|
Arteriogram
Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is performed by injecting a radio-opaque contrast agent into the blood vessel and imaging using X-ray based techniques such as fluoroscopy. The word itself comes from the Greek words ἀγγεῖον ''angeion'' 'vessel' and γράφειν ''graphein'' 'to write, record'. The film or image of the blood vessels is called an ''angiograph'', or more commonly an ''angiogram''. Though the word can describe both an arteriogram and a venogram, in everyday usage the terms angiogram and arteriogram are often used synonymously, whereas the term venogram is used more precisely. The term angiography has been applied to radionuclide angiography and newer vascular imaging techniques such as CO2 angiography, CT angiography and MR angiography. The term ''isotope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transverse Plane
The transverse plane (also known as the horizontal plane, axial plane and transaxial plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into Anatomical terms of location#Superior and inferior, superior and inferior sections. It is perpendicular to the coronal plane, coronal and sagittal plane, sagittal planes. List of clinically relevant anatomical planes * Transverse ''thoracic plane'' * ''Xiphosternal plane'' (or xiphosternal junction) * ''Transpyloric plane'' * ''Subcostal plane'' * ''Umbilical plane'' (or transumbilical plane) * ''Supracristal plane'' * ''Intertubercular plane'' (or transtubercular plane) * ''Interspinous plane'' Clinically relevant anatomical planes with associated structures * The transverse ''thoracic plane'' ** Plane through T4 & T5 vertebral junction and Sternal angle, sternal angle of Louis. ** Marks the: *** Attachment of costal cartilage of rib 2 at the sternal angle; *** Aortic arch (beginning and end); *** Upper margin of Superior vena cava, SVC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is a group of techniques based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to image blood vessels. Magnetic resonance angiography is used to generate images of arteries (and less commonly veins) in order to evaluate them for stenosis (abnormal narrowing), Vascular occlusion, occlusions, aneurysms (vessel wall dilatations, at risk of rupture) or other abnormalities. MRA is often used to evaluate the arteries of the neck and brain, the thoracic and abdominal aorta, the renal arteries, and the legs (the latter exam is often referred to as a "run-off"). Acquisition A variety of techniques can be used to generate the pictures of blood vessels, both artery, arteries and veins, based on flow effects or on contrast (inherent or pharmacologically generated). The most frequently applied MRA methods involve the use intravenous MRI contrast agent, contrast agents, particularly those containing gadolinium to shorten the Spin–lattice relaxation, ''T''1 of blood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jugular
The jugular veins are veins that take deoxygenated blood from the head back to the heart via the superior vena cava. The internal jugular vein descends next to the internal carotid artery and continues posteriorly to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Structure and Function There are two sets of jugular veins: external and internal. The left and right external jugular veins drain into the subclavian veins. The internal jugular veins join with the subclavian veins more medially to form the brachiocephalic veins. Finally, the left and right brachiocephalic veins join to form the superior vena cava, which delivers deoxygenated blood to the right atrium of the heart. The Jugular veins help carry blood from the heart to and from the brain. An average human brain weighs about 3 pounds, and gets about 15%-20% of the blood that the heart pumps out. It is important for the brain to get enough blood for many reasons. The jugular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femoral Artery
The femoral artery is a large artery in the thigh and the main arterial supply to the thigh and leg. The femoral artery gives off the deep femoral artery or profunda femoris artery and descends along the anteromedial part of the thigh in the femoral triangle. It enters and passes through the adductor canal, and becomes the popliteal artery as it passes through the adductor hiatus in the adductor magnus near the junction of the middle and distal thirds of the thigh. Structure The femoral artery enters the thigh from behind the inguinal ligament as the continuation of the external iliac artery. Here, it lies midway between the anterior superior iliac spine and the symphysis pubis (Mid-inguinal point). Segments In clinical parlance, the femoral artery has the following segments: *The common femoral artery (CFA) is the segment of the femoral artery between the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament and the branching point of the deep femoral artery/profunda femoris artery. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
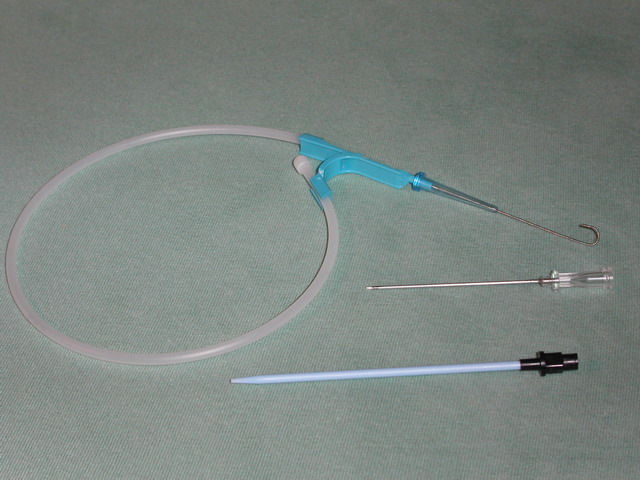
Seldinger Technique
The Seldinger technique, also known as Seldinger wire technique, is a medical procedure to obtain safe access to blood vessels and other hollow organs. It is named after Sven Ivar Seldinger (1921–1998), a Swedish radiologist who introduced the procedure in 1953. Uses The Seldinger technique is used for angiography, insertion of chest drains and central venous catheters, insertion of PEG tubes using the push technique, insertion of the leads for an artificial pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, and numerous other interventional medical procedures. Complications The initial puncture is with a sharp instrument, and this may lead to hemorrhage or perforation of the organ in question. Infection is a possible complication, and hence asepsis is practiced during most Seldinger procedures. Loss of the guidewire into the cavity or blood vessel is a significant and generally preventable complication. Description The desired vessel or cavity is punctured with a shar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sousa Pereira
Sousa refers to * John Philip Sousa (1854–1932), American composer of marches Sousa also may refer to: People * Sousa (surname), including other Portuguese variants such as Souza, de Sousa, D'Souza, etc. * João Sousa, Portuguese tennis player * Paulo Sousa, Portuguese football manager * Souza (footballer, born 1975), full name José Ivanaldo de Souza, Brazilian football attacking midfielder * Souza (footballer, born 1977), full name Sergio Roberto Pereira de Souza, Brazilian football midfielder * Souza (footballer, born 1979), full name Willamis de Souza Silva, Brazilian former football midfielder and television pundit * Souza (footballer, born 1982), full name Rodrigo de Souza Cardoso, Brazilian football striker * Souza (footballer, born 1988), full name Elierce Barbosa de Souza, Brazilian football defensive midfielder * Sousa (Brazilian footballer), full name Van Basty Sousa e Silva, (born 1994), Brazilian football midfielder Animals * ''Sousa'', genus making up the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fausto Lopo De Carvalho
Fausto Lopo Patrício de Carvalho (15 May 1890 – 23 May 1970), more commonly known as Fausto Lopo de Carvalho, was a Portuguese pulmonologist specialising in phthisiology, and the developer of pulmonary angiography in 1931, with Egas Moniz and Almeida Lima. He was the son of eminent phthisiologist Lopo de Carvalho (founder of the first sanatorium in Portugal, in Guarda), and his wife Leopoldina dos Anjos Patrício de Carvalho. He studied at the University of Coimbra, earning a degree in medicine with the highest possible grade (20 out of a possible 20) in 1916; after completing his medical studies he worked at the Guarda Sanatorium under his father's guidance, where he prepared his thesis for a doctorate, entitled '' Artificial Pneumothorax''. He taught Medical Propaedeutics, first at the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Coimbra and later at the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Lisbon, until 1934, when he was appointed to the newly-created Chair of Chest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reynaldo Dos Santos
Reynaldo dos Santos (3 December 1880 – 6 May 1970) was a Portuguese physician, writer, and art historian. As a physician, he was a pioneer in the fields of vascular surgery and urology; as an art historian, he published numerous works on 15th-century Portuguese art, including on the Manueline style and on the paintings of Nuno Gonçalves. Biography Reynaldo dos Santos was born in 1880 to Clemente José dos Santos (himself a physician) and Maria Amélia Pinheiro Santos, in the family home in Rua das Varinas, Vila Franca de Xira, a town in the outskirts of Lisbon. He concluded his primary and secondary studies in this town, before enrolling at the Medico-Surgical School in Lisbon, from which he graduated in 1903. Between 1902 and 1905, he was abroad in Paris and the main surgical centres of the United States, in Boston, Chicago, Rochester, Baltimore, Philadelphia, and New York. He earned his doctorate in Medicine in 1906, with his thesis titled "''Aspectos Cirúrgicos das Pancrea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arteriovenous Malformations
Arteriovenous malformation is an abnormal connection between arteries and veins, bypassing the capillary system. This vascular anomaly is widely known because of its occurrence in the central nervous system (usually cerebral AVM), but can appear in any location. Although many AVMs are asymptomatic, they can cause intense pain or bleeding or lead to other serious medical problems. AVMs are usually congenital and belong to the RASopathies. The genetic transmission patterns of AVMs are incomplete, but there are known genetic mutations (for instance in the epithelial line, tumor suppressor PTEN gene) which can lead to an increased occurrence throughout the body. Signs and symptoms Symptoms of AVM vary according to the location of the malformation. Roughly 88% of people with an AVM are asymptomatic; often the malformation is discovered as part of an autopsy or during treatment of an unrelated disorder (called in medicine an "incidental finding"); in rare cases, its expansion or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebral Angiography
Cerebral angiography is a form of angiography which provides images of blood vessels in and around the brain, thereby allowing detection of abnormalities such as arteriovenous malformations and aneurysms. It was pioneered in 1927 by the Portuguese neurologist Egas Moniz at the University of Lisbon, who also helped develop thorotrast for use in the procedure. Typically a catheter is inserted into a large artery (such as the femoral artery) and threaded through the circulatory system to the carotid artery, where a contrast agent is injected. A series of radiographs are taken as the contrast agent spreads through the brain's arterial system, then a second series as it reaches the venous system. For some applications cerebral angiography may yield better images than less invasive methods such as computed tomography angiography and magnetic resonance angiography. In addition, cerebral angiography allows certain treatments to be performed immediately, based on its findings. In recen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Lisbon
The University of Lisbon (ULisboa; pt, Universidade de Lisboa, ) is a public research university in Lisbon, and the largest university in Portugal. It was founded in 2013, from the merger of two previous public universities located in Lisbon, the former University of Lisbon (1911–2013) and the Technical University of Lisbon (1930–2013). History The first Portuguese university was established in Lisbon between 1288 and 1290, when Dinis I promulgated the letter ''Scientiae thesaurus mirabili'', granting several privileges to the students of the ''studium generale'' in Lisbon, proving that it was already founded on that date. There was an active participation in this educational activity by the Portuguese Crown and its king, through its commitment of part of the subsidy of the same, as by the fixed incomes of the Church. This institution moved several times between Lisbon and Coimbra, where it settled permanently in 1537. The current University of Lisbon is the result of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_Phase_Contrast_(PC)_sequence_MRI_of_arterial_dissections.jpg)