|
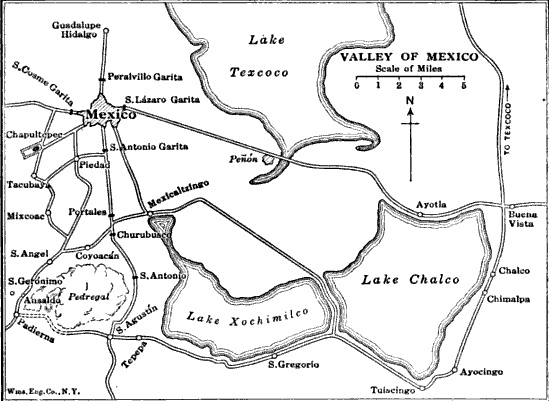
Battle Of Contreras
The Battle of Contreras, also known as the Battle of Padierna, took place on 19–20 August 1847, in one of the final encounters of the Mexican–American War, as invading U.S. forces under Winfield Scott approached the Mexican capital. American forces surprised and then routed the Mexican forces of General Gabriel Valencia, who had disobeyed General Antonio López de Santa Anna's orders for his forces' placement. Although the battle was an overwhelming victory for U.S. forces, there are few depictions of it in contemporary popular prints. The armies re-engaged the next day in the Battle of Churubusco. Background General Gabriel Valencia's army of the north was part of the forces that fought at the Battle of Buena Vista in February 1847, in which Santa Anna retreated before giving a crushing blow to the forces of Zachary Taylor. The Mexican forces were then divided in two, with one sent to Cerro Gordo and the other to San Luis Potosí. General Valencia was given the command of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Nebel
Carl Nebel (18 March 1805 – 4 June 1855) was a German engineer, architect and draughtsman,Thieme-Becker, entry "Nebel, Carl" best known for his detailed paintings and lithographic prints made from them of the Mexican landscape and people during the battles of the Mexican–American War. Biography Nebel was born in Altona, today a part of Hamburg. After studies in Hamburg and Paris, he travelled to America, where he was a resident of Mexico from 1829 until 1834. In 1836, he published in Paris his renowned illustrated work on that country—''Voyage pittoresque et archéologique dans la partie la plus intéressante du Méxique'', with 50 lithographs made from his paintings, twenty of which were hand-colored, and an introduction by Alexander von Humboldt.D. Sloan Rare Books: Auction 22: Nebel, Carl, "Voyage pittoresque et archéologique dans la partie la plus intéressante du Mexique"'. URL last accessed 2008-09-16. In 1851, he published together with journalist George Wilkins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalco De Diaz Covarrubias
Chalco may refer to: *Chalco de Díaz Covarrubias, or simply Chalco, seat of the municipality of Chalco, State of México *Chalco (altépetl), an altépetl or pre-Columbian city-state in central Mexico *Lake Chalco, endorheic lake formerly located in the Valley of Mexico *Chalco, Nebraska in northern Sarpy County, Nebraska, United States *Chalco Hills Recreation Area in Nebraska *Valle de Chalco Solidaridad, a municipality located in State of Mexico, Mexico *Chalco, Aluminum Corporation of China Limited *The Chalco system in A. A. Attanasio's ''The Last Legends of Earth'' See also *Calco *Chaco (other) Chaco may refer to: Places in South America * Chaco Basin, spanning Argentina, Bolivia, and Paraguay * Chaco Department, a historical department in Paraguay and proposed in Bolivia * Chaco Province, a province in the northeastern part of Argenti ... * Chalcon {{DEFAULTSORT:Chalco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picket (military)
A picket (archaically, picquet ariant form ''piquet'' is a soldier, or small unit of soldiers, placed on a defensive line forward of a friendly position to provide timely warning and screening against an enemy advance. It can also refer to any unit (e.g. a scout vehicle, surveillance aircraft or patrol ship) performing a similar function. A picket guarding a fixed position may be known as a sentry or guard. Origins Picket (Fr. , a pointed stake or peg, from , 'to point or pierce'), is thought to have originated in the French Army around 1690, from the circumstance that an infantry company on outpost duty dispersed its musketeers to watch, with a small group of pikemen called ''piquet'' remaining in reserve. It was in use in the British Army before 1735 and probably much earlier. Usage ''Picket'' now refers to a soldier or small unit of soldiers maintaining a watch. This may mean a watch for the enemy, or other types of watch e.g. fire picket. This can be likened to the art of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enfilade And Defilade
Enfilade and defilade are concepts in military tactics used to describe a military formation's exposure to enemy fire. A formation or position is "in enfilade" if weapon fire can be directed along its longest axis. A unit or position is "in defilade" if it uses natural or artificial obstacles to shield or conceal itself from enfilade and hostile fire. The strategies, named by the English during the Hundred Years' War, use the French '' enfiler'' ("to put on a string or sling") and ''défiler'' ("to slip away or off") spoken by English nobility of the time. Enfilade fire—gunfire directed against an enfiladed formation or position—is also commonly known as "flanking fire". Raking fire is the equivalent term in naval warfare. Strafing, firing on targets from a flying platform, is often done with enfilade fire. It is a very advantageous, and much sought for, position for the attacking force. Enfilade A formation or position is "in enfilade" if weapon fire can be dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert E
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lava Field
Lava fields are large, mostly flat areas of surface or subaquatic lava flows. Such features are generally composed of highly fluid basalt lava, and can extend for tens or hundreds of miles across the underlying terrain. Morphology and structure The final morphology of a lava field can reveal properties such as internal structure, composition, and mechanics of the lava flow when it was fluid. The ridges and patterns on top of the lava field show the direction of the channels and the oftentimes active lava tubes that may be underneath the solidified "crust." It can also reveal whether the lava flow can be classified as pāhoehoe or 'a'ā. The two main types of lava field structures are defined as sheet flow lava and pillow lava. Sheet flow lava appears like a wrinkled or folded sheet, while pillow lava is bulbous, and often looks like a pile of pillows atop one another. An important aspect of lava flow morphology is a phenomenon known as lava flow inflation. This occurs in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdalena Contreras
La Magdalena Contreras () is a borough (''demarcación territorial'') in the Mexico City. As of the 2010 census, it has a population of 239,086 inhabitants and is the third-least populous of Mexico City's boroughs. It lies at an elevation of above sea level. It is named after two historically important communities—La Magdalena Atlitic and Colonia Contreras. The northern end of the borough is urbanized. The rest of Magdalena Contreras, with its mountains and ravines, is designated as a conservation zone. However, urban sprawl has put pressure on these conservation areas. In an effort to preserve the area's forests and natural resources, the borough government has started promoting ecotourism. The largest ecotourism park is Los Dinamos where canyons and ravines are cut by streams and freshwater springs that eventually form the Río Magdalena, Mexico City’s only remaining free-flowing river. History The borough takes its name from the La Magdalena Atlitic, one of four communitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Ángel
San Ángel is a Colonia (Mexico), colonia or neighborhood of Mexico City, located in the southwest in Álvaro Obregón, D.F., Álvaro Obregón borough. Historically, it was a rural community, called Tenanitla in the pre-Hispanic period. Its current name is derived from the El Carmen monastery school called San Ángel Mártir. San Ángel remained a rural community, centered on the monastery until the 19th and 20th centuries, when the monastery was closed and when the area joined urban sprawl of Mexico City. However, the area still contains many of its former historic buildings and El Carmen is one of the most visited museums in the city. It is also home to an annual flower fair called the Feria de las Flores, held since 1856. In 1934, San Ángel was declared as a ''Pueblo Típico Pintoresco'' (Picturesque Typical Town); in 1987, due to presidential order, it was declared historical monument zone. Geography San Ángel is located in the southwest of the Federal District of Mexico alo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonio Lopez De Santa Anna
Antonio is a masculine given name of Etruscan origin deriving from the root name Antonius. It is a common name among Romance language-speaking populations as well as the Balkans and Lusophone Africa. It has been among the top 400 most popular male baby names in the United States since the late 19th century and has been among the top 200 since the mid 20th century. In the English language it is translated as Anthony, and has some female derivatives: Antonia, Antónia, Antonieta, Antonietta, and Antonella'. It also has some male derivatives, such as Anthonio, Antón, Antò, Antonis, Antoñito, Antonino, Antonello, Tonio, Tono, Toño, Toñín, Tonino, Nantonio, Ninni, Totò, Tó, Tonini, Tony, Toni, Toninho, Toñito, and Tõnis. The Portuguese equivalent is António (Portuguese orthography) or Antônio (Brazilian Portuguese). In old Portuguese the form Antão was also used, not just to differentiate between older and younger but also between more and less important. In Galician t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Agustín De Las Cuevas
Tlalpan ( nci, Tlālpan, , place on the earth, ) is a borough (''demarcación territorial'') in Mexico City. It is the largest borough, with over eighty percent under conservation as forest and other ecologically sensitive area. The rest, almost all of it on the northern edge, has been urban since the mid-20th century. When it was created in 1928, it was named after the most important settlement of the area, Tlalpan, which is referred to as “Tlalpan center” (Tlalpan centro) to distinguish it from the borough. This center, despite being in the urbanized zone, still retains much of its provincial atmosphere with colonial era mansions and cobblestone streets. Much of the borough's importance stems from its forested conservation areas, as it functions to provide oxygen to the Valley of Mexico and serves for aquifer recharge. Seventy percent of Mexico City's water comes from wells in this borough. However, the area is under pressure as its mountainous isolated location has attract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Chalco
Lake Chalco was an endorheic lake formerly located in the Valley of Mexico, and was important for Mesoamerican cultural development in central Mexico. The lake was named after the ancient city of Chalco on its former eastern shore. Geography Lake Chalco and the other Mexican great lakes (the brackish lakes Texcoco, Zumpango and Xaltocan and the freshwater Xochimilco) formed the ancient Basin of Mexico lake system. These lakes were home to many Mesoamerican cultures including the Toltecs and the Aztecs. Lake Chalco itself had a fresh water hydrologic structure due in large part to the artesian springs lining its south shore. This allowed extensive beds to be cultivated through the Aztec era. After the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, these beds fell into disuse and were largely abandoned. History Starting during the Aztec era and continuing into the 20th century, efforts were made to drain Lake Chalco and her sister lakes in order to avoid periodic flooding and to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gideon Johnson Pillow
Gideon Johnson Pillow (June 8, 1806 – October 8, 1878) was an American lawyer, politician, speculator, slaveowner, United States Army major general of volunteers during the Mexican–American War and Confederate brigadier general in the American Civil War. Before his military career, Pillow practiced law and was active in Democratic Party politics. He was a floor leader in support of the nomination of fellow-Tennessean James K. Polk at the 1844 Democratic National Convention. In 1847, Pillow was commissioned a brigadier general of volunteers to serve in the Mexican–American War, and was later promoted to major general. He performed reasonably well, and was wounded that year at Cerro Gordo and Chapultepec. However, controversy arose when, in a series of letters, Pillow tried to take what was perceived by some as undue credit for American victories at the expense of his commander, Major General Winfield Scott. Pillow was court-martialed for insubordination, but with Preside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |