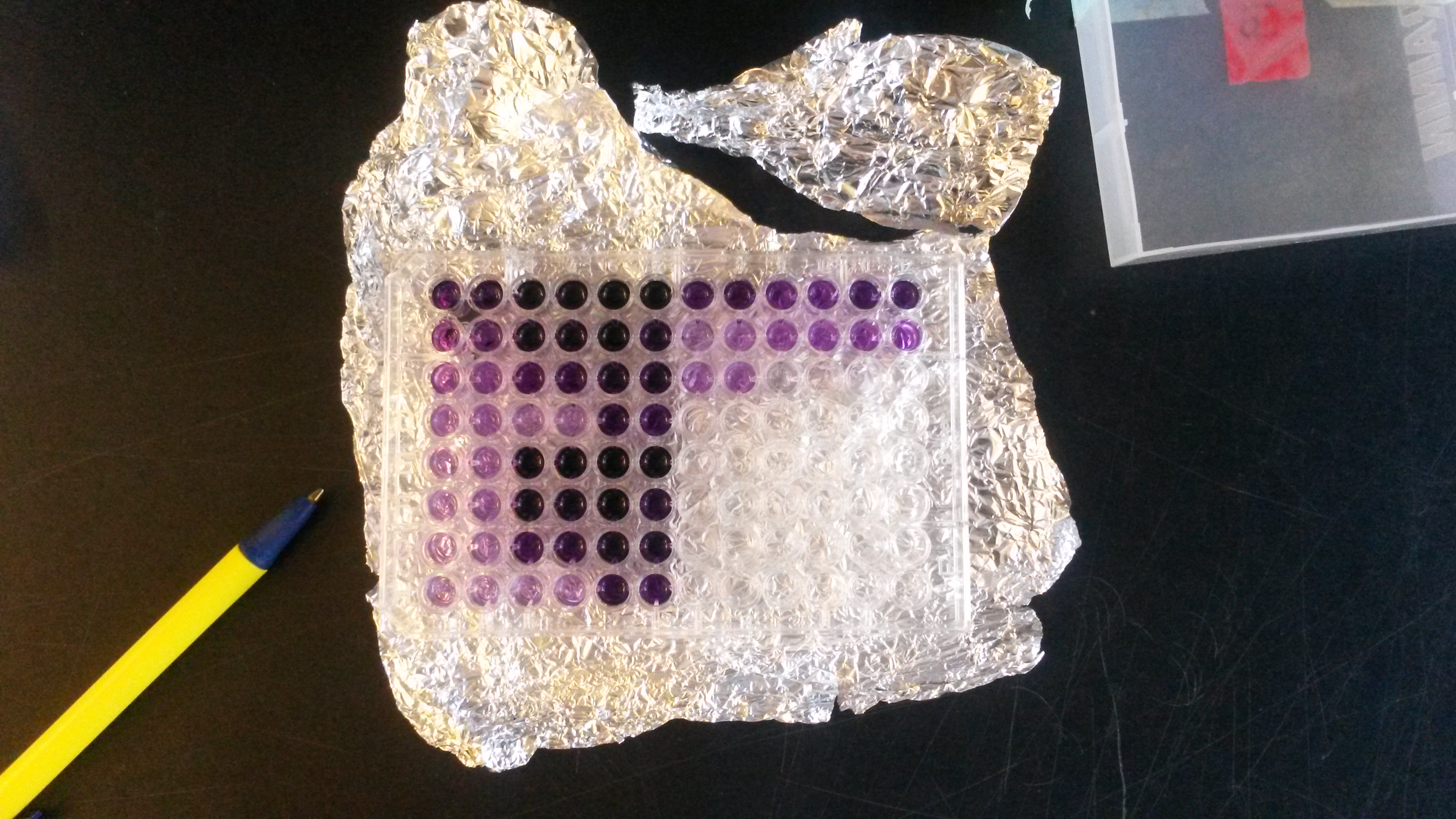
Bicinchoninic Acid Assay
The bicinchoninic acid assay (BCA assay), also known as the Smith assay, after its inventor, Paul K. Smith at the Pierce Chemical Company, now part of Thermo Fisher Scientific, is a biochemical assay for determining the total concentration of protein in a solution (0.5 μg/mL to 1.5 mg/mL), similar to Lowry protein assay, Bradford protein assay or biuret reagent. The total protein concentration is exhibited by a color change of the sample solution from green to purple in proportion to protein concentration, which can then be measured using colorimetric techniques. Mechanism A stock BCA solution contains the following ingredients in a highly alkaline solution with a pH 11.25: bicinchoninic acid, sodium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, sodium tartrate, and copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate. The BCA assay primarily relies on two reactions. First, the peptide bonds in protein reduce Cu2+ ions from the copper(II) sulfate to Cu1+ (a temperature dependent reaction). The amount of Cu2+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BCA Assay
The bicinchoninic acid assay (BCA assay), also known as the Smith assay, after its inventor, Paul K. Smith at the Pierce Chemical Company, now part of Thermo Fisher Scientific, is a biochemical assay for determining the total concentration of protein in a solution (0.5 μg/mL to 1.5 mg/mL), similar to Lowry protein assay, Bradford protein assay or biuret reagent. The total protein concentration is exhibited by a color change of the sample solution from green to purple in proportion to protein concentration, which can then be measured using colorimetric techniques. Mechanism A stock BCA solution contains the following ingredients in a highly alkaline solution with a pH 11.25: bicinchoninic acid, sodium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, sodium tartrate, and copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate. The BCA assay primarily relies on two reactions. First, the peptide bonds in protein reduce Cu2+ ions from the copper(II) sulfate to Cu1+ (a temperature dependent reaction). The amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Tartrate
Sodium tartrate (Na2C4H4O6) is a salt used as an emulsifier and a binding agent in food products such as jellies, margarine, and sausage casings. As a food additive, it is known by the E number E335. Because its crystal structure captures a very precise amount of water, it is also a common primary standard for Karl Fischer titration, a common technique to assay water content. See also * Monosodium tartrate Monosodium tartrate or sodium bitartrate is a sodium acid salt of tartaric acid. As a food additive it is used as an acidity regulator and is known by the E number E335. As an analytical reagent, it can be used in a test for ammonium cation which ... References External linksProperties of Sodium Tartrate at linanwindow Tartrates [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemistry Methods
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to biochemistry: Biochemistry – study of chemical processes in living organisms, including living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes. Applications of biochemistry * Testing ** Ames test – salmonella bacteria is exposed to a chemical under question (a food additive, for example), and changes in the way the bacteria grows are measured. This test is useful for screening chemicals to see if they mutate the structure of DNA and by extension identifying their potential to cause cancer in humans. ** Pregnancy test – one uses a urine sample and the other a blood sample. Both detect the presence of the hormone human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). This hormone is produced by the placenta shortly after implantation of the embryo into the uterine walls and accumulates. ** Breast cancer screening – identification of risk by testing for mutations in two genes&md ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biuret Test
Biuret is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a white solid that is soluble in hot water. A variety of organic derivatives are known. The term "biuret" also describes a family of organic compounds with the chemical formula , where are hydrogen, organyl or other groups. Also known as carbamylurea, it results from the condensation of two equivalents of urea. As such, it is an undesirable impurity in urea-based fertilizers. As biuret is toxic to plants, its percentage in fertilizers must be kept low. Preparation and structure The parent compound can be prepared by heating urea at 150 °C for ~6 hours until it gets slightly cloudy, then recrystallizing from water. After that, it can be recrystallized repeatedly from 2% sodium hydroxide solution and water to finally get base-free crystalline needles of the monohydrate which are free of cyanuric acid. While heating, a lot of ammonia is expelled: : Under related conditions, pyrolysis of urea affords triuret . In general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absorption Spectroscopy
Absorption spectroscopy refers to spectroscopic techniques that measure the absorption of radiation, as a function of frequency or wavelength, due to its interaction with a sample. The sample absorbs energy, i.e., photons, from the radiating field. The intensity of the absorption varies as a function of frequency, and this variation is the absorption spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is performed across the electromagnetic spectrum. Absorption spectroscopy is employed as an analytical chemistry tool to determine the presence of a particular substance in a sample and, in many cases, to quantify the amount of the substance present. Infrared and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy are particularly common in analytical applications. Absorption spectroscopy is also employed in studies of molecular and atomic physics, astronomical spectroscopy and remote sensing. There is a wide range of experimental approaches for measuring absorption spectra. The most common arrangement is to direct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale. The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm) or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, American spelling) is a units of measurement, unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), equal to one billionth (short scale) of a metre () and to 1000 picometres. One nanometre can be expressed in scientific notation as , and as metres. History The nanometre was formerly known as the millimicrometre – or, more commonly, the millimicron for short – since it is of a micron (micrometre), and was often denoted by the symbol mμ or (more rarely and confusingly, since it logically should refer to a ''millionth'' of a micron) as μμ. Etymology The name combines the SI prefix ''nano-'' (from the Ancient Greek , ', "dwarf") with the parent unit name ''metre'' (from Greek , ', "unit of measurement"). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associated with objects or materials based on their physical properties such as light absorption, reflection, or emission spectra. By defining a color space, colors can be identified numerically by their coordinates. Because perception of color stems from the varying spectral sensitivity of different types of cone cells in the retina to different parts of the spectrum, colors may be defined and quantified by the degree to which they stimulate these cells. These physical or physiological quantifications of color, however, do not fully explain the psychophysical perception of color appearance. Color science includes the perception of color by the eye and brain, the origin of color in materials, color theory in art, and the physics of electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelate
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are called chelants, chelators, chelating agents, or sequestering agents. They are usually organic compounds, but this is not a necessity, as in the case of zinc and its use as a maintenance therapy to prevent the absorption of copper in people with Wilson's disease. Chelation is useful in applications such as providing nutritional supplements, in chelation therapy to remove toxic metals from the body, as contrast agents in MRI scanning, in manufacturing using homogeneous catalysts, in chemical water treatment to assist in the removal of metals, and in fertilizers. Chelate effect The chelate effect is the greater affinity of chelating ligands for a metal ion than that of similar nonchelating (monodentate) ligands for the same metal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redox
Redox (reduction–oxidation, , ) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of substrate (chemistry), substrate change. Oxidation is the loss of Electron, electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is the gain of electrons or a decrease in the oxidation state. There are two classes of redox reactions: * ''Electron-transfer'' – Only one (usually) electron flows from the reducing agent to the oxidant. This type of redox reaction is often discussed in terms of redox couples and electrode potentials. * ''Atom transfer'' – An atom transfers from one substrate to another. For example, in the rusting of iron, the oxidation state of iron atoms increases as the iron converts to an oxide, and simultaneously the oxidation state of oxygen decreases as it accepts electrons released by the iron. Although oxidation reactions are commonly associated with the formation of oxides, other chemical species can serve the same function. In hydrogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
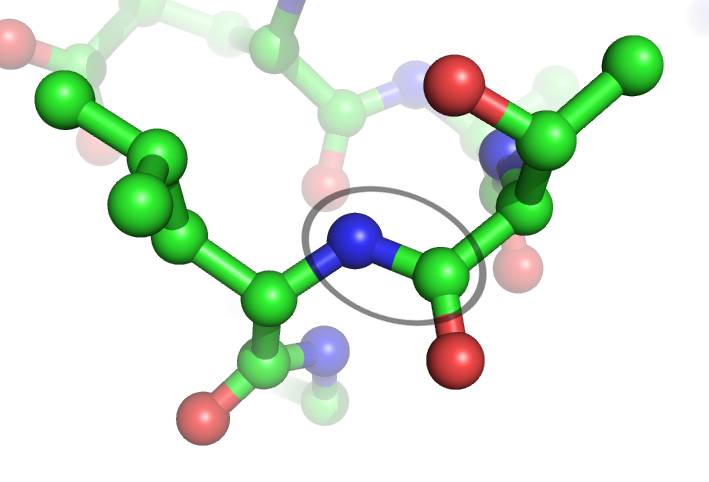
Peptide Bonds
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein chain. It can also be called a eupeptide bond to distinguish it from an isopeptide bond, which is another type of amide bond between two amino acids. Synthesis When two amino acids form a ''dipeptide'' through a ''peptide bond'', it is a type of condensation reaction. In this kind of condensation, two amino acids approach each other, with the non-side chain (C1) carboxylic acid moiety of one coming near the non-side chain (N2) amino moiety of the other. One loses a hydrogen and oxygen from its carboxyl group (COOH) and the other loses a hydrogen from its amino group (NH2). This reaction produces a molecule of water (H2O) and two amino acids joined by a peptide bond (−CO−NH−). The two joined amino acids are called a dipeptide. The am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper(II) Sulfate
Copper(II) sulfate, also known as copper sulphate, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It forms hydrates , where ''n'' can range from 1 to 7. The pentahydrate (''n'' = 5), a bright blue crystal, is the most commonly encountered hydrate of copper(II) sulfate. Older names for the pentahydrate include blue vitriol, bluestone, vitriol of copper,Antoine-François de Fourcroy, tr. by Robert Heron (1796) "Elements of Chemistry, and Natural History: To which is Prefixed the Philosophy of Chemistry". J. Murray and others, Edinburgh. Page 348. and Roman vitriol.Oxford University Press,Roman vitriol, Oxford Living Dictionaries. Accessed on 2016-11-13 It exothermically dissolves in water to give the aquo complex , which has octahedral molecular geometry. The structure of the solid pentahydrate reveals a polymeric structure wherein copper is again octahedral but bound to four water ligands. The centers are interconnected by sulfate anions to form chains. Anhydrous copper sulfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Bicarbonate
Sodium bicarbonate (IUPAC name: sodium hydrogencarbonate), commonly known as baking soda or bicarbonate of soda, is a chemical compound with the formula NaHCO3. It is a salt composed of a sodium cation ( Na+) and a bicarbonate anion ( HCO3−). Sodium bicarbonate is a white solid that is crystalline, but often appears as a fine powder. It has a slightly salty, alkaline taste resembling that of washing soda (sodium carbonate). The natural mineral form is nahcolite. It is a component of the mineral natron and is found dissolved in many mineral springs. Nomenclature Because it has long been known and widely used, the salt has many different names such as baking soda, bread soda, cooking soda, and bicarbonate of soda and can often be found near baking powder in stores. The term ''baking soda'' is more common in the United States, while ''bicarbonate of soda'' is more common in Australia, United Kingdom and Ireland. and in many northern/central European countries it is called ''Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |