|
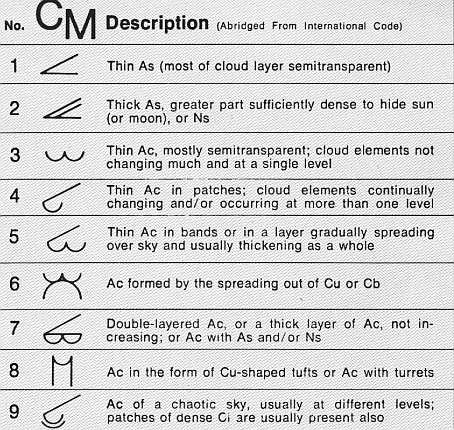
Altocumulus
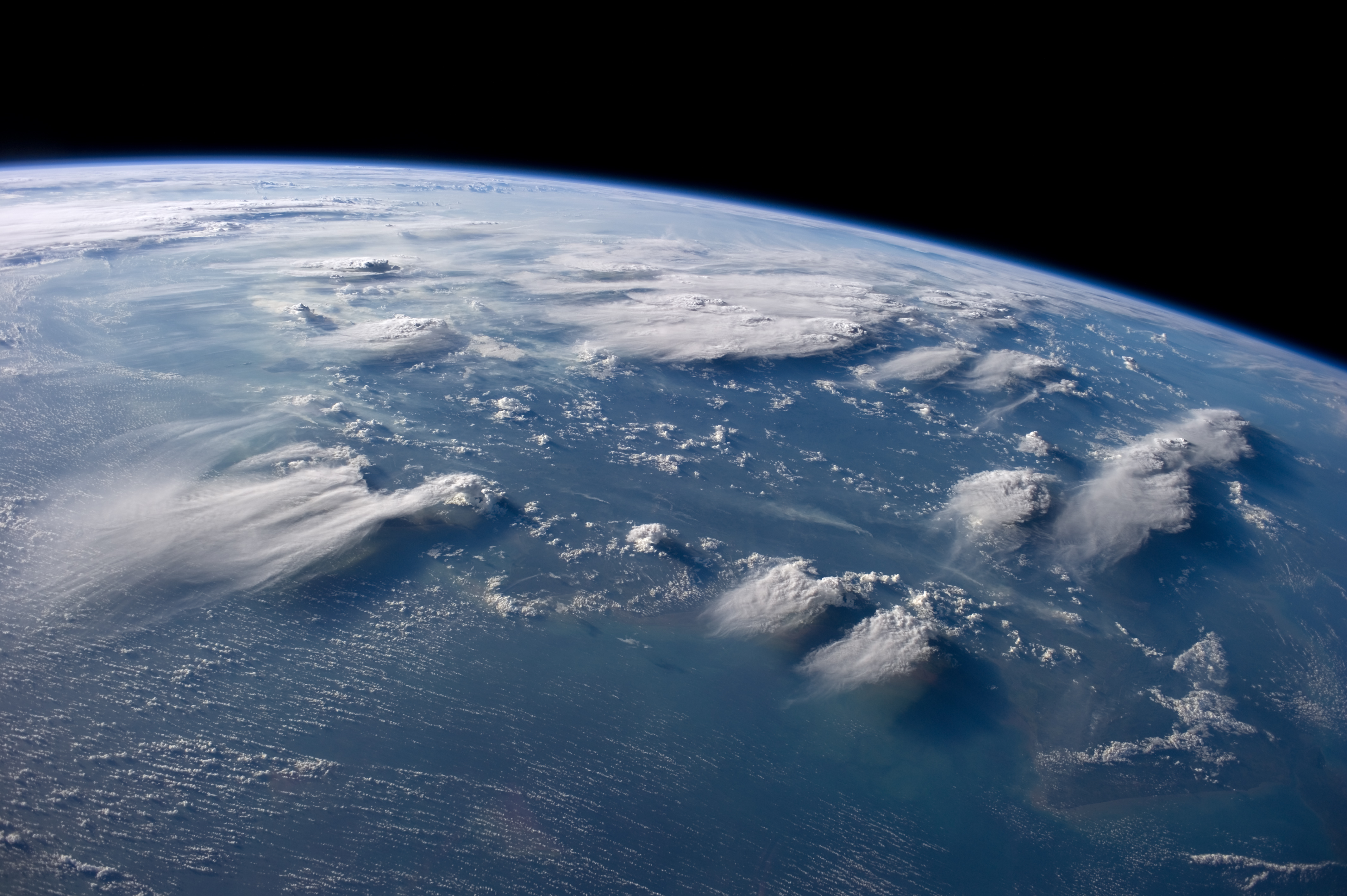
Altocumulus (From Latin ''Altus'', "high", ''cumulus'', "heaped") is a middle-altitude cloud genus that belongs mainly to the ''stratocumuliform'' physical category characterized by globular masses or rolls in layers or patches, the individual elements being larger and darker than those of cirrocumulus and smaller than those of stratocumulus. However, if the layers become tufted in appearance due to increased airmass instability, then the altocumulus clouds become more purely ''cumuliform'' in structure. Like other cumuliform and stratocumuliform clouds, altocumulus signifies convection. A sheet of partially conjoined altocumulus perlucidus is sometimes found preceding a weakening warm front, where the altostratus is starting to fragment, resulting in patches of altocumulus perlucidus between the areas of altostratus. Altocumulus is also commonly found between the warm and cold fronts in a depression, although this is often hidden by lower clouds. Towering altocumulus, known as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may compose the droplets and crystals. On Earth, clouds are formed as a result of saturation of the air when it is cooled to its dew point, or when it gains sufficient moisture (usually in the form of water vapor) from an adjacent source to raise the dew point to the ambient temperature. They are seen in the Earth's homosphere, which includes the troposphere, stratosphere, and mesosphere. Nephology is the science of clouds, which is undertaken in the cloud physics branch of meteorology. There are two methods of naming clouds in their respective layers of the homosphere, Latin and common name. Genus types in the troposphere, the atmospheric layer closest to Earth's surface, have Latin names because of the universal adoption of Luke Howard's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altocumulus Floccus
Altocumulus floccus is a cloud type named for its tuft-like, wooly appearance. The base of the cloud can form as low as , or as high as . They often form in clusters, or patches, and bases can vary in height with differing atmospheric conditions within the PBL. They are similar to Altocumulus castellanus, but often have a shallower vertical extent in comparison. Floccus clouds form when in the presence of conditional, often shallow, mid-level instability. On some occasions, such as the presence of a deeper unstable layer, these clouds can grow large enough to develop into thunderstorms A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are someti .... References Cumulus {{Cloud-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altocumulus Stratiformis
Altocumulus stratiformis is the most common species of the Altocumulus genus of clouds. They tend to form broad layers of individual, cell-like clumps, often separated from each other, though they sometimes can coagulate into a larger individual cloud. They often have a vertical extent of less than 500 m. Due to their formation dynamics, they are commonly associated with the imminent arrival of precipitation. Formation The presence of stratiformis clouds in the mid-levels of the atmosphere is indicative of some instability at that level; atmospheric pressure falls, often associated with nearby systems of low pressure, can depress the altitude of stratiformis into the lower atmosphere, often evolving into Nimbostratus A nimbostratus cloud is a multi-level, amorphous, nearly uniform and often dark grey cloud that usually produces continuous rain, snow or sleet but no lightning or thunder. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altocumulus Castellanus
In meteorology, Altocumulus castellanus or Altocumulus castellatus (ACCAS) is a cloud type named for its tower-like projections that billow upwards from the base of the cloud. The base of the cloud can form as low as 2,000 metres (6,500 feet), or as high as 6,000 metres (20,000 feet). They are very similar to cumulus congestus clouds, but at a higher level and with the cloud heaps joined at the base. Castellanus clouds are evidence of mid-atmospheric instability and a high mid-altitude lapse rate. They may be a harbinger of heavy showers and thunderstorms and, if surface-based convection can connect to the mid-tropospheric unstable layer, continued development of Castellanus clouds can produce cumulonimbus clouds. Altocumulus castellanus clouds are typically accompanied by moderate turbulence as well as potential icing conditions In aviation, icing conditions are atmospheric conditions that can lead to the formation of water ice on an aircraft. Ice accretion and accumulation c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mackerel Sky
A mackerel sky is a common term for clouds made up of rows of cirrocumulus or altocumulus clouds displaying an undulating, rippling pattern similar in appearance to fish scales; this is caused by high altitude atmospheric waves. Cirrocumulus appears almost exclusively with cirrus some way ahead of a warm front and is a reliable forecaster that the weather is about to change. When these high clouds progressively invade the sky and the barometric pressure begins to fall, precipitation associated with the disturbance is likely about 6 to 12 hours away. A thickening and lowering of cirrocumulus into middle-étage altostratus or altocumulus is a good sign that the warm front or low front has moved closer and it may start raining within less than six hours. The old rhymes "Mackerel sky, not twenty-four hours dry" and " Mares' tails and mackerel scales make lofty ships to carry low sails" both refer to this long-recognized phenomenon. Other phrases in weather lore take mackerel skies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altocumulus Mackerel Sky
A mackerel sky is a common term for clouds made up of rows of cirrocumulus or altocumulus clouds displaying an undulating, rippling pattern similar in appearance to fish scales; this is caused by high altitude atmospheric waves. Cirrocumulus appears almost exclusively with cirrus some way ahead of a warm front and is a reliable forecaster that the weather is about to change. When these high clouds progressively invade the sky and the barometric pressure begins to fall, precipitation associated with the disturbance is likely about 6 to 12 hours away. A thickening and lowering of cirrocumulus into middle-étage altostratus or altocumulus is a good sign that the warm front or low front has moved closer and it may start raining within less than six hours. The old rhymes "Mackerel sky, not twenty-four hours dry" and " Mares' tails and mackerel scales make lofty ships to carry low sails" both refer to this long-recognized phenomenon. Other phrases in weather lore take mackerel skies a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenticular Cloud
Lenticular clouds (Latin: ''Lenticularis'' lentil-shaped, from ''lenticula'' lentil) are stationary clouds that form mostly in the troposphere, typically in parallel alignment to the wind direction. They are often comparable in appearance to a lens or saucer. Nacreous clouds that form in the lower stratosphere sometimes have lenticular shapes. There are three main types of lenticular clouds: altocumulus standing lenticular (ACSL), stratocumulus standing lenticular (SCSL), and cirrocumulus standing lenticular (CCSL), varying in altitude above the ground. Because of their unique appearance, they have been suggested as an explanation for some unidentified flying object (UFO) sightings. Formation and appearance As air travels along the surface of the Earth, obstructions are often encountered, including natural features, such as mountains or hills, and artificial structures, such as buildings and other constructions, which disrupt the flow of air into "eddies", or areas of turb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratocumulus
A stratocumulus cloud, occasionally called a cumulostratus, belongs to a genus-type of clouds characterized by large dark, rounded masses, usually in groups, lines, or waves, the individual elements being larger than those in altocumulus, and the whole being at a lower height, usually below . Weak convective currents create shallow cloud layers because of drier, stable air above preventing continued vertical development. Historically, in English, this type of cloud has been referred to as a twain cloud for being a combination of two types of clouds. Description Occurrence Vast areas of subtropical and polar oceans are covered with massive sheets of stratocumulus. These may organize into distinctive patterns which are currently under active study. In subtropics, they cover the edges of the horse latitude climatological highs, and reduce the amount of solar energy absorbed in the ocean. When these drift over land the summer heat or winter cold is reduced. 'Dull weather' is a common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratocumulus
A stratocumulus cloud, occasionally called a cumulostratus, belongs to a genus-type of clouds characterized by large dark, rounded masses, usually in groups, lines, or waves, the individual elements being larger than those in altocumulus, and the whole being at a lower height, usually below . Weak convective currents create shallow cloud layers because of drier, stable air above preventing continued vertical development. Historically, in English, this type of cloud has been referred to as a twain cloud for being a combination of two types of clouds. Description Occurrence Vast areas of subtropical and polar oceans are covered with massive sheets of stratocumulus. These may organize into distinctive patterns which are currently under active study. In subtropics, they cover the edges of the horse latitude climatological highs, and reduce the amount of solar energy absorbed in the ocean. When these drift over land the summer heat or winter cold is reduced. 'Dull weather' is a common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunderstorms
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are sometimes called thundershowers. Thunderstorms occur in a type of cloud known as a cumulonimbus. They are usually accompanied by strong winds and often produce heavy rain and sometimes snow, sleet, or hail, but some thunderstorms produce little precipitation or no precipitation at all. Thunderstorms may line up in a series or become a rainband, known as a squall line. Strong or severe thunderstorms include some of the most dangerous weather phenomena, including large hail, strong winds, and tornadoes. Some of the most persistent severe thunderstorms, known as supercells, rotate as do cyclones. While most thunderstorms move with the mean wind flow through the layer of the troposphere that they occupy, vertical wind shear sometimes causes a dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virga
In meteorology, a virga, also called a dry storm, is an observable :wikt:fallstreak, streak or Precipitation shaft, shaft of precipitation (meteorology), precipitation falling from a cloud that Evaporation, evaporates or Sublimation (phase transition), sublimates before reaching the ground. A shaft of precipitation that does not evaporate before reaching the ground is a precipitation shaft. At high altitudes the precipitation (meteorology), precipitation falls mainly as ice crystals before melting and finally evaporating; this is often due to compressional heating, because the atmospheric pressure, air pressure increases closer to the ground. It is very common in desert, deserts and temperate climates. In North America, it is commonly seen in the Western United States and the Canadian Prairies. It is also very common in the Middle East, Australia, and North Africa. Virgae can cause varying weather effects, because as rain is changed from liquid to vapor form, it removes sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weather Front
A weather front is a boundary separating air masses for which several characteristics differ, such as air density, wind, temperature, and humidity. Disturbed and unstable weather due to these differences often arises along the boundary. For instance, cold fronts can bring bands of thunderstorms and cumulonimbus precipitation or be preceded by squall lines, while warm fronts are usually preceded by stratiform precipitation and fog. In summer, subtler humidity gradients are known as dry lines can trigger severe weather. Some fronts produce no precipitation and little cloudiness, although there is invariably always a wind shift. Cold fronts generally move from west to east, whereas warm fronts move poleward, although any direction is possible. Occluded fronts are a hybrid merge of the two, and stationary fronts are stalled in their motion. Cold fronts and cold occlusions move faster than warm fronts and warm occlusions because the dense air behind them can lift as well as push ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |