|
Antiderivatives
In calculus, an antiderivative, inverse derivative, primitive function, primitive integral or indefinite integral of a function is a differentiable function whose derivative is equal to the original function . This can be stated symbolically as . The process of solving for antiderivatives is called antidifferentiation (or indefinite integration), and its opposite operation is called ''differentiation'', which is the process of finding a derivative. Antiderivatives are often denoted by capital Roman letters such as and . Antiderivatives are related to definite integrals through the second fundamental theorem of calculus: the definite integral of a function over a closed interval where the function is Riemann integrable is equal to the difference between the values of an antiderivative evaluated at the endpoints of the interval. In physics, antiderivatives arise in the context of rectilinear motion (e.g., in explaining the relationship between position, velocity and accelera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
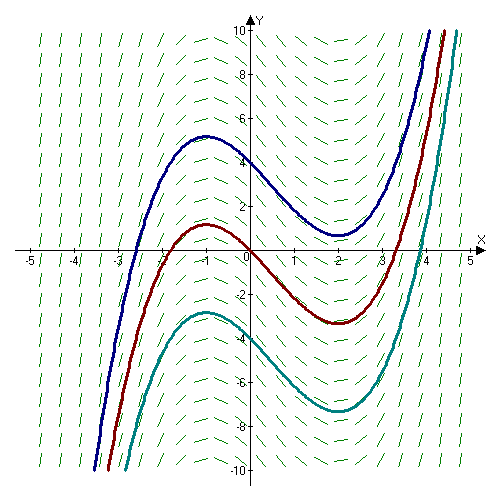
Constant Of Integration
In calculus, the constant of integration, often denoted by C (or c), is a constant term added to an antiderivative of a function f(x) to indicate that the indefinite integral of f(x) (i.e., the set of all antiderivatives of f(x)), on a connected domain, is only defined up to an additive constant. This constant expresses an ambiguity inherent in the construction of antiderivatives. More specifically, if a function f(x) is defined on an interval, and F(x) is an antiderivative of f(x), then the set of ''all'' antiderivatives of f(x) is given by the functions F(x) + C, where C is an arbitrary constant (meaning that ''any'' value of C would make F(x) + C a valid antiderivative). For that reason, the indefinite integral is often written as \int f(x) \, dx = F(x) + C, although the constant of integration might be sometimes omitted in lists of integrals for simplicity. Origin The derivative of any constant function is zero. Once one has found one antiderivative F(x) for a function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundamental Theorem Of Calculus
The fundamental theorem of calculus is a theorem that links the concept of differentiating a function (calculating its slopes, or rate of change at each time) with the concept of integrating a function (calculating the area under its graph, or the cumulative effect of small contributions). The two operations are inverses of each other apart from a constant value which depends on where one starts to compute area. The first part of the theorem, the first fundamental theorem of calculus, states that for a function , an antiderivative or indefinite integral may be obtained as the integral of over an interval with a variable upper bound. This implies the existence of antiderivatives for continuous functions. Conversely, the second part of the theorem, the second fundamental theorem of calculus, states that the integral of a function over a fixed interval is equal to the change of any antiderivative between the ends of the interval. This greatly simplifies the calculation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integral
In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that describes displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along with differentiation, integration is a fundamental, essential operation of calculus,Integral calculus is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. See and , for example. and serves as a tool to solve problems in mathematics and physics involving the area of an arbitrary shape, the length of a curve, and the volume of a solid, among others. The integrals enumerated here are those termed definite integrals, which can be interpreted as the signed area of the region in the plane that is bounded by the graph of a given function between two points in the real line. Conventionally, areas above the horizontal axis of the plane are positive while areas below are negative. Integrals also refer to the concept of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Definite Integral
In mathematics, an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that describes displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along with differentiation, integration is a fundamental, essential operation of calculus,Integral calculus is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. See and , for example. and serves as a tool to solve problems in mathematics and physics involving the area of an arbitrary shape, the length of a curve, and the volume of a solid, among others. The integrals enumerated here are those termed definite integrals, which can be interpreted as the signed area of the region in the plane that is bounded by the graph of a given function between two points in the real line. Conventionally, areas above the horizontal axis of the plane are positive while areas below are negative. Integrals also refer to the concept of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertical Translation
In Euclidean geometry, a translation is a geometric transformation that moves every point of a figure, shape or space by the same distance in a given direction. A translation can also be interpreted as the addition of a constant vector to every point, or as shifting the origin of the coordinate system. In a Euclidean space, any translation is an isometry. As a function If \mathbf is a fixed vector, known as the ''translation vector'', and \mathbf is the initial position of some object, then the translation function T_ will work as T_(\mathbf)=\mathbf+\mathbf. If T is a translation, then the image of a subset A under the function T is the translate of A by T . The translate of A by T_ is often written A+\mathbf . Horizontal and vertical translations In geometry, a vertical translation (also known as vertical shift) is a translation of a geometric object in a direction parallel to the vertical axis of the Cartesian coordinate system. Often, vertical transla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calculus
Calculus, originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the calculus of infinitesimals", is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations. It has two major branches, differential calculus and integral calculus; the former concerns instantaneous Rate of change (mathematics), rates of change, and the slopes of curves, while the latter concerns accumulation of quantities, and areas under or between curves. These two branches are related to each other by the fundamental theorem of calculus, and they make use of the fundamental notions of convergence (mathematics), convergence of infinite sequences and Series (mathematics), infinite series to a well-defined limit (mathematics), limit. Infinitesimal calculus was developed independently in the late 17th century by Isaac Newton and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz. Later work, including (ε, δ)-definition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velocity
Velocity is the directional speed of an object in motion as an indication of its rate of change in position as observed from a particular frame of reference and as measured by a particular standard of time (e.g. northbound). Velocity is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of bodies. Velocity is a physical vector quantity; both magnitude and direction are needed to define it. The scalar absolute value ( magnitude) of velocity is called , being a coherent derived unit whose quantity is measured in the SI ( metric system) as metres per second (m/s or m⋅s−1). For example, "5 metres per second" is a scalar, whereas "5 metres per second east" is a vector. If there is a change in speed, direction or both, then the object is said to be undergoing an ''acceleration''. Constant velocity vs acceleration To have a ''constant velocity'', an object must have a constant speed in a constant direction. Constant dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acceleration
In mechanics, acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Accelerations are vector quantities (in that they have magnitude and direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by the orientation of the ''net'' force acting on that object. The magnitude of an object's acceleration, as described by Newton's Second Law, is the combined effect of two causes: * the net balance of all external forces acting onto that object — magnitude is directly proportional to this net resulting force; * that object's mass, depending on the materials out of which it is made — magnitude is inversely proportional to the object's mass. The SI unit for acceleration is metre per second squared (, \mathrm). For example, when a vehicle starts from a standstill (zero velocity, in an inertial frame of reference) and travels in a straight line at increasing speeds, it is accelerating in the direction of travel. If the vehicle turns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0 (number)
0 (zero) is a number representing an empty quantity. In place-value notation such as the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, 0 also serves as a placeholder numerical digit, which works by multiplying digits to the left of 0 by the radix, usually by 10. As a number, 0 fulfills a central role in mathematics as the additive identity of the integers, real numbers, and other algebraic structures. Common names for the number 0 in English are ''zero'', ''nought'', ''naught'' (), ''nil''. In contexts where at least one adjacent digit distinguishes it from the letter O, the number is sometimes pronounced as ''oh'' or ''o'' (). Informal or slang terms for 0 include ''zilch'' and ''zip''. Historically, ''ought'', ''aught'' (), and ''cipher'', have also been used. Etymology The word ''zero'' came into the English language via French from the Italian , a contraction of the Venetian form of Italian via ''ṣafira'' or ''ṣifr''. In pre-Islamic time the word (Arabic ) had the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Displacement (geometry)
In geometry and mechanics, a displacement is a vector whose length is the shortest distance from the initial to the final position of a point P undergoing motion. It quantifies both the distance and direction of the net or total motion along a straight line from the initial position to the final position of the point trajectory. A displacement may be identified with the translation that maps the initial position to the final position. A displacement may be also described as a ''relative position'' (resulting from the motion), that is, as the final position of a point relative to its initial position . The corresponding displacement vector can be defined as the difference between the final and initial positions: s = x_\textrm - x_\textrm = \Delta In considering motions of objects over time, the instantaneous velocity of the object is the rate of change of the displacement as a function of time. The instantaneous speed, then, is distinct from velocity, or the time rate of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Function
Exponentiation is a mathematical operation, written as , involving two numbers, the '' base'' and the ''exponent'' or ''power'' , and pronounced as " (raised) to the (power of) ". When is a positive integer, exponentiation corresponds to repeated multiplication of the base: that is, is the product of multiplying bases: b^n = \underbrace_. The exponent is usually shown as a superscript to the right of the base. In that case, is called "''b'' raised to the ''n''th power", "''b'' (raised) to the power of ''n''", "the ''n''th power of ''b''", "''b'' to the ''n''th power", or most briefly as "''b'' to the ''n''th". Starting from the basic fact stated above that, for any positive integer n, b^n is n occurrences of b all multiplied by each other, several other properties of exponentiation directly follow. In particular: \begin b^ & = \underbrace_ \\ ex& = \underbrace_ \times \underbrace_ \\ ex& = b^n \times b^m \end In other words, when multiplying a base raised to one exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Value (mathematics)
In mathematics, value may refer to several, strongly related notions. In general, a mathematical value may be any definite mathematical object. In elementary mathematics, this is most often a number – for example, a real number such as or an integer such as 42. * The value of a variable or a constant is any number or other mathematical object assigned to it. * The value of a mathematical expression is the result of the computation described by this expression when the variables and constants in it are assigned values. * The value of a function, given the value(s) assigned to its argument(s), is the quantity assumed by the function for these argument values. For example, if the function is defined by , then assigning the value 3 to its argument yields the function value 10, since . If the variable, expression or function only assumes real values, it is called real-valued. Likewise, a complex-valued variable, expression or function only assumes complex values. See ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |