|
Battle Of Lucena
The Battle of Lucena, also called Battle of Martín González, was a war event in which Christian forces of the Crown of Castile were faced against the Muslim forces of the Emirate of Granada, Nasrid Emirate of Granada. It took place in the month of April of the year 1483, in the course of the Granada War, and in the course of it the Christian forces took Muhammad XII of Granada as prisoner. Description It was fought very close to the city of Lucena, Córdoba, Lucena, in the Province of Córdoba (Spain), province of Córdoba, Andalusia, Spain, south of the Sierra de Aras. The origin of the battle was the pretense of Muhammad XII of Granada (Boabdil) to take Lucena and perform a punishment raid against the Christians, to emulate the victory that his competitor, Muhammad XIII, Sultan of Granada, Muhammad XIII had won, that defeated the Christian forces at the Al-Sarquiyya (Córdoba). The Emirate of Granada was at that time experiencing a serious internal conflict between the sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconquista
The ' (Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the Nasrid kingdom of Granada in 1492, in which the Christian kingdoms expanded through war and conquered al-Andalus; the territories of Iberia ruled by Muslims. The beginning of the ''Reconquista'' is traditionally marked with the Battle of Covadonga (718 or 722), the first known victory by Christian military forces in Hispania since the 711 military invasion which was undertaken by combined Arab- Berber forces. The rebels who were led by Pelagius defeated a Muslim army in the mountains of northern Hispania and established the independent Christian Kingdom of Asturias. In the late 10th century, the Umayyad vizier Almanzor waged military campaigns for 30 years to subjugate the northern Christian kingdoms. His armies ravaged the north, even s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu L-Hasan Ali, Sultan Of Granada
Abu'l-Hasan Ali ibn Sa'd ( ar, أبو الحسن علي, Abū al-Ḥasan ‘Alī ibn Saʿd; d. 1485), known as Muley Hacén in Spanish (''Muley'' being derived from Arabic Mawlay = "My Lord"), was the twenty-first Nasrid ruler of the Emirate of Granada in Spain, from 1464 to 1482 and again from 1483 to 1485. Life The son of Sa'd, Abu'l-Hasan Ali became sultan in 1464, and in 1477 he refused to pay tribute to the Crown of Castile. In 1481 he ordered an invasion to the city of Zahara de la Sierra by surprise, killing and enslaving the unarmed Christian Zaharans. This action was taken by Isabella I of Castile as a reason to start the war against Granada. He was the father of Muhammad XII (also known as ''Boabdil''), the last sultan of Granada, by his relative Aixa. He abandoned Aixa to marry the former Christian slave Isabel de Solís, the daughter of Sancho Jiménez de Solís, ''Alcalde'' of La Peña de Martos, who he gave the name Zoraida or Soraya (Thuraya, "Star") after her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1480s In Spain
148 may refer to: *148 (number), a natural number *AD 148, a year in the 2nd century AD *148 BC, a year in the 2nd century BC *148 (album), an album by C418 *148 (Meiktila) Battery Royal Artillery *148 (New Jersey bus) See also * List of highways numbered 148 * {{Number disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Museum Of Toledo
The Museum of the Army (Spanish: ''Museo del Ejército'') is a national museum located in Toledo, Spain, attached to the Ministry of Defence. The collection was previously housed in Madrid, and the museum opened on its present site in 2010. It occupies two linked buildings, Toledo's historic Alcázar (castle) and a purpose-built extension. History The history of the museum began in 1803 when the royal military museum was established in a building in Madrid known as the Palacio de Monteleón. The building also served as a barracks for artillery units and it was attacked and looted by the French when they suppressed the Dos de Mayo Uprising of 1808. The museum was reestablished, but in 1827 it was divided into two sections: the Museo de Artillería and the Museo de Ingenieros. Later the collections were unified and housed in the Hall of Realms. In the twenty-first century the collections were moved from Madrid to Toledo. The new premises offered much more space, although the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boabdil Sword
Abu Abdallah Muhammad XII ( ar, أبو عبد الله محمد الثاني عشر, Abū ʿAbdi-llāh Muḥammad ath-thānī ʿashar) (c. 1460–1533), known in Europe as Boabdil (a Spanish rendering of the name ''Abu Abdallah''), was the 22nd and last Nasrid ruler of the Emirate of Granada in Iberia. Sultan Muhammad XII was the son of Abu l-Hasan Ali, Sultan of the Emirate of Granada whom he succeeded in 1482, as a result of both court intrigue and unrest amongst the population at large. Muhammad XII soon sought to gain prestige by invading Castile, but was taken prisoner at Lucena in 1483. Muhammad's father was then restored as ruler of Granada, to be replaced in 1485 by his uncle Muhammad XIII, also known as Abdullah ez Zagal. Muhammad obtained his freedom and Christian support to recover his throne in 1487, by consenting to hold Granada as a tributary kingdom under the Catholic monarchs. He further undertook not to intervene in the Siege of Málaga, in which Mála ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porcuna
Porcuna is a village and municipality in the province of Jaén in Andalusia, Spain, 42 km from Jaén and 50 km from Córdoba. The primary occupation of the 6,990 inhabitants is olive growing. The main tourist attractions are the tower of Boabdil, the ''Casa Piedra'', the ''Paseo de Jesús'' and the various hermitages. One of Porcuna's famous sons is the Baroque poet Juan del Valle y Caviedes, born here around 1645, who moved to Perú at an early age and wrote biting satirical works attacking the hypocrisy of the Colonial upper class society of Lima Lima ( ; ), originally founded as Ciudad de Los Reyes (City of The Kings) is the capital and the largest city of Peru. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón River, Chillón, Rímac River, Rímac and Lurín Rivers, in the desert zone of t .... See also * Bear of Porcuna * Torito of Porcuna References Municipalities in the Province of Jaén (Spain) {{Andalusia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
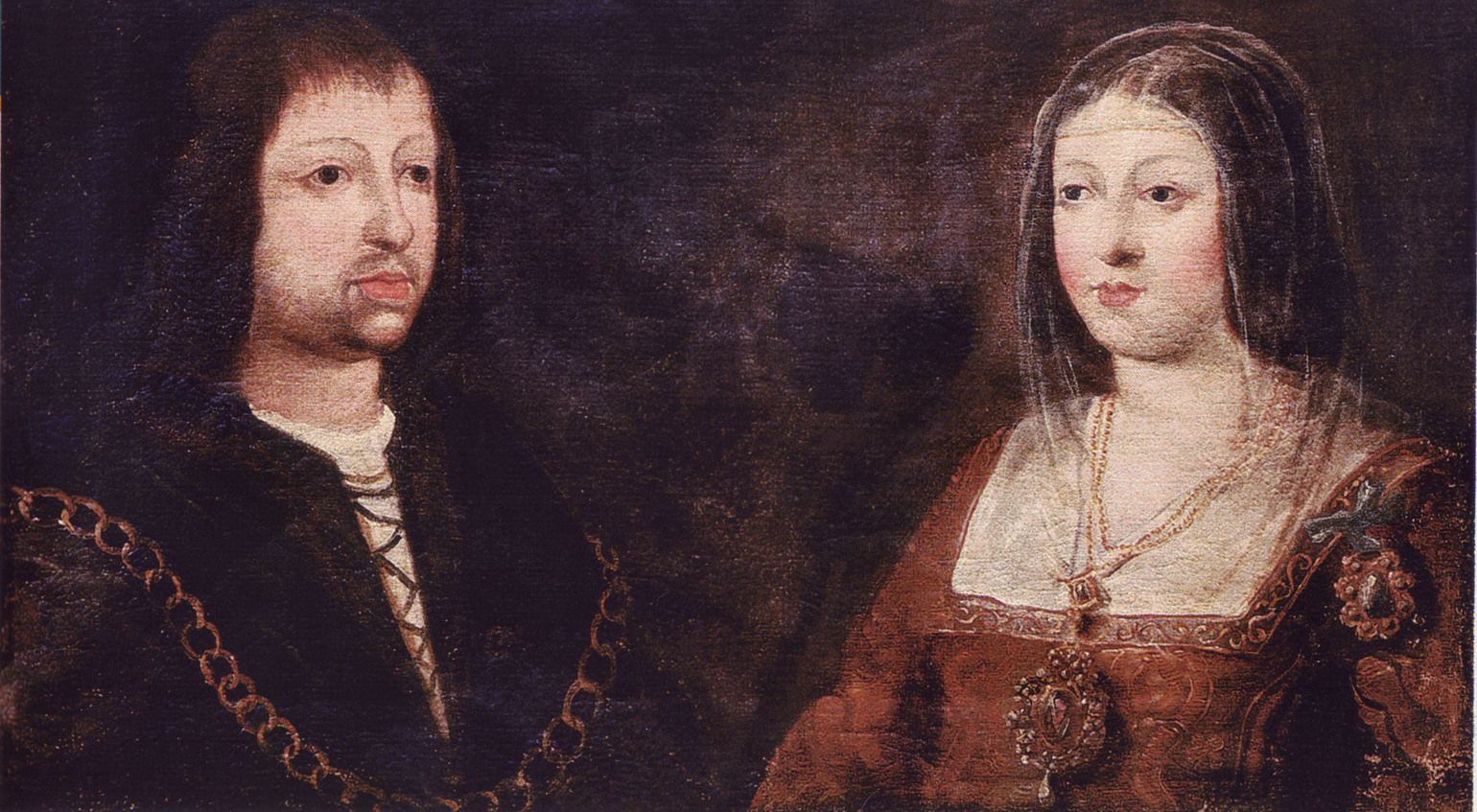
Ferdinand II Of Aragon
Ferdinand II ( an, Ferrando; ca, Ferran; eu, Errando; it, Ferdinando; la, Ferdinandus; es, Fernando; 10 March 1452 – 23 January 1516), also called Ferdinand the Catholic (Spanish: ''el Católico''), was King of Aragon and Sardinia from 1479, King of Sicily from 1468, King of Naples (as Ferdinand III) from 1504 and King of Navarre (as Ferdinand I) from 1512 until his death in 1516. He was also the nominal Duke of the ancient Duchies of Athens and Neopatria. He was King of Castile and León (as Ferdinand V) from 1475 to 1504, alongside his wife Queen Isabella I. From 1506 to 1516, he was the Regent of the Crown of Castile, making him the effective ruler of Castile. From 1511 to 1516, he styled himself as ''Imperator totius Africa'' (Emperor of All Africa) after having conquered Tlemcen and making the Zayyanid Sultan, Abu Abdallah V, his vassal. He was also the Grandmaster of the Spanish Military Orders of Santiago (1499-1516), Calatrava (1487-1516), Alcantara (1492- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs were Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon, whose marriage and joint rule marked the ''de facto'' unification of Spain. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being both descended from John I of Castile; to remove the obstacle that this consanguinity would otherwise have posed to their marriage under canon law, they were given a papal dispensation by Sixtus IV. They married on October 19, 1469, in the city of Valladolid; Isabella was eighteen years old and Ferdinand a year younger. It is generally accepted by most scholars that the unification of Spain can essentially be traced back to the marriage of Ferdinand and Isabella. Spain was formed as a dynastic union of two crowns rather than a unitary state, as Castile and Aragon remained separate kingdoms until the Nueva Planta decrees of 1707–16. The court of Ferdinand and Isabella was constantly on the move, in order to bolster local support for the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABC (newspaper)
''ABC'' () is a Spanish national daily newspaper. It is the second largest general-interest newspaper in Spain, number one in Madrid, and the oldest newspaper still operating in Madrid. Along with '' El Mundo'' and '' El País'', it is one of Spain’s three newspapers of record. History and profile ''ABC'' was first published in Madrid on 1 January 1903 by Torcuato Luca de Tena y Álvarez-Ossorio. The founding publishing house was Prensa Española, which was led by the founder of the paper, Luca de Tena. The paper started as a weekly newspaper, turning daily in June 1905. In 1928 ABC had two editions, one for Madrid and the other for Seville. The latter was named ''ABC de Sevilla''. On 20 July 1936, shortly after the Spanish Civil War began, ''ABC'' in Madrid was seized by the republican government, which changed the paper's politics to support the Republicans. The same year '' Blanco y Negro'', a magazine, became its supplement. The ''ABC'' printed in Seville was supportive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle Of Moral
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a palace, which is not fortified; from a fortress, which was not always a residence for royalty or nobility; from a ''pleasance'' which was a walled-in residence for nobility, but not adequately fortified; and from a fortified settlement, which was a public defence – though there are many similarities among these types of construction. Use of the term has varied over time and has also been applied to structures such as hill forts and 19th-20th century homes built to resemble castles. Over the approximately 900 years when genuine castles were built, they took on a great many forms with many different features, although some, such as curtain walls, arrowslits, and portcullises, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabra, Spain
Cabra is a rural town in Córdoba province, Andalusia, Spain and the site of former bishopric Egabro. It lies along the route between Córdoba and Málaga in the south of Spain. It is an entrance point to the Parque Natural de las Sierras Subbéticas. Although the main activity in Cabra is primary industry, it is noted as a source of red polished limestone. As a settlement, Cabra has existed over centuries, under many different rulers. In 2005, the municipality had a population of 20,940, most of whom (19,523) lived in Cabra township. Geography Cabra is located in the Province of Córdoba in the autonomous community of Andalusia in southern Spain. The municipality's mean altitude is and it covers . The town is built in a valley between the Sierra de Cabra and the Sierra de Montilla, which together form the watershed between the rivers Cabra and Guadajoz. It has a population density of 91.4 inhabitants per km². The geographical mean coordinates are , from the province' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count Of Cabra
Count of Cabra is a Spanish noble title created by King Henry IV of Castile on 2 November 1455 for Diego Fernandez de Cordova and Montemayor, 1st Viscount of Iznájar. The titleholder is a Grandee of Spain, the third oldest such title in Spain. The name refers to the Andalusian municipality of Cabra in the province of Córdoba. The title is carried by the head of the House of Cabra. Count of Cabra before 1455 Prior to the concession of the countship of Cabra to Diego Fernández de Córdoba and Montemayor, Henry II of Castile had granted the title to Henry of Castile (1380–1404), his natural son with Juana de Sousa of Córdoba, who died without descendants as the 1st Duke of Medina Sidonia Duke of Medina Sidonia ( es, Duque de Medina Sidonia) is a peerage grandee title of Spain in Medina-Sidonia, holding the oldest extant dukedom in the kingdom, first awarded by King John II of Castile in 1380. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |