|
Alpha-viniferin
α-Viniferin is a stilbene trimer. It can be isolated from ''Caragana chamlagu'' and from '' Caragana sinica'' and from the stem bark of ''Dryobalanops aromatica''. It is also present in relation to resistance to ''Botrytis cinerea'' and ''Plasmopara viticola'' in ''Vitis vinifera'' and ''Vitis riparia''.Disease resistance of Vitis spp. and the production of the stress metabolites resveratrol, epsilon -viniferin, alpha -viniferin and pterostilbene. Langcake P, Physiological Plant Pathology, 1981, Vol. 18, No. 2, pages 213-226abstract) It has been shown to inhibit acetylcholinesterase Acetylcholinesterase (HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme Enzymes () are proteins that a .... References Resveratrol oligomers Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors {{Aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimer (chemistry)
In chemistry, a trimer (; ) is a molecule or polyatomic anion formed by combination or association of three molecules or ions of the same substance. In technical jargon, a trimer is a kind of oligomer derived from three identical precursors often in competition with polymerization. Examples Alkyne trimerisation In 1866, Marcellin Berthelot reported the first example of cyclotrimerization, the conversion of acetylene to benzene. This process was commercialized: : Nitrile trimerization Symmetrical 1,3,5-triazines are prepared by trimerization of certain nitriles such as cyanogen chloride or cyanimide. Cyanogen chloride and cyanogen bromide each trimerize at elevated temperatures over a carbon catalyst. The chloride gives cyanuric chloride: : The bromide has an extended shelflife when refrigerated. Like the chloride, it undergoes ab exothermic trimerisation to form cyanuric bromide. This reaction is catalyzed by traces of bromine, metal salts, acids and bases. For this reason ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caragana Chamlagu
''Caragana sinica'' () is a species belonging to the genus ''Caragana''. ''Caragana sinica'' is known to produce the stilbenoid trimers alpha-viniferin, α-viniferin, showing acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity, and miyabenol C, a protein kinase C inhibitorNaturally Occurring Protein Kinase C Inhibitors; II. Isolation of Oligomeric Stilbenes from Caragana sinica. Palaniappan Kulanthaivel, William P. Janzen, Lawrence M. Ballas, Jack B. Jiang, Chang-Qi Hu, James W. Darges, Jan C. Seldin, Divann J. Cofield and Laurel M. Adams, Planta Med, 1995, 61(1), pages 41-44, and two stilbene tetramers kobophenol A, and carasinol B. References Hedysareae Medicinal plants of Asia {{Faboideae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caragana Sinica , and carasinol B. ''Caragana sinica'' () is a species belonging to the genus ''Caragana''. ''Caragana sinica'' is known to produce the stilbenoid trimers α-viniferin, showing acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity, and miyabenol C, a protein kinase C inhibitorNaturally Occurring Protein Kinase C Inhibitors; II. Isolation of Oligomeric Stilbenes from Caragana sinica. Palaniappan Kulanthaivel, William P. Janzen, Lawrence M. Ballas, Jack B. Jiang, Chang-Qi Hu, James W. Darges, Jan C. Seldin, Divann J. Cofield and Laurel M. Adams, Planta Med, 1995, 61(1), pages 41-44, and two stilbene tetramers kobophenol A Kobophenol A is a stilbenoid. It is a tetramer of resveratrol. It can be isolated from '' Caragana chamlagu'', [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dryobalanops Aromatica
''Dryobalanops aromatica'', commonly known as Borneo camphor, camphor tree, Malay camphor, or Sumatran camphor, is a species of critically endangered plant in the family Dipterocarpaceae. The species name ''aromatica'' is derived from Latin (''aromaticus'' meaning spice-like) and refers to the smell of the dammar (resin). This species was one of the main sources of camphor and attracted early Arab traders to Borneo, at that time being worth more than gold, and used for incense and perfumes. It is found in Sumatra, peninsular Malaysia, and Borneo. It is a large emergent tree, up to 65 m or even 75 m tall, found in mixed dipterocarp forests on deep humic yellow sandy soils. It is a heavy hardwood sold under the trade names of Kapur. It is recorded from at least two protected areas ( Lambir and Gunung Mulu National Parks). Bergenin, malaysianol A, laevifonol, ampelopsin E, α-viniferin, ε-viniferin and diptoindonesin A can be isolated from the stem bark of ''D. aromatica''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botrytis Cinerea
''Botrytis cinerea'' is a necrotrophic fungus that affects many plant species, although its most notable hosts may be wine grapes. In viticulture, it is commonly known as "botrytis bunch rot"; in horticulture, it is usually called "grey mould" or "gray mold". The fungus gives rise to two different kinds of infections on grapes. The first, grey rot, is the result of consistently wet or humid conditions, and typically results in the loss of the affected bunches. The second, noble rot, occurs when drier conditions follow wetter, and can result in distinctive sweet dessert wines, such as Sauternes (wine), Sauternes or the Aszú of Tokaji/Grasă de Cotnari. The species name ''Botrytis cinerea'' is derived from the Latin for "grapes like ashes"; although poetic, the "grapes" refers to the bunching of the fungal spores on their Conidium, conidiophores, and "ashes" just refers to the greyish colour of the spores ''en masse''. The fungus is usually referred to by its anamorph (asexual form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmopara Viticola
''Plasmopara viticola'', the causal agent of grapevine downy mildew, is a heterothallic oomycete that overwinters as oospores in leaf litter and soil. In the spring, oospores germinate to produce macrosporangia, which under wet condition release zoospores. Zoospores are splashed by rain into the canopy, where they swim to and infect through stomata. After 7–10 days, yellow lesions appear on foliage. During favorable weather, the lesions sporulate and new secondary infections occur. Description ''Plasmopara viticola'', also known as grape downy mildew, is considered to be the most devastating disease of grapevines in climates with relatively warm and humid summers. It was first observed in 1834 by Schweinitz on ''Vitis aestivalis'' in the southeastern United States. Shortly after this first observation, the pathogen was introduced to European countries where it played a devastating role in the yield and production of their grapes, and consequently their wine. France was among th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitis Vinifera
''Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, is a species of flowering plant, native to the Mediterranean region, Central Europe, and southwestern Asia, from Morocco and Portugal north to southern Germany and east to northern Iran. There are currently between 5,000 and 10,000 varieties of ''Vitis vinifera'' grapes though only a few are of commercial significance for wine and table grape production. The wild grape is often classified as ''Vitis vinifera'' ''sylvestris'' (in some classifications considered ''Vitis sylvestris''), with ''Vitis vinifera'' ''vinifera'' restricted to cultivated forms. Domesticated vines have hermaphrodite flowers, but ''sylvestris'' is dioecious (male and female flowers on separate plants) and pollination is required for fruit to develop. Grapes can be eaten fresh or dried to produce raisins, sultanas, and currants. Grape leaves are used in the cuisine of many cultures. The fresh grapes can also be processed into juice that is fermented to make wine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitis Riparia
''Vitis riparia'' Michx, with common names riverbank grape or frost grape, is a vine indigenous to North America. As a climbing or trailing vine, it is widely distributed across central and eastern Canada and the central and northeastern parts of the United States, from Quebec to Texas, and eastern Montana to Nova Scotia. There are reports of isolated populations in the northwestern USA, but these are probably naturalized. It is long-lived and capable of reaching into the upper canopy of the tallest trees. It produces dark fruit that are appealing to both birds and people, and has been used extensively in commercial viticulture as grafted rootstock and in hybrid grape breeding programs. ''Riverbank grape'' is a translation of the scientific name ''Vitis riparia''; means "of riverbanks" in Latin, deriving from "riverbank". Description Mature vines have loose, fissured bark, and may attain several inches in diameter. Leaves are alternate, often with opposite tendrils or infl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholinesterase
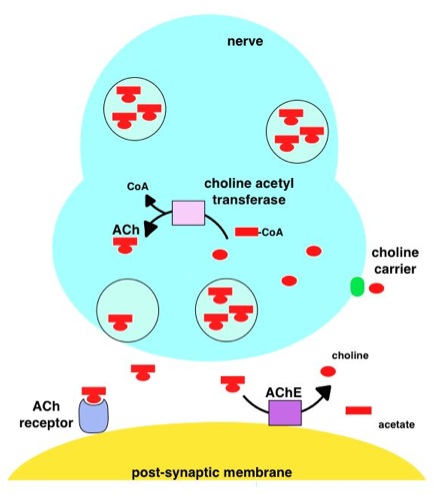
Acetylcholinesterase (HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ... that catalysis, catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters: : acetylcholine + H2O = choline + acetate It is found at mainly neuromuscular junctions and in chemical synapses of the cholinergic type, where its activity serves to terminate neurotransmission, synaptic transmission. It belongs to the carboxylesterase family of enzymes. It is the primary target of inhibition by organophosphorus compounds such as nerve agents and pesticides. Enzyme structure and mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resveratrol Oligomers
Resveratrol (3,5,4′-trihydroxy-''trans''-stilbene) is a stilbenoid, a type of natural phenol, and a phytoalexin produced by several plants in response to injury or when the plant is under attack by pathogens, such as bacteria or fungi. Sources of resveratrol in food include the skin of grapes, blueberries, raspberries, mulberries, and peanuts. Although commonly used as a dietary supplement and studied in laboratory models of human diseases, there is no high-quality evidence that resveratrol improves lifespan or has a substantial effect on any human disease. Research Resveratrol has been studied for its potential therapeutic use, with little evidence of anti-disease effects or health benefits in humans. Cardiovascular disease There is no evidence of benefit from resveratrol in people who already have heart disease. A 2018 meta-analysis found no effect on systolic or diastolic blood pressure; a sub-analysis revealed a 2 mmHg decrease in systolic pressure only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)