|
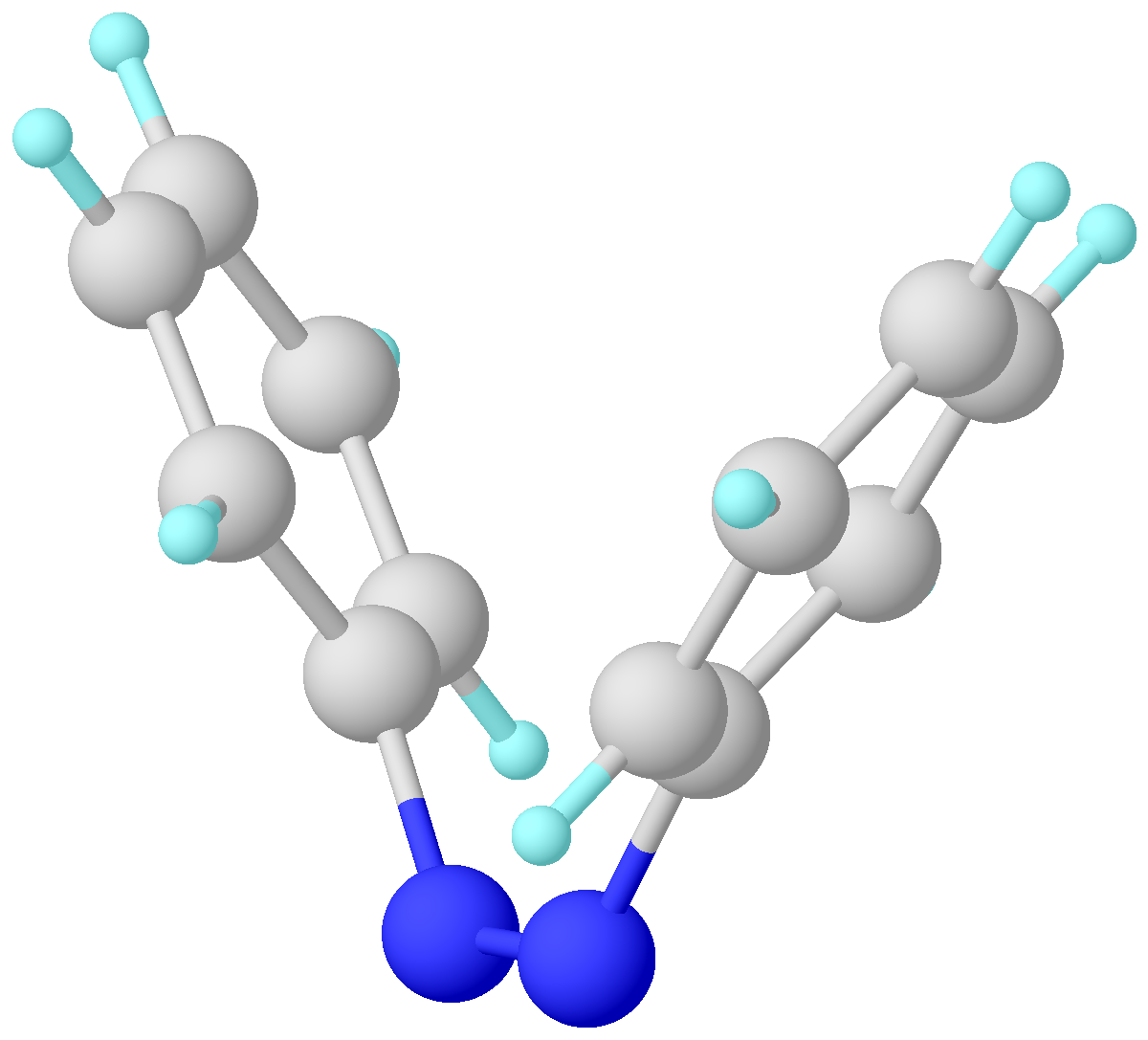
Azobenzene
Azobenzene is a photoswitchable chemical compound composed of two phenyl rings linked by a N=N double bond. It is the simplest example of an aryl azo compound. The term 'azobenzene' or simply 'azo' is often used to refer to a wide class of similar compounds. These azo compounds are considered as derivatives of diazene (diimide), and are sometimes referred to as 'diazenes'. The diazenes absorb light strongly and are common dyes. Structure and synthesis ''trans''-Azobenzene is planar. The N-N distance is 1.189 Å. ''cis''-Azobenzene is nonplanar with a C-N=N-C dihedral angle of 173.5°. The N-N distance is 1.251 Å. Azobenzene was first described by Eilhard Mitscherlich in 1834. Yellowish-red crystalline flakes of azobenzene were obtained in 1856. Its original preparation is similar to the modern one. According to the 1856 method, nitrobenzene is reduced by iron filings in the presence of acetic acid. In the modern synthesis, zinc is the reductant in the presence of a base. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azobenzene Isomerization
Azobenzene is a photoswitchable chemical compound composed of two phenyl rings linked by a N=N double bond. It is the simplest example of an aryl azo compound. The term 'azobenzene' or simply 'azo' is often used to refer to a wide class of similar compounds. These azo compounds are considered as derivatives of diazene (diimide), and are sometimes referred to as 'diazenes'. The diazenes absorb light strongly and are common dyes. Structure and synthesis ''trans''-Azobenzene is planar. The N-N distance is 1.189 Å. ''cis''-Azobenzene is nonplanar with a C-N=N-C dihedral angle of 173.5°. The N-N distance is 1.251 Å. Azobenzene was first described by Eilhard Mitscherlich in 1834. Yellowish-red crystalline flakes of azobenzene were obtained in 1856. Its original preparation is similar to the modern one. According to the 1856 method, nitrobenzene is reduced by iron filings in the presence of acetic acid. In the modern synthesis, zinc is the reductant in the presence of a base. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoisomerization
In chemistry, photoisomerization is a form of isomerization induced by photoexcitation. Both reversible and irreversible photoisomerizations are known for photoswitchable compounds. The term "photoisomerization" usually, however, refers to a reversible process. Applications Photoisomerization of the compound retinal in the eye allows for vision. Photoisomerizable substrates have been put to practical use, for instance, in pigments for rewritable CDs, DVDs, and 3D optical data storage solutions. In addition, interest in photoisomerizable molecules has been aimed at molecular devices, such as molecular switches, molecular motors, and molecular electronics. Another class of device that uses the photoisomerization process is as an additive in liquid crystals to change their linear and nonlinear properties. Due to the photoisomerization is possible to induce a molecular reorientation in the liquid crystal bulk, which is used in holography, as spatial filter or optical switchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoswitch
A photoswitch is a type of molecule that can change its structural geometry and chemical properties upon irradiation with electromagnetic radiation. Although often used interchangeably with the term molecular machine, a switch does not perform work upon a change in its shape whereas a machine does. However, photochromic compounds are the necessary building blocks for light driven molecular motors and machines. Upon irradiation with light, photoisomerization about double bonds in the molecule can lead to changes in the cis- or trans- configuration. These photochromic molecules are being considered for a range of applications. Chemical structures and properties A photochromic compound can change its configuration or structure upon irradiation with light. Several examples of photochromic compounds include: azobenzene, spiropyran, merocyanine, diarylethene, spirooxazine, fulgide, hydrazone, nobormadiene, thioindigo, acrylamide-azobenzene-quaternary ammonia, donor-acceptor Stenhous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoswitch
A photoswitch is a type of molecule that can change its structural geometry and chemical properties upon irradiation with electromagnetic radiation. Although often used interchangeably with the term molecular machine, a switch does not perform work upon a change in its shape whereas a machine does. However, photochromic compounds are the necessary building blocks for light driven molecular motors and machines. Upon irradiation with light, photoisomerization about double bonds in the molecule can lead to changes in the cis- or trans- configuration. These photochromic molecules are being considered for a range of applications. Chemical structures and properties A photochromic compound can change its configuration or structure upon irradiation with light. Several examples of photochromic compounds include: azobenzene, spiropyran, merocyanine, diarylethene, spirooxazine, fulgide, hydrazone, nobormadiene, thioindigo, acrylamide-azobenzene-quaternary ammonia, donor-acceptor Stenhous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrosynthesis
Electrosynthesis in chemistry is the synthesis of chemical compounds in an electrochemical cell. Compared to ordinary redox reaction, electrosynthesis sometimes offers improved selectivity and yields. Electrosynthesis is actively studied as a science and also has industrial applications. Electrooxidation has potential for wastewater treatment as well. Experimental setup The basic setup in electrosynthesis is a galvanic cell, a potentiostat and two electrodes. Typical solvent and electrolyte combinations minimizes electrical resistance. Protic conditions often use alcohol-water or dioxane-water solvent mixtures with an electrolyte such as a soluble salt, acid or base. Aprotic conditions often use an organic solvent such as acetonitrile or dichloromethane with electrolytes such as lithium perchlorate or tetrabutylammonium salts. The choice of electrodes with respect to their composition and surface area can be decisive. For example, in aqueous conditions the competing reactions i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrosobenzene
Nitrosobenzene is the organic compound with the formula C6H5NO. It is one of the prototypical organic nitroso compounds. Characteristic of its functional group, it is a dark green species that exists in equilibrium with its pale yellow dimer. Both monomer and dimer are diamagnetic. Monomer-dimer equilibrium Nitrosobenzene and other nitrosoarenes typically participate in a monomer-dimer equilibrium. The dimers are often favored in the solid state, whereas the deeply colored monomers are favored in dilute solution or at higher temperatures. The dimers can be formulated as Ar(O−)N+=N+(O−)Ar. They exist as ''cis''- and ''trans''-isomers due to the presence of the N–N double bond. The dimers are sometimes called azobenzenedioxides. The cis-trans isomerization occurs via the intermediacy of the monomer. In the case of nitrosobenzene itself, the metastable monomeric form could be prepared by sublimation onto a cold finger. The monomeric material is selectively sublimed due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
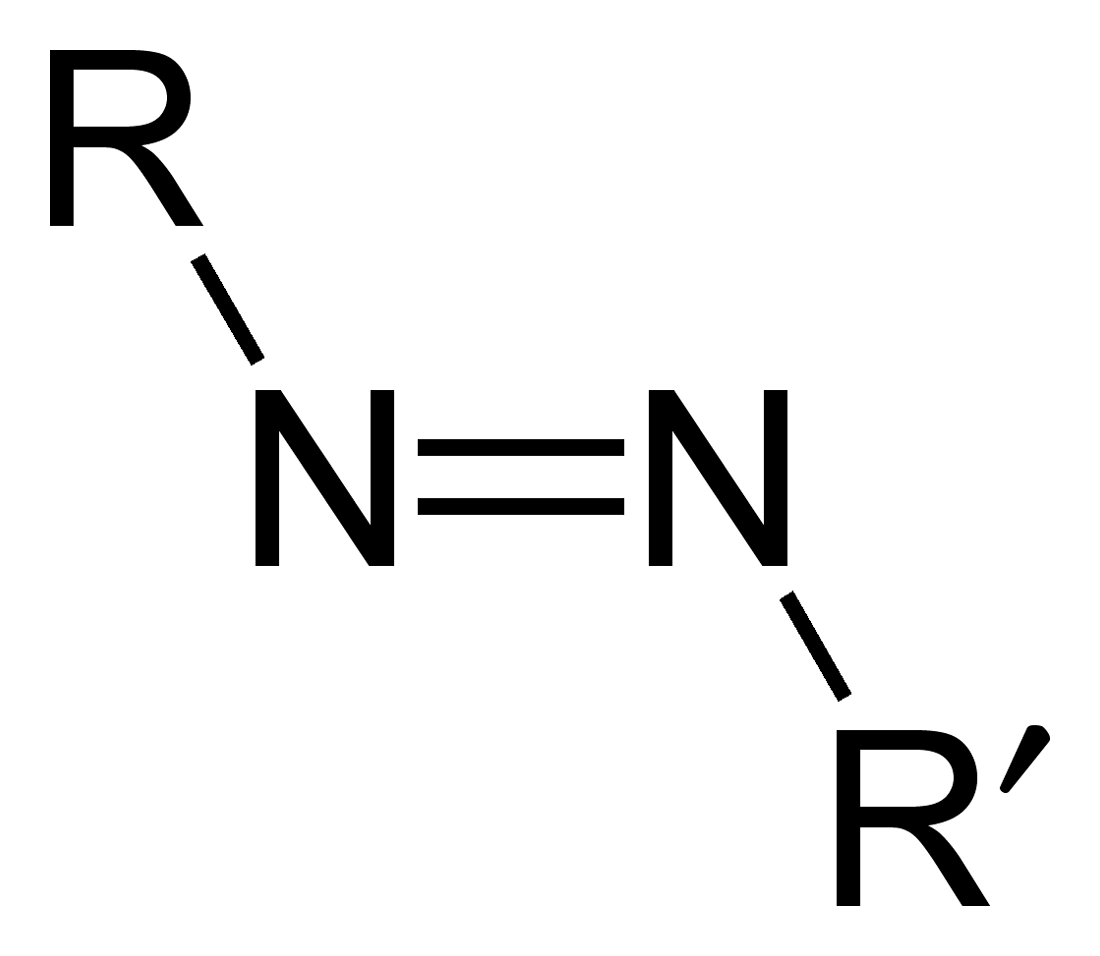
Azo Compound
Azo compounds are organic compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl (, in which R and R′ can be either aryl or alkyl groups). IUPAC defines azo compounds as: "Derivatives of diazene (diimide), , wherein both hydrogens are substituted by hydrocarbyl groups, e.g. azobenzene or diphenyldiazene." The more stable derivatives contain two aryl groups. The group is called an ''azo group'' (, ). Many textile and leather articles are dyed with azo dyes and pigments. Aryl azo compounds Aryl azo compounds are usually stable, crystalline species. Azobenzene is the prototypical aromatic azo compound. It exists mainly as the ''trans'' isomer, but upon illumination, converts to the ''cis'' isomer. Aromatic azo compounds can be synthesized by azo coupling, which entails an electrophilic substitution reaction where an aryl diazonium cation is attacked by another aryl ring, especially those substituted with electron-donating groups: :ArN2+ + Ar'H -> ArN=NAr' + H+ Since diaz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrobenzene
Nitrobenzene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5 NO2. It is a water-insoluble pale yellow oil with an almond-like odor. It freezes to give greenish-yellow crystals. It is produced on a large scale from benzene as a precursor to aniline. In the laboratory, it is occasionally used as a solvent, especially for electrophilic reagents. Production Nitrobenzene is prepared by nitration of benzene with a mixture of concentrated sulfuric acid, water, and nitric acid. This mixture is sometimes called "mixed acid." The production of nitrobenzene is one of the most dangerous processes conducted in the chemical industry because of the exothermicity of the reaction (Δ''H'' = −117 kJ/mol). World capacity for nitrobenzene in 1985 was about 1,700,000 tonnes. The nitration process involves formation of the nitronium ion (NO2+), followed by an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction of it with benzene. The nitronium ion is generated by the reaction of nitric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eilhard Mitscherlich
Eilhard Mitscherlich (; 7 January 179428 August 1863) was a German chemist, who is perhaps best remembered today for his discovery of the phenomenon of crystallographic isomorphism in 1819. Early life and work Mitscherlich was born at Neuende (now a part of Wilhelmshaven) in the Lordship of Jever, where his father was pastor. His uncle, Christoph Wilhelm Mitscherlich (1760–1854), professor at the University of Göttingen, was in his day a celebrated scholar. Eilhard Mitscherlich was educated at Jever by the historian Friedrich Christoph Schlosser, and in 1811 went to the University of Heidelberg devoting himself to philology, with an emphasis on the Persian language. In 1813 he went to Paris to seek permission to join the embassy which Napoleon I of France was establishing in Persia. The abdication of Napoleon Bonaparte in 1814 put an end to this, and Mitscherlich resolved to study medicine in order that he might enjoy that freedom of travel usually allowed in the East to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azoxybenzene
Azoxybenzene is organic compound with the formula C6H5N(O)NC6H5. It is a yellow, low-melting solid. The molecule has a planar C2N2O core. The N-N and N-O bond lengths are nearly the same at 1.23 Å. Preparation It can be prepared by partial reduction of nitrobenzene. This reaction is proposed to proceed via the intermediacy of phenylhydroxylamine and nitrosobenzene: :PhNHOH + PhNO → PhN(O)NPh + H2O Another option is the oxidation of aniline by hydrogen peroxide Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3% ..., in acetonitrile at 50 ºC. In this reaction, the pH should be kept around 8, to activate the hydrogen peroxide and avoid too much oxygen evolution at the same time. First, the acetonitrile is oxidized, forming an imine hydroperoxide. Then, this intermediate o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazobenzene
Hydrazobenzene (1,2-diphenylhydrazine) is an aromatic organic compound consisting of two aniline groups joined via their nitrogen atoms. It is an important industrial chemical used in the manufacture of dyes, pharmaceuticals, and hydrogen peroxide Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3% .... References {{aromatic-compound-stub Hydrazines Anilines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |