|
Anthopleurin
Anthopleurin is a toxin from the venom of the sea anemones ''Anthopleura xanthogrammica'' and ''Anthopleura elegantissima''. These anemones use anthopleurin as a pheromone to quickly withdraw their tentacles in the presence of predators. Anthopleurin has four isoforms (Anthopleurin-A, -B, -C, and -Q). Their working mechanism is based on binding to sodium channels, which leads to increased excitation especially in cardiac myocytes.Moran Y, Gordon D, Gurevitz M. "Sea anemone toxins affecting voltage-gated sodium channels—molecular and evolutionary features". ''Toxicon'' 2009, 54(8): 1089–1101. Function in sea anemones Anthopleurin functions both as a toxin as well as a pheromone. When a predator approaches the anemone, their reaction is to withdraw their tentacles and oral disc. These are the preferred attack sites for predators, because the concentration of anthopleurin is the lowest in these sites. The body region of the sea-anemone that is exposed to the predator contains the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxin
A toxin is a naturally occurring organic poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. Toxins occur especially as a protein or conjugated protein. The term toxin was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849–1919) and is derived from the word toxic. Toxins can be small molecules, peptides, or proteins that are capable of causing disease on contact with or absorption by body tissues interacting with biological macromolecules such as enzymes or cellular receptors. Toxins vary greatly in their toxicity, ranging from usually minor (such as a bee sting) to potentially fatal even at extremely low doses (such as botulinum toxin). Toxins are largely secondary metabolites, which are organic compounds that are not directly involved in an organism's growth, development, or reproduction, instead often aiding it in matters of defense. Terminology Toxins are often distinguished from other chemical agents strictly based on their biological origin. Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
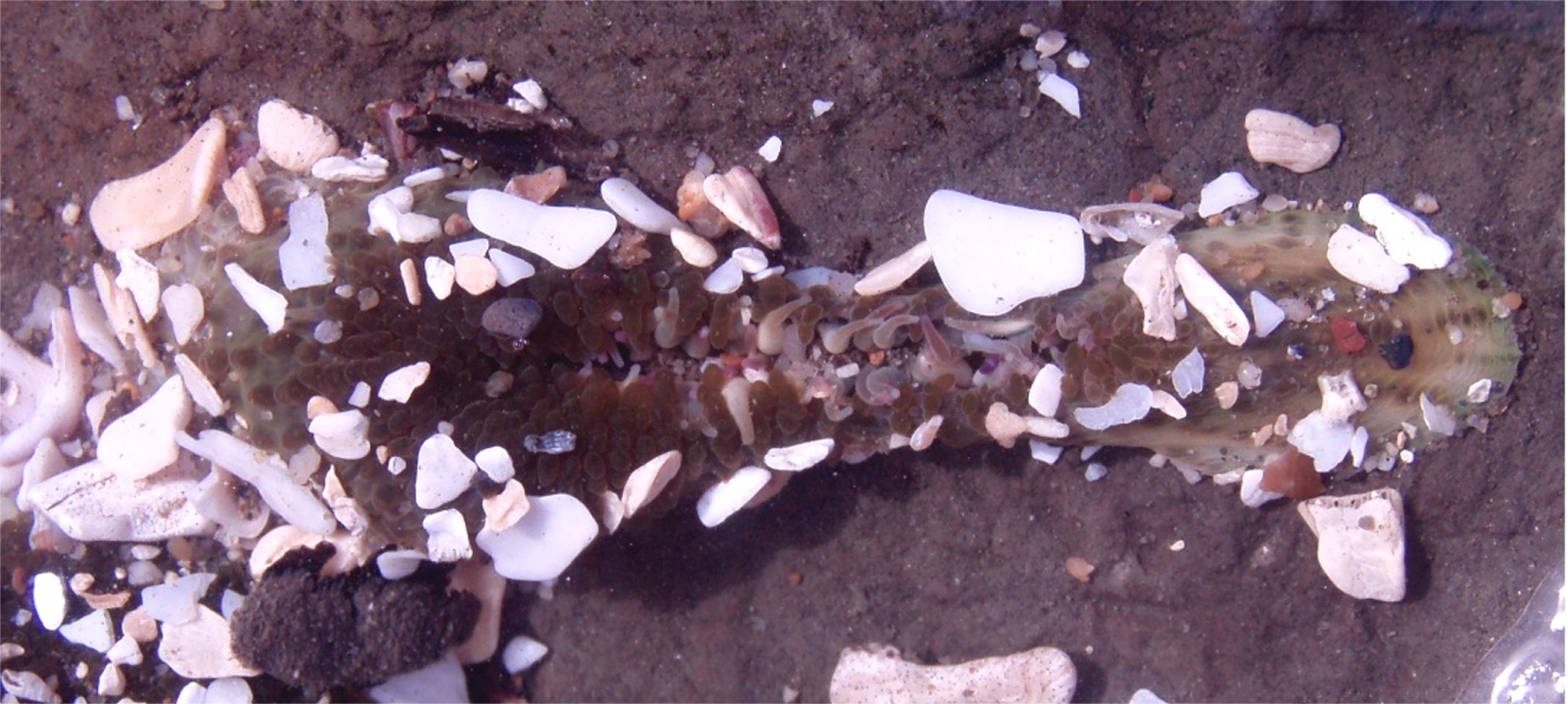
Anthopleura Xanthogrammica
''Anthopleura xanthogrammica'', or the giant green anemone, is a species of intertidal sea anemone of the family Actiniidae. Other common names for this anemone include green surf anemone, giant green sea anemone, green anemone, giant tidepool anemone, anemone, and rough anemone. Description The column width and height can reach a maximum of 17.5 and 30 cm, respectively. The crown of tentacles can be as wide as 25 cm in diameter, while the column, itself, tends to be widest at the base in order to offer a more stable connection to the rocks. It has a broad, flat oral disk surface and no striping, banding, or other markings. Coloration If ''A. xanthogrammica'' is exposed to proper amounts of sunlight, it can appear bright green when submerged under water. When not submerged, it appears dark green or brown. This is because the anemone tends to close up and "droop" and its now exposed column is actually dark green and slightly brown, but the hidden tentacles and ora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthopleura Elegantissima
The aggregating anemone (''Anthopleura elegantissima''), or clonal anemone, is the most abundant species of sea anemone found on rocky, tide swept shores along the Pacific coast of North America. This cnidarian hosts endosymbiotic algae called zooxanthellae that contribute substantially to primary productivity in the intertidal zone. The aggregating anemone has become a model organism for the study of temperate cnidarian-algal symbioses. Description The polyps of the aggregating anemone reach up to eight cm across the oral disk with approximately 100 tentacles in three or four rows around the margins of the oral disk. Most are olive to bright green (depending on the species of algal symbionts present) with tentacles tipped in pink. Individuals that live in microhabitats that are deficient in photosynthetically active radiation (PAR), such as under docks or in caves, lack symbionts and are pale yellow to white in color. Range Pacific coast of North America from Alaska, United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Channel
Sodium channels are integral membrane proteins that form ion channels, conducting sodium ions (Na+) through a cell's membrane. They belong to the superfamily of cation channels and can be classified according to the trigger that opens the channel for such ions, i.e. either a voltage-change ("voltage-gated", "voltage-sensitive", or "voltage-dependent" sodium channel; also called "VGSCs" or "Nav channel") or a binding of a substance (a ligand) to the channel (ligand-gated sodium channels). In excitable cells such as neurons, myocytes, and certain types of glia, sodium channels are responsible for the rising phase of action potentials. These channels go through three different states called resting, active and inactive states. Even though the resting and inactive states would not allow the ions to flow through the channels the difference exists with respect to their structural conformation. Selectivity Sodium channels are highly selective for the transport of ions across cell membr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myocyte
A muscle cell is also known as a myocyte when referring to either a cardiac muscle cell (cardiomyocyte), or a smooth muscle cell as these are both small cells. A skeletal muscle cell is long and threadlike with many nuclei and is called a muscle fiber. Muscle cells (including myocytes and muscle fibers) develop from embryonic precursor cells called myoblasts. Myoblasts fuse to form multinucleated skeletal muscle cells known as syncytia in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle cells and cardiac muscle cells both contain myofibrils and sarcomeres and form a striated muscle tissue. Cardiac muscle cells form the cardiac muscle in the walls of the heart chambers, and have a single central nucleus. Cardiac muscle cells are joined to neighboring cells by intercalated discs, and when joined in a visible unit they are described as a ''cardiac muscle fiber''. Smooth muscle cells control involuntary movements such as the peristalsis contractions in the esophagus and stomach. Sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inotrope
An inotrope is an agent that alters the force or energy of muscular contractions. Negatively inotropic agents weaken the force of muscular contractions. Positively inotropic agents increase the strength of muscular contraction. The term ''inotropic state'' is most commonly used in reference to various drugs that affect the strength of contraction of heart muscle. However, it can also refer to pathological conditions. For example, enlarged heart muscle can increase inotropic state, whereas dead heart muscle can decrease it. Medical uses Both positive and negative inotropes are used in the management of various cardiovascular conditions. The choice of agent depends largely on specific pharmacological effects of individual agents with respect to the condition. One of the most important factors affecting inotropic state is the level of calcium in the cytoplasm of the muscle cell. Positive inotropes usually increase this level, while negative inotropes decrease it. However, not al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aspartate Transaminase
Aspartate transaminase (AST) or aspartate aminotransferase, also known as AspAT/ASAT/AAT or (serum) glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT, SGOT), is a pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)-dependent transaminase enzyme () that was first described by Arthur Karmen and colleagues in 1954. AST catalyzes the reversible transfer of an α-amino group between aspartate and glutamate and, as such, is an important enzyme in amino acid metabolism. AST is found in the liver, heart, skeletal muscle, kidneys, brain, red blood cells and gall bladder. Serum AST level, serum ALT (alanine transaminase) level, and their ratio (AST/ALT ratio) are commonly measured clinically as biomarkers for liver health. The tests are part of blood panels. The half-life of total AST in the circulation approximates 17 hours and, on average, 87 hours for ''mitochondrial'' AST. Aminotransferase is cleared by Liver sinusoidal endothelial cell, sinusoidal cells in the liver. Function Aspartate transaminase catalyzes the inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
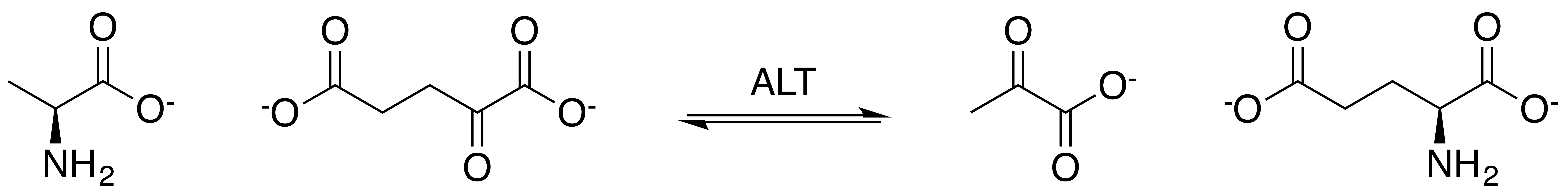
Alanine Transaminase
Alanine transaminase (ALT) is a transaminase enzyme (). It is also called alanine aminotransferase (ALT or ALAT) and was formerly called serum glutamate-pyruvate transaminase or serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (SGPT) and was first characterized in the mid-1950s by Arthur Karmen and colleagues. ALT is found in plasma and in various body tissues but is most common in the liver. It catalyzes the two parts of the alanine cycle. Serum ALT level, serum AST (aspartate transaminase) level, and their ratio (AST/ALT ratio) are commonly measured clinically as biomarkers for liver health. The tests are part of blood panels. The half-life of ALT in the circulation approximates 47 hours. Aminotransferase is cleared by sinusoidal cells in the liver. Function ALT catalyzes the transfer of an amino group from L-alanine to α-ketoglutarate, the products of this reversible transamination reaction being pyruvate and L-glutamate. : L-alanine + α-ketoglutarate ⇌ pyruvate + L-glutama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesnarinone
Vesnarinone ( INN) is a cardiotonic agent. A mixed phosphodiesterase 3 inhibitor and ion-channel modifier that has modest, dose-dependent, positive inotropic activity, but minimal negative chronotropic activity. Vesnarinone improves ventricular performance most in patients with the worst degree of heart failure Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, a .... References External links * N-benzoylpiperazines Inotropic agents PDE3 inhibitors Catechol ethers Phenylpiperazines 2-Quinolones {{cardiovascular-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Engineering
Biological engineering or bioengineering is the application of principles of biology and the tools of engineering to create usable, tangible, economically-viable products. Biological engineering employs knowledge and expertise from a number of pure and applied sciences, such as mass and heat transfer, kinetics, biocatalysts, biomechanics, bioinformatics, separation and purification processes, bioreactor design, surface science, fluid mechanics, thermodynamics, and polymer science. It is used in the design of medical devices, diagnostic equipment, biocompatible materials, renewable energy, ecological engineering, agricultural engineering, process engineering and catalysis, and other areas that improve the living standards of societies. Examples of bioengineering research include bacteria engineered to produce chemicals, new medical imaging technology, portable and rapid disease diagnostic devices, prosthetics, biopharmaceuticals, and tissue-engineered organs. Bioengineering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperpolarization (biology)
Hyperpolarization is a change in a cell's membrane potential that makes it more negative. It is the opposite of a depolarization. It inhibits action potentials by increasing the stimulus required to move the membrane potential to the action potential threshold. Hyperpolarization is often caused by efflux of K+ (a cation) through K+ channels, or influx of Cl– (an anion) through Cl– channels. On the other hand, influx of cations, e.g. Na+ through Na+ channels or Ca2+ through Ca2+ channels, inhibits hyperpolarization. If a cell has Na+ or Ca2+ currents at rest, then inhibition of those currents will also result in a hyperpolarization. This voltage-gated ion channel response is how the hyperpolarization state is achieved. In neurons, the cell enters a state of hyperpolarization immediately following the generation of an action potential. While hyperpolarized, the neuron is in a refractory period that lasts roughly 2 milliseconds, during which the neuron is unabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Potential
Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell. That is, there is a difference in the energy required for electric charges to move from the internal to exterior cellular environments and vice versa, as long as there is no acquisition of kinetic energy or the production of radiation. The concentration gradients of the charges directly determine this energy requirement. For the exterior of the cell, typical values of membrane potential, normally given in units of milli volts and denoted as mV, range from –80 mV to –40 mV. All animal cells are surrounded by a membrane composed of a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded in it. The membrane serves as both an insulator and a diffusion barrier to the movement of ions. Transmembrane proteins, also known as ion transporter or ion pump proteins, actively push ions across the membrane and establish concentration gradi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |