|
Average Variance Extracted
In statistics (classical test theory), average variance extracted (AVE) is a measure of the amount of variance that is captured by a construct in relation to the amount of variance due to measurement error. History The average variance extracted was first proposed by Fornell & Larcker (1981). Calculation The average variance extracted can be calculated as follows: : \text = \frac Here, k is the number of items, \lambda_i the factor loading of item i and \operatorname( e_i ) the variance In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expected value of the squared deviation from the mean of a random variable. The standard deviation (SD) is obtained as the square root of the variance. Variance is a measure of dispersion ... of the error of item i. Role for assessing discriminant validity The average variance extracted has often been used to assess discriminant validity based on the following "rule of thumb": the positive square root of the AVE for each o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
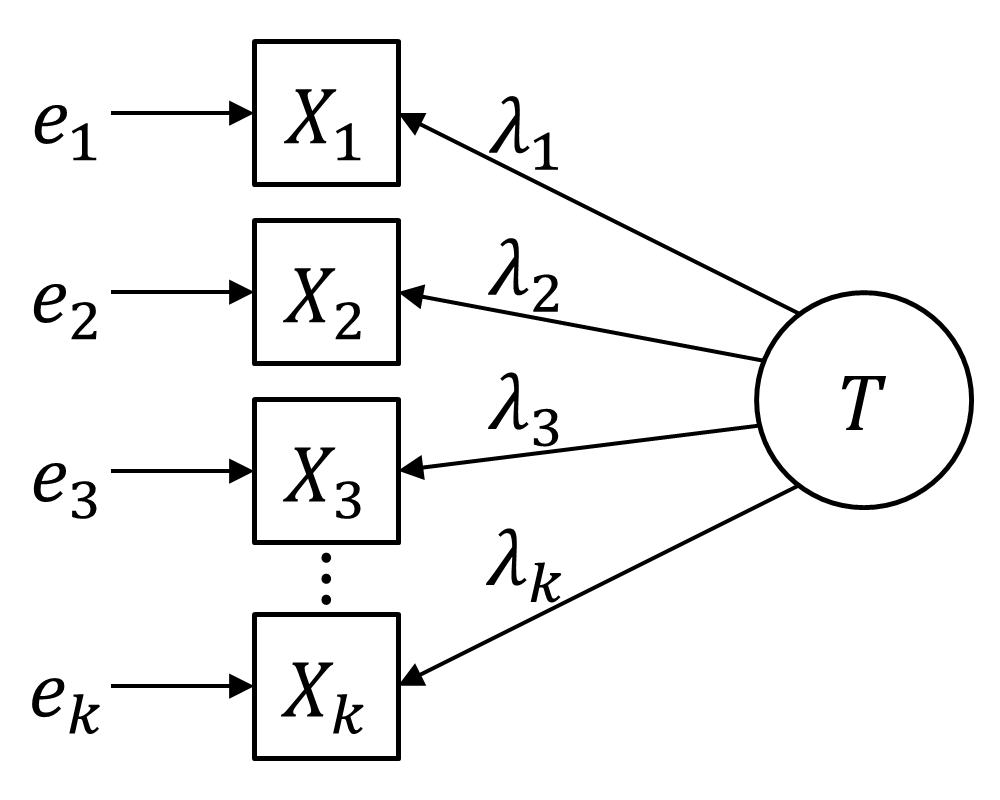
Congeneric Measurement Model
Congener may refer to: * Congener (biology), organisms within the same genus * Congener (chemistry), related chemicals, e.g., elements in the same group of the periodic table * Congener (beverages), a substance other than ethanol produced during the fermentation of alcoholic beverages Species * ''Agabus congener'', a beetle in the family Dytiscidae * ''Amata congener'', a moth in the family Erebidae * ''Amyema congener'', a flowering plant in the family Loranthaceae * ''Arthroplea congener'', a mayfly in the family Arthropleidae * ''Elaphropus congener'', a ground beetle in the family Carabidae * ''Gemmula congener'', a sea snail in the family Turridae * ''Heterachthes congener'', a beetle in the family Cerambycidae * ''Lestes congener'', a damselfly in the family Lestidae * ''Megacyllene congener ''Megacyllene congener'' is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae The longhorn beetles (Cerambycidae), also known as long-horned or longicorns (whose larvae are often refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments. When census data (comprising every member of the target population) cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Classical Test Theory
Classical test theory (CTT) is a body of related psychometric theory that predicts outcomes of psychological Test (assessment), testing such as the difficulty of items or the ability of test-takers. It is a theory of testing based on the idea that a person's observed or obtained score on a test is the sum of a true score (error-free score) and an error score. Generally speaking, the aim of classical test theory is to understand and improve the Reliability (psychometric), reliability of psychological tests. ''Classical test theory'' may be regarded as roughly synonymous with ''true score theory''. The term "classical" refers not only to the chronology of these models but also contrasts with the more recent psychometric theories, generally referred to collectively as item response theory, which sometimes bear the appellation "modern" as in "modern latent trait theory". Classical test theory as we know it today was codified by and described in classic texts such as and . The descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Factor Loading
Factor analysis is a statistical method used to describe variability among observed, correlated variables in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved variables called factors. For example, it is possible that variations in six observed variables mainly reflect the variations in two unobserved (underlying) variables. Factor analysis searches for such joint variations in response to unobserved latent variables. The observed variables are modelled as linear combinations of the potential factors plus "error" terms, hence factor analysis can be thought of as a special case of errors-in-variables models. Simply put, the factor loading of a variable quantifies the extent to which the variable is related to a given factor. A common rationale behind factor analytic methods is that the information gained about the interdependencies between observed variables can be used later to reduce the set of variables in a dataset. Factor analysis is commonly used in psychometrics, personal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expected value of the squared deviation from the mean of a random variable. The standard deviation (SD) is obtained as the square root of the variance. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out from their average value. It is the second central moment of a distribution, and the covariance of the random variable with itself, and it is often represented by \sigma^2, s^2, \operatorname(X), V(X), or \mathbb(X). An advantage of variance as a measure of dispersion is that it is more amenable to algebraic manipulation than other measures of dispersion such as the expected absolute deviation; for example, the variance of a sum of uncorrelated random variables is equal to the sum of their variances. A disadvantage of the variance for practical applications is that, unlike the standard deviation, its units differ from the random variable, which is why the standard devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Discriminant Validity
In psychology, discriminant validity tests whether concepts or measurements that are not supposed to be related are actually unrelated. Campbell and Fiske (1959) introduced the concept of discriminant validity within their discussion on evaluating test validity. They stressed the importance of using both discriminant and convergent validation techniques when assessing new tests. A successful evaluation of discriminant validity shows that a test of a concept is not highly correlated with other tests designed to measure theoretically different concepts. In showing that two scales do not correlate, it is necessary to correct for attenuation In physics, attenuation (in some contexts, extinction) is the gradual loss of flux intensity through a Transmission medium, medium. For instance, dark glasses attenuate sunlight, lead attenuates X-rays, and water and air attenuate both light and ... in the correlation due to measurement error. It is possible to calculate the extent to which the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Structural Equation Model
Structural equation modeling (SEM) is a diverse set of methods used by scientists for both observational and experimental research. SEM is used mostly in the social and behavioral science fields, but it is also used in epidemiology, business, and other fields. A common definition of SEM is, "...a class of methodologies that seeks to represent hypotheses about the means, variances, and covariances of observed data in terms of a smaller number of 'structural' parameters defined by a hypothesized underlying conceptual or theoretical model,". SEM involves a model representing how various aspects of some phenomenon are thought to causally connect to one another. Structural equation models often contain postulated causal connections among some latent variables (variables thought to exist but which can't be directly observed). Additional causal connections link those latent variables to observed variables whose values appear in a data set. The causal connections are represented using ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tau-equivalent Reliability
Cronbach's alpha (Cronbach's \alpha), also known as tau-equivalent reliability (\rho_T) or coefficient alpha (coefficient \alpha), is a reliability coefficient and a measure of the internal consistency of tests and measures. It was named after the American psychologist Lee Cronbach. Numerous studies warn against using Cronbach's alpha unconditionally. Statisticians regard reliability coefficients based on structural equation modeling (SEM) or generalizability theory as superior alternatives in many situations. History In his initial 1951 publication, Lee Cronbach described the coefficient as ''Coefficient'' ''alpha'' and included an additional derivation. ''Coefficient alpha'' had been used implicitly in previous studies, but his interpretation was thought to be more intuitively attractive relative to previous studies and it became quite popular. * In 1967, Melvin Novick and Charles Lewis proved that it was equal to reliability if the true scores of the compared tests or me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Congeneric Reliability
In statistical models applied to psychometrics, congeneric reliability \rho_C ("rho C")Cho, E. (2016). Making reliability reliable: A systematic approach to reliability coefficients. Organizational Research Methods, 19(4), 651–682. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428116656239 a single-administration test score reliability (i.e., the reliability of persons over items holding occasion fixed) coefficient, commonly referred to as composite reliability, construct reliability, and coefficient omega. \rho_C is a structural equation model (SEM)-based reliability coefficients and is obtained from a unidimensional model. \rho_C is the second most commonly used reliability factor after tau-equivalent reliability(\rho_T; also known as Cronbach's alpha), and is often recommended as its alternative. History and names A quantity similar (but not mathematically equivalent) to congeneric reliability first appears in the appendix to McDonald's 1970 paper on factor analysis, labeled \theta.Although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Measurement Model
Measurement is the quantification of attributes of an object or event, which can be used to compare with other objects or events. In other words, measurement is a process of determining how large or small a physical quantity is as compared to a basic reference quantity of the same kind. The scope and application of measurement are dependent on the context and discipline. In natural sciences and engineering, measurements do not apply to nominal properties of objects or events, which is consistent with the guidelines of the International Vocabulary of Metrology (VIM) published by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM). However, in other fields such as statistics as well as the social and behavioural sciences, measurements can have multiple levels, which would include nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio scales. Measurement is a cornerstone of trade, science, technology and quantitative research in many disciplines. Historically, many measurement systems exist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |