|
Beating Against The Wind
Tacking is a sailing maneuver by which a sailing vessel, whose desired course is into the wind, turns its bow toward and through the wind so that the direction from which the wind blows changes from one side of the boat to the other, allowing progress in the desired direction. The opposite maneuver to tacking is called 'jibe', or 'wearing' on square-rigged ships, that is, turning the stern through the wind. No sailing vessel can move directly upwind, though that may be the desired direction, making this an essential maneuver of a sailing ship. A series of tacking moves, in a zig-zag fashion, is called beating, and allows sailing in the desired direction. This maneuver is used for different effects in races, where one ship is not only sailing in a desired direction, but also concerned with slowing the progress of competitors. The need for tacking Sailing ships cannot proceed directly into the wind, but often need to go in that direction. Movement is achieved by tacking. If a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sailing
Sailing employs the wind—acting on sails, wingsails or kites—to propel a craft on the surface of the ''water'' (sailing ship, sailboat, raft, windsurfer, or kitesurfer), on ''ice'' (iceboat) or on ''land'' (land yacht) over a chosen course, which is often part of a larger plan of navigation. From prehistory until the second half of the 19th century, sailing craft were the primary means of maritime trade and transportation; exploration across the seas and oceans was reliant on sail for anything other than the shortest distances. Naval power in this period used sail to varying degrees depending on the current technology, culminating in the gun-armed sailing warships of the Age of Sail. Sail was slowly replaced by steam as the method of propulsion for ships over the latter part of the 19th century – seeing a gradual improvement in the technology of steam through a number of stepwise developments. Steam allowed scheduled services that ran at higher average speeds than sail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crosswind
A crosswind is any wind that has a perpendicular component to the line or direction of travel. This affects the aerodynamics of many forms of transport. Moving non-parallel to the wind's direction creates a crosswind component on the object and thus increasing the apparent wind on the object; such use of cross wind travel is used to advantage by sailing craft, kiteboarding craft, power kiting, etc. On the other side, crosswind moves the path of vehicles sideways and can be a hazard. Definition When winds are not parallel to or directly with/against the line of travel, the wind is said to have a crosswind ''component''; that is, the force can be separated into two vector components: * the headwind or tailwind component in the direction of motion, * the crosswind component perpendicular to the former. A vehicle behaves as though it is directly experiencing a lateral effect of the magnitude of the crosswind component only. The crosswind component is computed by multiplying the win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainsail
A mainsail is a sail rigged on the main mast of a sailing vessel. * On a square rigged vessel, it is the lowest and largest sail on the main mast. * On a fore-and-aft rigged vessel, it is the sail rigged aft of the main mast. The sail's foot is normally attached to a boom. (In extremely heavy weather, the mainsail may be lowered, and a much smaller trysail hoisted in its place). Historical fore-and-aft rigs used a four-sided gaff rigged mainsail, sometimes setting a gaff topsail above it. Whereas once the mainsail was typically the largest sail, today the mainsail may be smaller than the jib or genoa; Prout catamarans typically have a mainmast stepped further aft than in a standard sloop, so that the mainsail is much smaller than the foresail. Bermuda rig The modern Bermuda rig uses a triangular mainsail aft of the mast, closely coordinated with a jib for sailing upwind. A large overlapping jib or genoa is often larger than the mainsail. In downwind conditions (with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proa
Proas are various types of multi-hull outrigger sailboats of the Austronesian peoples. The terms were used for native Austronesian ships in European records during the Colonial era indiscriminately, and thus can confusingly refer to the double-ended single-outrigger boats of Oceania, the double-outrigger boats of Island Southeast Asia, and sometimes ships with no outriggers or sails at all. In its most common usage, the term ''proa'' refers to the Pacific proas which consist of two (usually) unequal-length parallel hulls. It is sailed so that one hull is kept to windward, and the other to leeward. It is double-ended, since it needs to " shunt" to reverse direction when tacking. It is most famously used for the ''sakman'' ships of the Chamorro people of the Northern Marianas, which were known as the "flying proas" for their remarkable speed. In Island Southeast Asia, the term ''proa'' may also sometimes be used, but the terms perahu, prau, prahu, paraw and prow are more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiteboarding
Kiteboarding or kitesurfing is a sport that involves using wind power with a large power kite to pull a rider across a water, land, or snow surface. It combines aspects of paragliding, surfing, windsurfing, skateboarding, snowboarding, and wakeboarding. Kiteboarding is among the less expensive and the more convenient sailing sports. After some concepts emerged in the late 1970s and early 1980s and some designs were successfully tested, the sport received a wider audience in the late 1990s and became mainstream at the turn of the century. It has freestyle, wave-riding, and racing competitions. The sport held the speed sailing record, reaching before being eclipsed by the Vestas Sailrocket. Worldwide, there are 1.5 million kitesurfers, while the industry sells around 100,000 to 150,000 kites per year. Most power kites are leading edge inflatable kites or foil kites attached by about of flying lines to a control bar and a harness. The kitesurfer rides on either a bidire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windsurfing
Windsurfing is a wind propelled water sport that is a combination of sailing and surfing. It is also referred to as "sailboarding" and "boardsailing", and emerged in the late 1960s from the aerospace and surf culture of California. Windsurfing gained a popular following across Europe and North America by the late 1970s and had achieved significant global popularity by the 1980s. Windsurfing became an olympic sport in 1984. Newer variants include windfoiling, kiteboarding and wingfoiling. Hydrofoil fins under the board allow the boards to safely lift out of the water and fly silently and smoothly above the surface even in lighter winds. Windsurfing is a recreational, family friendly sport, most popular at flat water locations around the world that offer safety and accessibility for beginner and intermediate participants. Technique and equipment have evolved over the years Major competitive disciplines include slalom, wave and freestyle. Increasingly, "foiling" is replacing trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fore-and-aft Rig
A fore-and-aft rig is a sailing vessel rigged mainly with sails set along the line of the keel, rather than perpendicular to it as on a square rigged vessel. Description Fore-and-aft rigged sails include staysails, Bermuda rigged sails, gaff rigged sails, gaff sails, gunter rig, lateen sails, lug sails, tanja sails, the spanker sail on a square rig and crab claw sails. Fore-and-aft rigs include: * Rigs with one mast: the proa, the catboat, the sloop, the cutter * Rigs with two masts: the ketch, the yawl * Rigs with two or more masts: the schooner Barques and barquentines are partially square rigged and partially fore-and-aft rigged. A rig which combines both on a foremast is known as a hermaphroditic rig. History Austronesia The fore-and-aft rig is believed to have been first developed independently by the Austronesian peoples some time around 1500 BC with the invention of the crab claw sail. It is suggested that it evolved from a more primitive "V"-shaped "square" s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
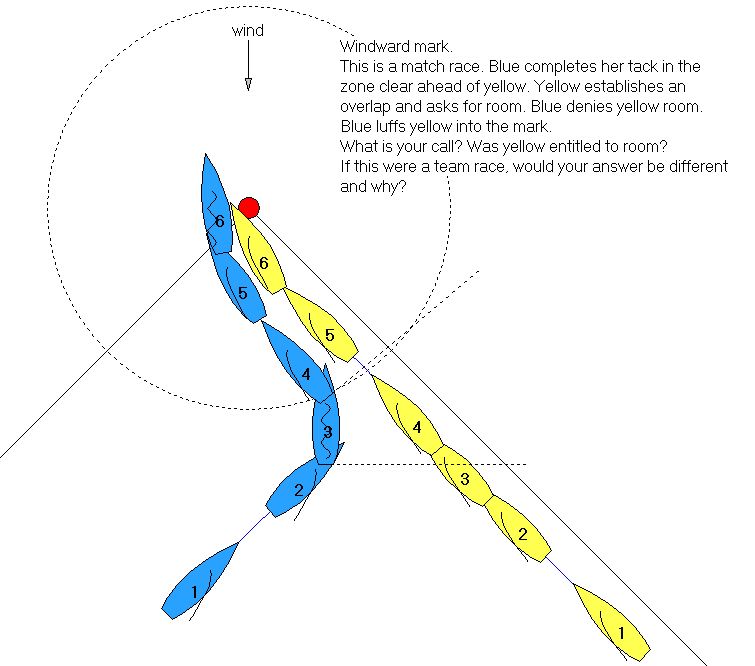
Racing Rules Of Sailing
The Racing Rules of Sailing (often abbreviated to RRS) govern the conduct of yacht racing, windsurfing, kitesurfing, model boat racing, dinghy racing and virtually any other form of racing around a course with more than one vessel while powered by the wind. A new revision is published every four years (after the Olympic Games) by World Sailing, the sport's world governing body. Full information on the rules can be viewed at World Sailing. Contents of the Rules Racing Rules of Sailing were most dramatically simplified in 1997 since the 1940s. The new document contains four main rules art 2, Section A # Boats on a port tack shall keep clear of boats on starboard tack (Rule 10). # When boats are on the same tack and overlapped, the boat to windward (the boat closest to the wind) shall keep clear of a leeward boat (Rule 11). # When boats are on the same tack and not overlapped, the boat that is astern shall keep clear of the boat ahead. (Rule 12). # When a boat is tacking (chan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lee Side
Windward () and leeward () are terms used to describe the direction of the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. along the direction towards which the wind is going. The side of a ship that is towards the leeward is its "lee side". If the vessel is heeling under the pressure of crosswind, the lee side will be the "lower side". During the Age of Sail, the term ''weather'' was used as a synonym for ''windward'' in some contexts, as in the ''weather gage''. Because it captures rain, the windward side of a mountain tends to be wet compared to the leeward it blocks. Origin The term "lee" comes from the middle-low German word // meaning "where the sea is not exposed to the wind" or "mild". The terms Luv and Lee (engl. Windward and Leeward) have been in use since the 17th century. Usage Windward and leeward directions (and the points o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodynamic
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dynamics and its subfield of gas dynamics. The term ''aerodynamics'' is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, the difference being that "gas dynamics" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, and is not limited to air. The formal study of aerodynamics began in the modern sense in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag were recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics were directed toward achieving heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Otto Lilienthal in 1891. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer simulations has formed a rational basis for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manchester and Duluth; these access the sea via rivers or canals. Because of their roles as ports of entry for immigrants as well as soldiers in wartime, many port cities have experienced dramatic multi-ethnic and multicultural changes throughout their histories. Ports are extremely important to the global economy; 70% of global merchandise trade by value passes through a port. For this reason, ports are also often densely populated settlements that provide the labor for processing and handling goods and related services for the ports. Today by far the greatest growth in port development is in Asia, the continent with some of the world's largest and busiest ports, such as Singapore and the Chinese ports of Shanghai and Ningbo-Zhou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinghy Sailing
Dinghy sailing is the activity of sailing small boats by using five essential controls: * the sails * the foils (i.e. the daggerboard or centreboard and rudder and sometimes lifting foils as found on the Moth) * the trim (forward/rear angle of the boat in the water) * side-to-side balance of the dinghy by hiking or movement of the crew, particularly in windy weather ("move fast or swim") * the choice of route (in terms of existing and anticipated wind shifts, possible obstacles, other water traffic, currents, tides etc.) When racing, the above skills need to be refined and additional skills and techniques learned, such as the application of the "racing rules of sailing", boat handling skills when starting and when rounding marks, and knowledge of tactics and strategy. Racing tactics include positioning the boat at different angles. To improve speed when racing, sailors should position themselves at the windward direction (closest to the direction of the wind) in order to get " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |