|
Battle Of Covadonga
The Battle of Covadonga took place in 718 or 722 between the army of Pelagius the Visigoth and the army of the Umayyad Caliphate. Fought near Covadonga in the Picos de Europa, either in 718 or 722, it resulted in a victory for the forces of Pelagius. It is traditionally regarded as the foundational event of the Kingdom of Asturias and thus the initial point of the Christian ' ("reconquest") of Spain after the Umayyad conquest of 711. __TOC__ Prelude According to texts written by Mozarabs in northern Hispania during the late ninth century, the Visigoths in 718 elected a nobleman named Pelagius (c.685–737) as their ''princeps'', or leader. Pelagius, the first monarch of the Asturian Kingdom, son of Favila, who had been a dignitary at the court of the Visigoth King Egica (687–700), established his headquarters at Cangas de Onís, Asturias and incited an uprising against the Umayyad Muslims. From the beginning of the Muslim invasion of Hispania, refugees and combatants from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reconquista
The ' (Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the Nasrid kingdom of Granada in 1492, in which the Christian kingdoms expanded through war and conquered al-Andalus; the territories of Iberia ruled by Muslims. The beginning of the ''Reconquista'' is traditionally marked with the Battle of Covadonga (718 or 722), the first known victory by Christian military forces in Hispania since the 711 military invasion which was undertaken by combined Arab- Berber forces. The rebels who were led by Pelagius defeated a Muslim army in the mountains of northern Hispania and established the independent Christian Kingdom of Asturias. In the late 10th century, the Umayyad vizier Almanzor waged military campaigns for 30 years to subjugate the northern Christian kingdoms. His armies ravaged the north, even s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty ( ar, ٱلْأُمَوِيُّون, ''al-ʾUmawīyūn'', or , ''Banū ʾUmayyah'', "Sons of Umayya ibn Abd Shams, Umayyah"). Uthman ibn Affan (r. 644–656), the third of the Rashidun caliphs, was also a member of the clan. The family established dynastic, hereditary rule with Mu'awiya I, Muawiya ibn Abi Sufyan, long-time governor of Syria (region), Greater Syria, who became the sixth caliph after the end of the First Fitna in 661. After Mu'awiyah's death in 680, conflicts over the succession resulted in the Second Fitna, and power eventually fell into the hands of Marwan I from another branch of the clan. Greater Syria remained the Umayyads' main power base thereafter, with Damascus serving as their capital. The Umayyads c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to Cap de Creus on the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coast. It reaches a maximum altitude of at the peak of Aneto. For the most part, the main crest forms a divide between Spain and France, with the microstate of Andorra sandwiched in between. Historically, the Crown of Aragon and the Kingdom of Navarre extended on both sides of the mountain range. Etymology In Greek mythology, Pyrene (mythology), Pyrene is a princess who eponym, gave her name to the Pyrenees. The Greek historiography, Greek historian Herodotus says Pyrene is the name of a town in Celts, Celtic Europe. According to Silius Italicus, she was the virgin daughter of Bebryx, a king in Narbonensis, Mediterranean Gaul by whom the hero Hercules was given hospitality during his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during Republican era, Cisalpina was annexed in 42 BC to Roman Italy), and Germany west of the Rhine. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Belgica, and Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture, which extended across all of Gaul, as well as east to Raetia, Noricum, Pannonia, and southwestern Germania during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. During the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, Gaul fell under Roman rule: Gallia Cisalpina was conquered in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri and the Teutons, who were in turn defeated by the Romans by 103 BC. Julius Caesar finally subdued the remaining parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narbonne
Narbonne (, also , ; oc, Narbona ; la, Narbo ; Late Latin:) is a commune in France, commune in Southern France in the Occitania (administrative region), Occitanie Regions of France, region. It lies from Paris in the Aude Departments of France, department, of which it is a Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture. It is located about from the shores of the Mediterranean Sea and was historically a prosperous port. From the 14th century it declined following a change in the course of the river Aude (river), Aude. It is marginally the largest commune in Aude. But the capital of the Aude department is the smaller commune of Carcassonne. Geography Narbonne is linked to the nearby Canal du Midi and the river Aude (river), Aude by the Canal de la Robine, which runs through the centre of town. It is very close to the A9 motorway, which connects Montpellier and Nîmes to Perpignan and, across the border, to Barcelona in Spain. There is also a recently renovated train station which se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages. Moors are not a distinct or self-defined people. The 1911 ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' observed that the term had "no real ethnological value." Europeans of the Middle Ages and the early modern period variously applied the name to Arabs and North African Berbers, as well as Muslim Europeans. The term has also been used in Europe in a broader, somewhat derogatory sense to refer to Muslims in general,Menocal, María Rosa (2002). ''Ornament of the World: How Muslims, Jews and Christians Created a Culture of Tolerance in Medieval Spain''. Little, Brown, & Co. , p. 241 especially those of Arab or Berber descent, whether living in Spain or North Africa. During the colonial era, the Portuguese introduced the names " Ceylon Moors" and "Indian Moors" in South Asia and Sri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Córdoba, Spain
Córdoba (; ),, Arabic: قُرطبة DIN 31635, DIN: . or Cordova () in English, is a city in Andalusia, Spain, and the capital of the Province of Córdoba (Spain), province of Córdoba. It is the third most populated Municipalities in Spain, municipality in Andalusia and the 11th overall in the country. The city primarily lies on the right bank of the Guadalquivir, in the south of the Iberian Peninsula. Once a Roman settlement, it was taken over by the Visigothic Kingdom, Visigoths, followed by the Umayyad conquest of Hispania, Muslim conquests in the eighth century and later becoming the capital of the Umayyad Caliphate of Córdoba. During these Islamic Golden Age, Muslim periods, Córdoba was transformed into a world leading center of education and learning, producing figures such as Maimonides, Averroes, Ibn Hazm, and Al-Zahrawi, and by the 10th century it had grown to be the second-largest city in Europe. Following the Siege of Córdoba (1236), Christian conquest in 1236, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jizya
Jizya ( ar, جِزْيَة / ) is a per capita yearly taxation historically levied in the form of financial charge on dhimmis, that is, permanent Kafir, non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The jizya tax has been understood in Islam as a fee for protection provided by the Muslim ruler to non-Muslims, for the exemption from military service for non-Muslims, for the permission to practice a non-Muslim faith with some communal autonomy in a Muslim state, and as material proof of the non-Muslims' submission to the Muslim state and its laws. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Social Sciences'' 24:4, Oxford; pp. 99–100. and the application of jizya varied in the course of Islamic history. However, scholars largely agree that early Muslim rulers adapted existing systems of taxation and tribute that were established under previous rulers of the conquered lands, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basques
The Basques ( or ; eu, euskaldunak ; es, vascos ; french: basques ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Basques are indigenous to, and primarily inhabit, an area traditionally known as the Basque Country ( eu, Euskal Herria) — a region that is located around the western end of the Pyrenees on the coast of the Bay of Biscay and straddles parts of north-central Spain and south-western France. Etymology The English word ''Basque'' may be pronounced or and derives from the French ''Basque'' (), itself derived from Gascon ''Basco'' (pronounced ), cognate with Spanish ''Vasco ''(pronounced ). Those, in turn, come from Latin ''Vascō'' (pronounced ; plural '' Vascōnes''—see history section below). The Latin generally evolved into the bilabials and in Gascon and Spanish, probably under the influence of Basque and the related Aquitania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantabri
The Cantabri ( grc-gre, Καντάβροι, ''Kantabroi'') or Ancient Cantabrians, were a pre-Ancient Rome, Roman people and large tribal federation that lived in the northern coastal region of ancient Iberia in the second half of the first millennium BC. These peoples and their territories were incorporated into the Roman Province of Hispania Tarraconensis in 19 BC, following the Cantabrian Wars. Name ' is a Latinisation of names, Latinized form of a local name, presumably meaning "Highlanders" and deriving from the linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed root *''cant''- ("mountain") in Ligurian language (ancient), Ancient Ligurian. During the High and Late Middle Ages, as well as Modern Period, the name refers usually to the Basques. Geography Cantabria, the land of the Cantabri, originally comprised much of the highlands of the northern Spanish Atlantic coast, including the whole of modern Cantabria province, eastern Asturias, nearby mountainous regions of Castile and Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galicians
Galicians ( gl, galegos, es, gallegos, link=no) are a Celtic-Romance ethnic group from Spain that is closely related to the Portuguese people and has its historic homeland is Galicia, in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. Two Romance languages are widely spoken and official in Galicia: the native Galician and Spanish. Etymology The ethnonym of the Galicians (''galegos'') derives directly from the Latin ''Gallaeci'' or ''Callaeci'', itself an adaptation of the name of a local Celtic tribe known to the Greeks as Καλλαϊκoί (''Kallaikoí''). They lived in what is now Galicia and northern Portugal and were defeated by the Roman General Decimus Junius Brutus Callaicus in the 2nd century BCE and later conquered by Augustus. The Romans later applied that name to all the people who shared the same culture and language in the north-west, from the Douro River valley in the south to the Cantabrian Sea in the north and west to the Navia River. That encompassed such tribes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
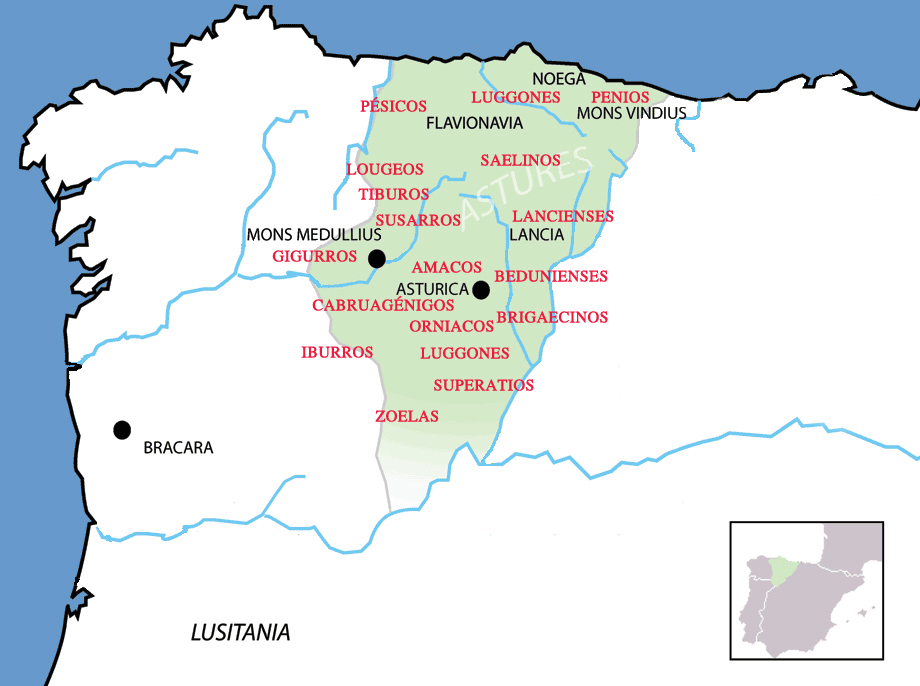
Astures
The Astures or Asturs, also named Astyrs, were the Hispano-Celtic inhabitants of the northwest area of Hispania that now comprises almost the entire modern autonomous community of Principality of Asturias, the modern province of León, and the northern part of the modern province of Zamora (all in Spain), and eastern Trás os Montes in Portugal. They were a horse-riding highland cattle-raising people who lived in circular huts of stone drywall construction. The Albiones were a major tribe from western Asturias. Isidore of Seville gave an etymology as coming from a ''river Asturia'', identified by David Magie with Órbigo river in the plain of León, by others the modern Esla river. Location The Asturian homeland encompassed the modern autonomous community of Asturias and the León, eastern Lugo, Orense, and northern Zamora provinces, along with the northeastern tip of the Portuguese region of Trás-os-Montes. Here they held the towns of ''Lancia'' (Villasabariego – Leó ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |