|
Alternating Bit Protocol
Alternating bit protocol (ABP) is a simple network protocol operating at the data link layer ( OSI layer 2) that retransmits lost or corrupted messages using FIFO semantics. It can be seen as a special case of a sliding window protocol where a simple timer restricts the order of messages to ensure receivers send messages in turn while using a window of 1 bit. Design Messages are sent from transmitter A to receiver B. Assume that the channel from A to B is initialized and that there are no messages in transit. Each message from A to B contains a data part and a one-bit sequence number, i.e., a value that is 0 or 1. B has two acknowledge codes that it can send to A: ACK0 and ACK1. When A sends a message, it resends it continuously, with the same sequence number, until it receives an acknowledgment from B that contains the same sequence number. When that happens, A complements (flips) the sequence number and starts transmitting the next message. When B receives a message ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Network Protocol
A communication protocol is a system of rules that allows two or more entities of a communications system to transmit information via any variation of a physical quantity. The protocol defines the rules, syntax, semantics, and synchronization of communication and possible error recovery methods. Protocols may be implemented by hardware, software, or a combination of both. Communicating systems use well-defined formats for exchanging various messages. Each message has an exact meaning intended to elicit a response from a range of possible responses predetermined for that particular situation. The specified behavior is typically independent of how it is to be implemented. Communication protocols have to be agreed upon by the parties involved. To reach an agreement, a protocol may be developed into a technical standard. A programming language describes the same for computations, so there is a close analogy between protocols and programming languages: ''protocols are to communicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
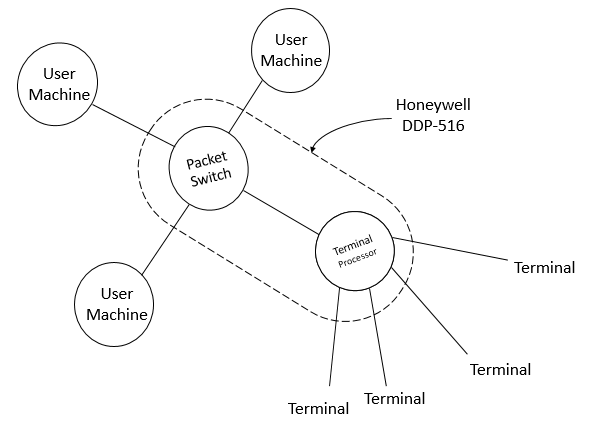
Donald Davies
Donald Watts Davies, (7 June 1924 – 28 May 2000) was a Welsh computer scientist and Internet pioneer who was employed at the UK National Physical Laboratory (NPL). During 1965-67 he invented modern data communications, including packet switching, high-speed routers, layered communication protocols, hierarchical computer networks and the essence of the end-to-end principle, concepts that are used today in computer networks worldwide. He envisioned, in 1966, that there would be a "single network" for data and telephone communications. Davies proposed and studied a commercial national data network in the United Kingdom and designed and built the first implementation of packet switching in the local-area NPL network in 1966-69 to demonstrate the technology. Many of the wide-area packet-switched networks built in the late 1960s and 1970s were similar "in nearly all respects" to his original 1965 design. Davies' work influenced the ARPANET in the United States and the CYCLAD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Negative-acknowledge Character
In data networking, telecommunications, and computer buses, an acknowledgement (ACK) is a signal that is passed between communicating processes, computers, or devices to signify acknowledgment, or receipt of message, as part of a communications protocol. Correspondingly a negative-acknowledgement (NAK or NACK) is a signal that is sent to reject a previously received message or to indicate some kind of error. Acknowledgments and negative acknowledgments inform a sender of the receiver's state so that it can adjust its own state accordingly. Acknowledgment signal types The ASCII code point for ACK is 0x06 (binary 0000 0110). By convention a receiving device sends an ACK to indicate it successfully received a message. ASCII also provides a NAK code point (0x15, binary 0001 0101) which can be used to indicate the receiving device cannot, or will not, comply with the message. Unicode provides visible symbols for these ASCII characters, U+2406 (␆) and U+2415 (␕). ACK and NAK ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Information Theory
Information theory is the mathematical study of the quantification (science), quantification, Data storage, storage, and telecommunications, communication of information. The field was established and formalized by Claude Shannon in the 1940s, though early contributions were made in the 1920s through the works of Harry Nyquist and Ralph Hartley. It is at the intersection of electronic engineering, mathematics, statistics, computer science, Neuroscience, neurobiology, physics, and electrical engineering. A key measure in information theory is information entropy, entropy. Entropy quantifies the amount of uncertainty involved in the value of a random variable or the outcome of a random process. For example, identifying the outcome of a Fair coin, fair coin flip (which has two equally likely outcomes) provides less information (lower entropy, less uncertainty) than identifying the outcome from a roll of a dice, die (which has six equally likely outcomes). Some other important measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Acknowledge Character
In data networking, telecommunications, and computer buses, an acknowledgement (ACK) is a signal that is passed between communicating processes, computers, or devices to signify acknowledgment, or receipt of message, as part of a communications protocol. Correspondingly a negative-acknowledgement (NAK or NACK) is a signal that is sent to reject a previously received message or to indicate some kind of error. Acknowledgments and negative acknowledgments inform a sender of the receiver's state so that it can adjust its own state accordingly. Acknowledgment signal types The ASCII code point for ACK is 0x06 (binary 0000 0110). By convention a receiving device sends an ACK to indicate it successfully received a message. ASCII also provides a NAK code point (0x15, binary 0001 0101) which can be used to indicate the receiving device cannot, or will not, comply with the message. Unicode provides visible symbols for these ASCII characters, U+2406 (␆) and U+2415 (␕). ACK and NAK ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
European Informatics Network
In telecommunications, packet switching is a method of grouping data into short messages in fixed format, i.e. '' packets,'' that are transmitted over a digital network. Packets consist of a header and a payload. Data in the header is used by networking hardware to direct the packet to its destination, where the payload is extracted and used by an operating system, application software, or higher layer protocols. Packet switching is the primary basis for data communications in computer networks worldwide. During the early 1960s, American engineer Paul Baran developed a concept he called ''distributed adaptive message block switching'', with the goal of providing a fault-tolerant, efficient routing method for telecommunication messages as part of a research program at the RAND Corporation, funded by the United States Department of Defense. His ideas contradicted then-established principles of pre-allocation of network bandwidth, exemplified by the development of telecomm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
ARPANET
The Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET) was the first wide-area packet-switched network with distributed control and one of the first computer networks to implement the TCP/IP protocol suite. Both technologies became the technical foundation of the Internet. The ARPANET was established by the Advanced Research Projects Agency (now DARPA) of the United States Department of Defense. Building on the ideas of J. C. R. Licklider, Robert Taylor (computer scientist), Bob Taylor initiated the ARPANET project in 1966 to enable resource sharing between remote computers. Taylor appointed Lawrence Roberts (scientist), Larry Roberts as program manager. Roberts made the key decisions about the request for proposal to build the network. He incorporated Donald Davies' concepts and designs for packet switching, and sought input from Paul Baran on dynamic routing. In 1969, ARPA awarded the contract to build the Interface Message Processors (IMPs) for the network to Bolt Berane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
NPL Network
The NPL network, or NPL Data Communications Network, was a local area computer network operated by the National Physical Laboratory (United Kingdom), National Physical Laboratory (NPL) in London that pioneered the concept of packet switching. Based on designs conceived by Donald Davies in 1965, development work began in 1966. Construction began in 1968 and elements of the first version of the network, the Mark I, became operational in early 1969 then fully operational in January 1970. The Mark II version operated from 1973 until 1986. The NPL network was the first computer network to implement packet switching and the first to use high-speed links. Its original design, along with the innovations implemented in the ARPANET and the CYCLADES network, laid down the technical foundations of the modern Internet. Origins In 1965, Donald Davies, who was later appointed to head of the NPL Division of Computer Science, proposed a commercial national data network in the United Kingdom b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
National Physical Laboratory (United Kingdom)
The National Physical Laboratory (NPL) is the national measurement standards laboratory of the United Kingdom. It sets and maintains physical standards for British industry. Founded in 1900, the NPL is one of the oldest metrology institutes in the world. Research and development work at the laboratory has contributed to the advancement of many disciplines of science, including the development of early computers in the late 1940s and 1950s, construction of the first accurate atomic clock in 1955, and the invention and first implementation of packet switching in the 1960s, which is today one of the fundamental technologies of the Internet. The former heads of NPL include many individuals who were pillars of the British scientific establishment. NPL is based at Bushy Park in Teddington, southwest London. It is operated by NPL Management Ltd, a company owned by the Department for Science, Innovation and Technology, and is one of the most extensive government laboratories in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Philips
Koninklijke Philips N.V. (), simply branded Philips, is a Dutch multinational health technology company that was founded in Eindhoven in 1891. Since 1997, its world headquarters have been situated in Amsterdam, though the Benelux headquarters is still in Eindhoven. The company gained its royal honorary title in 1998. Philips was founded by Gerard Philips and his father Frederik, with their first products being light bulbs. Through the 20th century, it grew into one of the world's largest electronics conglomerates, with global market dominance in products ranging from kitchen appliances and electric shavers to light bulbs, televisions, cassettes, and compact discs (both of which were invented by Philips). At one point, it played a dominant role in the entertainment industry (through PolyGram). However, intense competition from primarily East Asian competitors throughout the 1990s and 2000s led to a period of downsizing, including the divestment of its lighting and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Data Link Layer
The data link layer, or layer 2, is the second layer of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. This layer is the protocol layer that transfers data between nodes on a network segment across the physical layer. The data link layer provides the functional and procedural means to transfer data between network entities and may also provide the means to detect and possibly correct errors that can occur in the physical layer. The data link layer is concerned with local delivery of frames between nodes on the same level of the network. Data-link frames, as these protocol data units are called, do not cross the boundaries of a local area network. Inter-network routing and global addressing are higher-layer functions, allowing data-link protocols to focus on local delivery, addressing, and media arbitration. In this way, the data link layer is analogous to a neighborhood traffic cop; it endeavors to arbitrate between parties contending for access to a medium, without c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Negation
In logic, negation, also called the logical not or logical complement, is an operation (mathematics), operation that takes a Proposition (mathematics), proposition P to another proposition "not P", written \neg P, \mathord P, P^\prime or \overline. It is interpreted intuitively as being true when P is false, and false when P is true. For example, if P is "Spot runs", then "not P" is "Spot does not run". An operand of a negation is called a ''negand'' or ''negatum''. Negation is a unary operation, unary logical connective. It may furthermore be applied not only to propositions, but also to notion (philosophy), notions, truth values, or interpretation (logic), semantic values more generally. In classical logic, negation is normally identified with the truth function that takes ''truth'' to ''falsity'' (and vice versa). In intuitionistic logic, according to the Brouwer–Heyting–Kolmogorov interpretation, the negation of a proposition P is the proposition whose proofs are the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |