|
Autoinflammatory
Periodic fever syndromes are a set of disorders characterized by recurrent episodes of systemic and organ-specific inflammation. Unlike autoimmune disorders such as systemic lupus erythematosus, in which the disease is caused by abnormalities of the adaptive immune system, people with autoinflammatory diseases do not produce autoantibodies or antigen-specific T or B cells. Instead, the autoinflammatory diseases are characterized by errors in the innate immune system. The syndromes are diverse, but tend to cause episodes of fever, joint pains, skin rashes, abdominal pains and may lead to chronic complications such as amyloidosis. Most autoinflammatory diseases are genetic and present during childhood. The most common genetic autoinflammatory syndrome is familial Mediterranean fever, which causes short episodes of fever, abdominal pain, serositis, lasting less than 72 hours. It is caused by mutations in the MEFV gene, which codes for the protein pyrin. Pyrin is a protein n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Familial Mediterranean Fever
Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) is a hereditary inflammatory disorder. FMF is an autoinflammatory disease caused by mutations in Mediterranean fever gene, which encodes a 781–amino acid protein called pyrin. While all ethnic groups are susceptible to FMF, it usually occurs in people of Mediterranean origin—including Sephardic Jews, Mizrahi Jews, Ashkenazi Jews, Assyrian People, Assyrians, Armenians, Azerbaijanis, Levantine people, Levantines, Kurds, Greeks, Turkish people, Turks and Italians. The disorder has been given various names, including familial paroxysmal polyserositis, periodic peritonitis, recurrent polyserositis, benign paroxysmal peritonitis, periodic disease or periodic fever, Reimann periodic disease or Reimann syndrome, Siegal-Cattan-Mamou disease, and Wolff periodic disease. Note that "periodic fever" can also refer to any of the periodic fever syndromes. Signs and symptoms Attacks There are seven types of attacks. Ninety percent of all patients have t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Familial Mediterranean Fever
Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF) is a hereditary inflammatory disorder. FMF is an autoinflammatory disease caused by mutations in Mediterranean fever gene, which encodes a 781–amino acid protein called pyrin. While all ethnic groups are susceptible to FMF, it usually occurs in people of Mediterranean origin—including Sephardic Jews, Mizrahi Jews, Ashkenazi Jews, Assyrian People, Assyrians, Armenians, Azerbaijanis, Levantine people, Levantines, Kurds, Greeks, Turkish people, Turks and Italians. The disorder has been given various names, including familial paroxysmal polyserositis, periodic peritonitis, recurrent polyserositis, benign paroxysmal peritonitis, periodic disease or periodic fever, Reimann periodic disease or Reimann syndrome, Siegal-Cattan-Mamou disease, and Wolff periodic disease. Note that "periodic fever" can also refer to any of the periodic fever syndromes. Signs and symptoms Attacks There are seven types of attacks. Ninety percent of all patients have t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canakinumab
Canakinumab (International Nonproprietary Name, INN), sold under the brand name Ilaris, is a medication for the treatment of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SJIA) and active Still's disease, including adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD). It is a human monoclonal antibody targeted at IL1B, interleukin-1 beta. It has no cross-reactivity with other members of the interleukin-1 family, including interleukin-1 alpha. Common side effects include infections (colds and upper respiratory tract infections), abdominal pain and injection-site reactions. Medical uses Canakinumab was approved for the treatment of cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS) by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in June 2009 and by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in October 2009. Text was copied from this source which is © European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged. CAPS is a spectrum of autoinflammatory syndromes including Familial Cold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
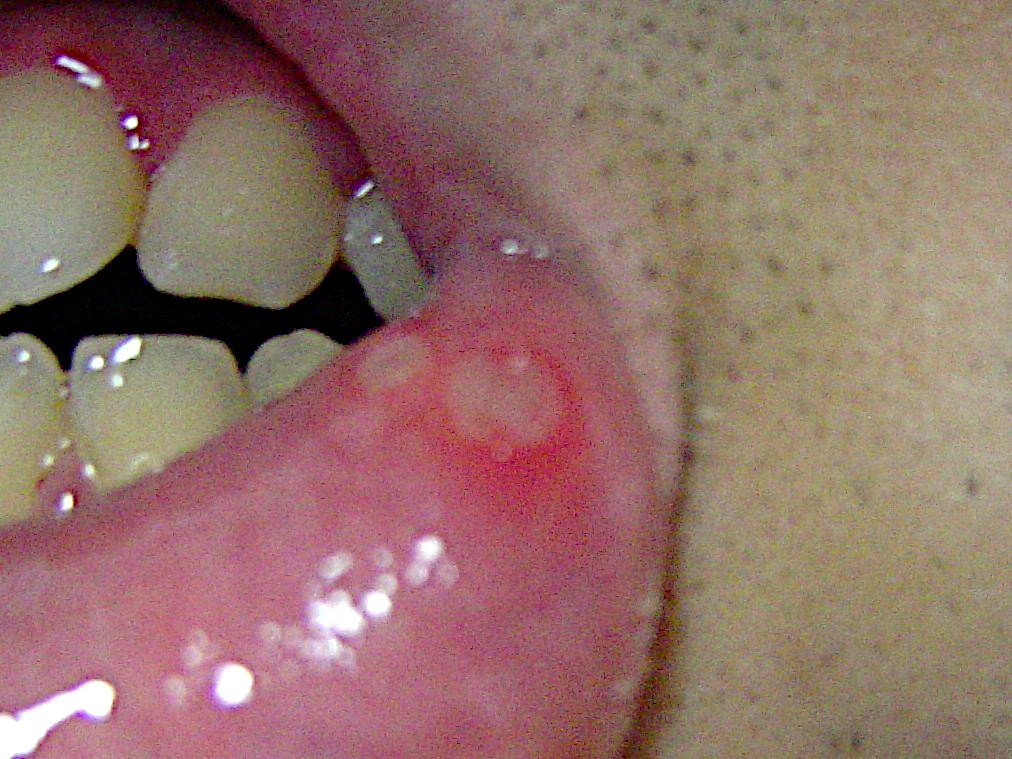
PFAPA
Periodic fever, aphthous stomatitis, pharyngitis and adenitis syndrome is a medical condition, typically occurring in young children, in which high fever occurs periodically at intervals of about 3-5 weeks, frequently accompanied by aphthous-like ulcers, pharyngitis and/or cervical adenitis ( cervical lymphadenopathy). The syndrome was described in 1987 and named two years later. Signs and symptoms The key symptoms of PFAPA are those in its name: periodic high fever at intervals of about 3–5 weeks, as well as aphthous ulcers, pharyngitis and/or adenitis. In between episodes, and even during the episodes, the children appear healthy. At least 6 months of episodes. Diagnosis requires recurrent negative throat cultures and that other causes (such as EBV, CMV, FMF) be excluded. Cause The cause of PFAPA is unknown. It is frequently discussed together with other periodic fever syndromes. Possible causes include primarily genetic factors or it may be due to an initial infection. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and Functio laesa, loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immune system, innate immunity, as compared to adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoimmune Disorder
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly any body part can be involved. Common symptoms can be diverse and transient, ranging from mild to severe, and generally include low grade fever and feeling tired. The cause is unknown. Some autoimmune diseases such as lupus run in families, and certain cases may be triggered by infections or other environmental factors. Some common diseases that are generally considered autoimmune include celiac disease, diabetes mellitus type 1, graves' disease, inflammatory bowel disease, multiple sclerosis, alopecia areata, addison’s disease, pernicious anemia, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and systemic lupus erythematosus. The diagnosis can be difficult to determine. Treatment depends on the type and severity of the condition. Nonsteroidal a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphthous Stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis, or recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS), is a common condition characterized by the repeated formation of benign and non- contagious mouth ulcers (aphthae) in otherwise healthy individuals. The informal term ''canker sore'' is also used, mainly in North America, although it may also refer to other types of mouth ulcers. The cause is not completely understood but involves a T cell-mediated immune response triggered by a variety of factors which may include nutritional deficiencies, local trauma, stress, hormonal influences, allergies, genetic predisposition, certain foods, dehydration, some food additives, or some hygienic chemical additives like SDS (common in toothpaste). These ulcers occur periodically and heal completely between attacks. In the majority of cases, the individual ulcers last about 7–10 days, and ulceration episodes occur 3–6 times per year. Most appear on the non-keratinizing epithelial surfaces in the mouth – i.e. anywhere exce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is inflammation of the back of the throat, known as the pharynx. It typically results in a sore throat and fever. Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, difficulty swallowing, swollen lymph nodes, and a hoarse voice. Symptoms usually last 3–5 days, but can be longer depending on cause. Complications can include sinusitis and acute otitis media. Pharyngitis is a type of upper respiratory tract infection. Most cases are caused by a viral infection. Strep throat, a bacterial infection, is the cause in about 25% of children and 10% of adults. Uncommon causes include other bacteria such as ''gonococcus'', fungi, irritants such as smoke, allergies, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Specific testing is not recommended in people who have clear symptoms of a viral infection, such as a cold. Otherwise, a rapid antigen detection test or throat swab is recommended. PCR testing is becoming commonly used as it is as good as taking a throat swab but gives a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenitis
Adenitis is a general term for an inflammation of a gland. Often it is used to refer to lymphadenitis which is the inflammation of a lymph node. Classification Lymph node adenitis ''Lymph adenitis'' or ''lymph node adenitis'' is caused by infection in lymph nodes. The infected lymph nodes typically become enlarged, warm and tender. A swelling of lymph nodes due to growth of lymph cells is called lymphadenopathy. Types include: * Neck ** Cervical adenitis is an inflammation of a lymph node in the neck. ** Tuberculous adenitis ( scrofula) is a tuberculous infection of the skin of the neck caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''. Non-tuberculous adenitis can also be caused by ''Mycobacterium scrofulaceum'' or ''Mycobacterium avium''. * Abdomen ** Mesenteric adenitis is an inflammation of the mesenteric lymph nodes in the abdomen. It can be caused by the bacterium ''Yersinia enterocolitica''.Ellis H, Calne R, Watson C. ''Lecture Notes on General Surgery'' tenth edition, p. 28. If i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatology
Rheumatology (Greek ''ῥεῦμα'', ''rheûma'', flowing current) is a branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis and management of disorders whose common feature is inflammation in the bones, muscles, joints, and internal organs. Rheumatology covers more than 100 different complex diseases, collectively known as rheumatic diseases, which includes many forms of arthritis as well as lupus and Sjögren's syndrome. Doctors who have undergone formal training in rheumatology are called rheumatologists. Many of these diseases are now known to be disorders of the immune system, and rheumatology has significant overlap with immunology, the branch of medicine that studies the immune system. Rheumatologist A rheumatologist is a physician who specializes in the field of medical sub-specialty called rheumatology. A rheumatologist holds a board certification after specialized training. In the United States, training in this field requires four years undergraduate school, four year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adult-onset Still's Disease
Adult-onset Still's disease (AOSD) is a form of Still's disease, a rare systemic autoinflammatory disease characterized by the classic triad of fevers, joint pain, and a distinctive salmon-colored bumpy rash. The disease is considered a diagnosis of exclusion. Levels of the iron-binding protein ferritin may be extremely elevated with this disorder. AOSD may present in a similar manner to other inflammatory diseases and to autoimmune diseases, which must be ruled out before making the diagnosis. Prognosis is usually favorable but manifestations of the disease affecting the lungs, heart, or kidneys may occasionally cause severe life-threatening complications. It is treated first with corticosteroids such as prednisone. Medications that block the action of interleukin-1, such as anakinra, can be effective treatments when standard steroid treatments are insufficient. Obvious similarities exist with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (also known as "juvenile-onset Still's disease"), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic-onset Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Systemic-onset juvenile idiopathic arthritis (or the juvenile onset form of Still's disease) is a type of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) with extra-articular manifestations like fever and rash apart from arthritis. It was originally called systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis or Still's disease. Predominantly extra-articular manifestations like high fevers, rheumatic rash, enlargement of the liver and spleen, enlargement of the lymph nodes, and anemia. Other manifestations include inflammation of the pleura, inflammation of the pericardium, inflammation of the heart's muscular tissue, and inflammation of the peritoneum are also seen. It is sometimes called "juvenile-onset Still's disease" to distinguish it from adult-onset Still's disease. However, there is some evidence that the main difference between two conditions is the age of onset. Presentation Systemic JIA is characterized by arthritis, fever, which typically is higher than the low-grade fever associate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
