|
Astrocytic
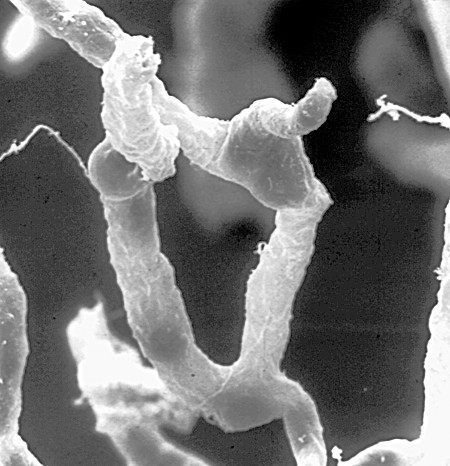
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endothelial cells that form the blood–brain barrier, provision of nutrients to the nervous tissue, maintenance of extracellular ion balance, regulation of cerebral blood flow, and a role in the repair and scarring process of the brain and spinal cord following infection and traumatic injuries. The proportion of astrocytes in the brain is not well defined; depending on the counting technique used, studies have found that the astrocyte proportion varies by region and ranges from 20% to 40% of all glia. Another study reports that astrocytes are the most numerous cell type in the brain. Astrocytes are the major source of cholesterol in the central nervous system. Apolipoprotein E transports cholesterol from astrocytes to neurons and other glial ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) is a protein that is encoded by the ''GFAP'' gene in humans. It is a type III intermediate filament (IF) protein that is expressed by numerous cell types of the central nervous system (CNS), including astrocytes and ependymal cells during development. GFAP has also been found to be expressed in glomeruli and peritubular fibroblasts taken from rat kidneys, Leydig cells of the testis in both hamsters and humans, human keratinocytes, human osteocytes and chondrocytes and stellate cells of the pancreas and liver in rats. GFAP is closely related to the other three non-epithelial type III IF family members, vimentin, desmin and peripherin, which are all involved in the structure and function of the cell’s cytoskeleton. GFAP is thought to help to maintain astrocyte mechanical strength as well as the shape of cells, but its exact function remains poorly understood, despite the number of studies using it as a cell marker. The protein was named and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glial Scar
Glial scar formation (gliosis) is a reactive cellular process involving astrogliosis that occurs after injury to the central nervous system. As with scarring in other organs and tissues, the glial scar is the body's mechanism to protect and begin the healing process in the nervous system. In the context of neurodegeneration, formation of the glial scar has been shown to have both beneficial and detrimental effects. Particularly, many neuro-developmental inhibitor molecules are secreted by the cells within the scar that prevent complete physical and functional recovery of the central nervous system after injury or disease. On the other hand, absence of the glial scar has been associated with impairments in the repair of the blood brain barrier. Scar components The glial scar is composed of several components briefly discussed below. Reactive astrocytes Reactive astrocytes are the main cellular component of the glial scar. After injury, astrocytes undergo morphological changes, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood–brain Barrier
The blood–brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective semipermeable membrane, semipermeable border of endothelium, endothelial cells that prevents solutes in the circulating blood from ''non-selectively'' crossing into the extracellular fluid of the central nervous system where neurons reside. The blood–brain barrier is formed by endothelial cells of the Capillary, capillary wall, astrocyte end-feet ensheathing the capillary, and pericytes embedded in the capillary basement membrane. This system allows the passage of some small molecules by passive transport, passive diffusion, as well as the selective and active transport of various nutrients, ions, organic anions, and macromolecules such as glucose and amino acids that are crucial to neural function. The blood–brain barrier restricts the passage of pathogens, the diffusion of solutes in the blood, and Molecular mass, large or Hydrophile, hydrophilic molecules into the cerebrospinal fluid, while allowing the diffusion of Hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron Migration
The development of the nervous system, or neural development (neurodevelopment), refers to the processes that generate, shape, and reshape the nervous system of animals, from the earliest stages of embryonic development to adulthood. The field of neural development draws on both neuroscience and developmental biology to describe and provide insight into the cellular and molecular mechanisms by which complex nervous systems develop, from nematodes and fruit flies to mammals. Defects in neural development can lead to malformations such as holoprosencephaly, and a wide variety of neurological disorders including limb paresis and paralysis, balance and vision disorders, and seizures, and in humans other disorders such as Rett syndrome, Down syndrome and intellectual disability. Overview of vertebrate brain development The vertebrate central nervous system (CNS) is derived from the ectoderm—the outermost germ layer of the embryo. A part of the dorsal ectoderm becomes specifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroscience
Neuroscience is the scientific study of the nervous system (the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nervous system), its functions and disorders. It is a multidisciplinary science that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, developmental biology, cytology, psychology, physics, computer science, chemistry, medicine, statistics, and Mathematical Modeling, mathematical modeling to understand the fundamental and emergent properties of neurons, glia and neural circuits. The understanding of the biological basis of learning, memory, behavior, perception, and consciousness has been described by Eric Kandel as the "epic challenge" of the Biology, biological sciences. The scope of neuroscience has broadened over time to include different approaches used to study the nervous system at different scales. The techniques used by neuroscientists have expanded enormously, from molecular biology, molecular and cell biology, cellular studies of individual neurons to neuroimaging, imaging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gliotransmitter
Gliotransmitters are chemicals released from glial cells that facilitate neuronal communication between neurons and other glial cells. They are usually induced from Ca2+ signaling, although recent research has questioned the role of Ca2+ in gliotransmitters and may require a revision of the relevance of gliotransmitters in neuronal signalling in general. While gliotransmitters can be released from any glial cell, including oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, and microglia, they are primarily released from astrocytes. Astrocytes rely on gap junctions for coupling, and are star-like in shape, which allows them to come into contact with many other synapses in various regions of the brain. Their structure also makes them capable of bidirectional signaling. It is estimated that astrocytes can make contact with over 100,000 synapses, allowing them to play an essential role in synaptic transmission. While gliotransmission primarily occurs between astrocytes and neurons, gliotransmission is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column (backbone). The backbone encloses the central canal of the spinal cord, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). In humans, the spinal cord begins at the occipital bone, passing through the foramen magnum and then enters the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it ends. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around long in adult men and around long in adult women. The diameter of the spinal cord ranges from in the cervical and lumbar regions to in the thoracic area. The spinal cord functions primarily in the transmission of nerve signals from the motor cortex to the body, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Astrocyte
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedality, bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex Human brain, brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from family, families and kinship networks to political state (polity), states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, norm (sociology), social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate Phenomenon, phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate Filaments
Intermediate filaments (IFs) are cytoskeletal structural components found in the cells of vertebrates, and many invertebrates. Homologues of the IF protein have been noted in an invertebrate, the cephalochordate ''Branchiostoma''. Intermediate filaments are composed of a family of related proteins sharing common structural and sequence features. Initially designated 'intermediate' because their average diameter (10 nm) is between those of narrower microfilaments (actin) and wider myosin filaments found in muscle cells, the diameter of intermediate filaments is now commonly compared to actin microfilaments (7 nm) and microtubules (25 nm). Animal intermediate filaments are subcategorized into six types based on similarities in amino acid sequence and protein structure. Most types are cytoplasmic, but one type, Type V is a nuclear lamin. Unlike microtubules, IF distribution in cells show no good correlation with the distribution of either mitochondria or endopla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pia Mater
Pia mater ( or ),Entry "pia mater" in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary ', retrieved 2012-07-28. often referred to as simply the pia, is the delicate innermost layer of the , the membranes surrounding the and . ''Pia mater'' is medieval Latin meaning "tender mother". The other two meningeal membr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular System
The ventricular system is a set of four interconnected cavities known as cerebral ventricles in the brain. Within each ventricle is a region of choroid plexus which produces the circulating cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The ventricular system is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord from the fourth ventricle, allowing for the flow of CSF to circulate. All of the ventricular system and the central canal of the spinal cord are lined with ependyma, a specialised form of epithelium connected by tight junctions that make up the blood–cerebrospinal fluid barrier. Structure The system comprises four ventricles: * lateral ventricles right and left (one for each hemisphere) * third ventricle * fourth ventricle There are several foramina, openings acting as channels, that connect the ventricles. The interventricular foramina (also called the foramina of Monro) connect the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle through which the cerebrospinal fluid can flow. Ventric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
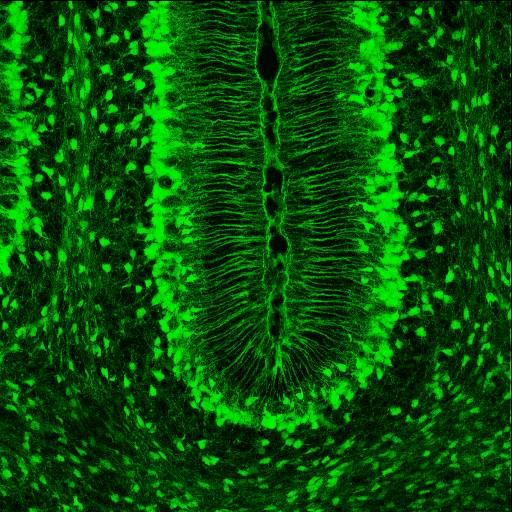
Radial Glial Cell
Radial glial cells, or radial glial progenitor cells (RGPs), are bipolar-shaped progenitor cells that are responsible for producing all of the neurons in the cerebral cortex. RGPs also produce certain lineages of glia, including astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Their cell bodies (somata) reside in the embryonic ventricular zone, which lies next to the developing ventricular system. During development, newborn neurons use radial glia as scaffolds, traveling along the radial glial fibers in order to reach their final destinations. Despite the various possible fates of the radial glial population, it has been demonstrated through clonal analysis that most radial glia have restricted, unipotent or multipotent, fates. Radial glia can be found during the neurogenic phase in all vertebrates (studied to date). The term "radial glia" refers to the morphological characteristics of these cells that were first observed: namely, their radial processes and their similarity to astrocytes, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |