|
Annulyne
Annulynes or dehydroannulenes are conjugated monocyclic hydrocarbons with alternating single and double bonds in addition to at least one triple bond. They are related to annulenes, which only have alternating single and double bonds. The smallest member of this class is nnulyne but is never observed because the molecule carries too much angle strain. The next member is nnulyne or benzyne which is a reactive intermediate well known in organic chemistry. nnulyne is known to exist but quickly dimerizes or trimerizes; the compound has been trapped as its radical anion and observed by EPR spectroscopy. 0nnulyne, like nnulyne, only exists in theory. 2nnulyne has been observed in 2005 by Stevenson et al. in solution by NMR spectroscopy at room temperature. Reaction of 1,5-hexadiyne and potassium tert-butoxide was reported to yield two isomers 5,9-di-''trans''- 2annulyne and 3,11-di-''trans''- 2nnulyne in a 1:1 ratio. The proposed reaction sequence involved an unspecified elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annulyne
Annulynes or dehydroannulenes are conjugated monocyclic hydrocarbons with alternating single and double bonds in addition to at least one triple bond. They are related to annulenes, which only have alternating single and double bonds. The smallest member of this class is nnulyne but is never observed because the molecule carries too much angle strain. The next member is nnulyne or benzyne which is a reactive intermediate well known in organic chemistry. nnulyne is known to exist but quickly dimerizes or trimerizes; the compound has been trapped as its radical anion and observed by EPR spectroscopy. 0nnulyne, like nnulyne, only exists in theory. 2nnulyne has been observed in 2005 by Stevenson et al. in solution by NMR spectroscopy at room temperature. Reaction of 1,5-hexadiyne and potassium tert-butoxide was reported to yield two isomers 5,9-di-''trans''- 2annulyne and 3,11-di-''trans''- 2nnulyne in a 1:1 ratio. The proposed reaction sequence involved an unspecified elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annulenes
Annulenes are monocyclic hydrocarbons that contain the maximum number of non-cumulated or conjugated double bonds (' mancude'). They have the general formula CnHn (when ''n'' is an even number) or C''n''H''n''+1 (when ''n'' is an odd number). The IUPAC naming conventions are that annulenes with 7 or more carbon atoms are named as 'n''nnulene, where ''n'' is the number of carbon atoms in their ring, though sometimes the smaller annulenes are referred to using the same notation, and benzene is sometimes referred to simply as annulene. The first three even annulenes are cyclobutadiene, benzene, and cyclooctatetraene ( nnulene). Some annulenes, namely cyclobutadiene, cyclodecapentaene ( 0nnulene), cyclododecahexaene ( 2nnulene) and cyclotetradecaheptaene ( 4nnulene), are unstable, with cyclobutadiene extremely so. In the related annulynes, one double bond is replaced by a triple bond. Aromaticity Annulenes may be ''aromatic'' (benzene, nnulene and 8nnulene), ''non-aromatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annulene
Annulenes are monocyclic hydrocarbons that contain the maximum number of non-cumulated or conjugated double bonds (' mancude'). They have the general formula CnHn (when ''n'' is an even number) or C''n''H''n''+1 (when ''n'' is an odd number). The IUPAC naming conventions are that annulenes with 7 or more carbon atoms are named as 'n''nnulene, where ''n'' is the number of carbon atoms in their ring, though sometimes the smaller annulenes are referred to using the same notation, and benzene is sometimes referred to simply as annulene. The first three even annulenes are cyclobutadiene, benzene, and cyclooctatetraene ( nnulene). Some annulenes, namely cyclobutadiene, cyclodecapentaene ( 0nnulene), cyclododecahexaene ( 2nnulene) and cyclotetradecaheptaene ( 4nnulene), are unstable, with cyclobutadiene extremely so. In the related annulynes, one double bond is replaced by a triple bond. Aromaticity Annulenes may be ''aromatic'' (benzene, nnulene and 8nnulene), ''non-aromat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Tert-butoxide
Potassium ''tert''-butoxide is the chemical compound with the formula K+(CH3)3CO−. This colourless solid is a strong base (pKa of conjugate acid around 17), which is useful in organic synthesis. It exists as a tetrameric cubane-type cluster. It is often seen written in chemical literature as potassium ''t''-butoxide. The compound is often depicted as a salt, and it often behaves as such, but it is not ionized in solution. Preparation Potassium ''t''-butoxide is commercially available as a solution and as a solid, but it is often generated ''in situ'' for laboratory use because samples are so sensitive and older samples are often of poor quality. It is prepared by the reaction of dry ''tert''-butyl alcohol with potassium metal. The solid is obtained by evaporating these solutions followed by heating the solid. The solid can be purified by sublimation at 220 °C and 1 mmHg. Sublimation can also take place at 140 °C and 0.01 hPa. It is advisable to cover the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biphenyl
Biphenyl (also known as diphenyl, phenylbenzene, 1,1′-biphenyl, lemonene or BP) is an organic compound that forms colorless crystals. Particularly in older literature, compounds containing the functional group consisting of biphenyl less one hydrogen (the site at which it is attached) may use the prefixes xenyl or diphenylyl. It has a distinctively pleasant smell. Biphenyl is an aromatic hydrocarbon with a molecular formula (C6H5)2. It is notable as a starting material for the production of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), which were once widely used as dielectric fluids and heat transfer agents. Biphenyl is also an intermediate for the production of a host of other organic compounds such as emulsifiers, optical brighteners, crop protection products, and plastics. Biphenyl is insoluble in water, but soluble in typical organic solvents. The biphenyl molecule consists of two connected phenyl rings. Properties and occurrence Biphenyl occurs naturally in coal tar, crude oil, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
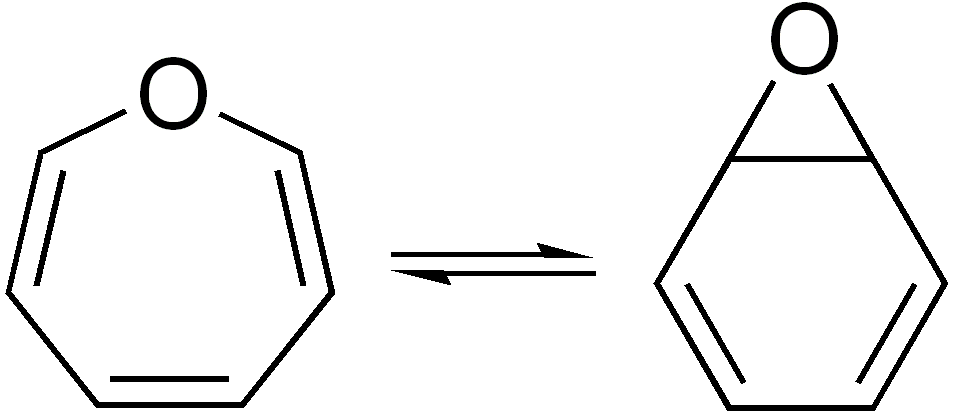
Valence Isomerization
In organic chemistry, two molecules are valence isomers when they are constitutional isomers that can interconvert through pericyclic reactions. Benzene There are many valence isomers one can draw for the C6H6 formula benzene. Some were originally proposed for benzene itself before the actual structure of benzene was known. Others were later synthesized in lab. Some have been observed to isomerize to benzene, whereas others tend to undergo other reactions instead, or isomerize by ways other than pericyclic reactions. Image:Benzene-2D-flat.png, Benzene Image:Historic Benzene Formulae Dewar(1867) V.1.svg, Dewar benzene Image:Prisman2.svg, Prismane Image:Benzvalene.png, Benzvalene Image:Bicycloprop-2-enyl.svg, Bicyclopropenyl Cyclooctatetraene The valence isomers are not restricted to isomers of benzene. Valence isomers are also seen in the series (CH)8. Due to the larger number of units, the number of possible valence isomers is also greater and at least 21: Image:Cyclooctatet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Sondheimer
Franz Sondheimer FRS (17 May 1926 – 11 February 1981) was a German-born British professor of chemistry. In 1960, he was awarded the Israel Prize for his contributions to science. Biography Franz Sondheimer was born in Stuttgart on 17 May 1926, the second son of Max and Ida Sondheimer. His father ran the family glue manufacturing business. His elder brother, Ernst, was Professor of Mathematics at Westfield College. Having business connections in England, Max Sondheimer managed to get his family to London in September 1937. Sondheimer, knowing no English, began his schooling in England first at Southend and then at Hailey School in Bournemouth. In 1940, having passed Common Entrance, he attended the part of Highgate School remaining in London, where he obtained School Certificate in nine subjects in 1942. A little over a year later he gained entrance to Imperial College, where he studied until the end of the war, coming top of his year in the final examination. He was awarded a P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic Ring Current
An aromatic ring current is an effect observed in aromatic molecules such as benzene and naphthalene. If a magnetic field is directed perpendicular to the plane of the aromatic system, a ring current is induced in the delocalized π electrons of the aromatic ring. This is a direct consequence of Ampère's law; since the electrons involved are free to circulate, rather than being localized in bonds as they would be in most non-aromatic molecules, they respond much more strongly to the magnetic field. The ring current creates its own magnetic field. Outside the ring, this field is in the same direction as the externally applied magnetic field; inside the ring, the field counteracts the externally applied field. As a result, the net magnetic field outside the ring is greater than the externally applied field alone, and is less inside the ring. Aromatic ring currents are relevant to NMR spectroscopy, as they dramatically influence the chemical shifts of 1H nuclei ("protons") in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Shift
In nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of an atomic nucleus relative to a standard in a magnetic field. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of a molecule. Chemical shifts are also used to describe signals in other forms of spectroscopy such as photoemission spectroscopy. Some atomic nuclei possess a magnetic moment ( nuclear spin), which gives rise to different energy levels and resonance frequencies in a magnetic field. The total magnetic field experienced by a nucleus includes local magnetic fields induced by currents of electrons in the molecular orbitals (note that electrons have a magnetic moment themselves). The electron distribution of the same type of nucleus (e.g. ) usually varies according to the local geometry (binding partners, bond lengths, angles between bonds, and so on), and with it the local magnetic field at each nucleus. This is reflected in the spin energy le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical Ion
In organic chemistry, a radical anion is a free radical species that carries a negative charge. Radical anions are encountered in organic chemistry as reduced derivatives of polycyclic aromatic compounds, e.g. sodium naphthenide. An example of a non-carbon radical anion is the superoxide anion, formed by transfer of one electron to an oxygen molecule. Radical anions are typically indicated by M^. Polycyclic radical anions Many aromatic compounds can undergo one-electron reduction by alkali metals. The electron is transferred from the alkali metal ion to an unoccupied antibonding p-p п* orbital of the aromatic molecule. This transfer is usually only energetically favorable if the aprotic solvent efficiently solvates the alkali metal ion. Effective solvents are those that bind to the alkali metal cation: diethyl ether < < |