|
Adermatoglyphia
Adermatoglyphia is an extremely rare genetic disorder that prevents the development of fingerprints. Five extended families worldwide are known to be affected by this condition. The disorder was informally nicknamed "immigration delay disease" by Professor Peter Itin after his first patient had trouble traveling to the U.S. without any fingerprints for identification. __TOC__ Case study In 2007 an isolated finding was published regarding the description of a person from Switzerland who lacked fingerprints. The phenotype was mapped to chromosome 4q22. In the splice-site of a 3' exon of the gene for SMARCAD1-helicase, a point mutation was detected. It results in a shortened form of the skin-specific protein. The heterozygous expression of the mutation In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fingerprint
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfaces such as glass or metal. Deliberate impressions of entire fingerprints can be obtained by ink or other substances transferred from the peaks of friction ridges on the skin to a smooth surface such as paper. Fingerprint records normally contain impressions from the pad on the last joint of fingers and thumbs, though fingerprint cards also typically record portions of lower joint areas of the fingers. Human fingerprints are detailed, nearly unique, difficult to alter, and durable over the life of an individual, making them suitable as long-term markers of human identity. They may be employed by police or other authorities to identify individuals who wish to conceal their identity, or to identify people who are incapacitated or deceased and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMARCAD1
SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A containing DEAD/H box 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SMARCAD1'' gene. Proper expression of SMARCAD1 may be important to fingerprint development, and the disruption of its expression is believed to cause adermatoglyphia Adermatoglyphia is an extremely rare genetic disorder that prevents the development of fingerprints. Five extended families worldwide are known to be affected by this condition. The disorder was informally nicknamed "immigration delay disease" by ..., the absence of fingerprints. References Further reading * * * * * * * {{gene-4-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development (a ''de novo'' mutation), or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene (autosomal recessive inheritance) or from a parent with the disorder (autosomal dominant inheritance). When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA (due to their size). There are well over 6,000 known genet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zürich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2020 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federal assembly-independent directorial republic with elements of a direct democracy , leader_title1 = Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Walter Thurnherr , legislature = Federal Assembly , upper_house = Council of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological properties, its behavior, and the products of behavior. An organism's phenotype results from two basic factors: the expression of an organism's genetic code, or its genotype, and the influence of environmental factors. Both factors may interact, further affecting phenotype. When two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species, the species is called polymorphic. A well-documented example of polymorphism is Labrador Retriever coloring; while the coat color depends on many genes, it is clearly seen in the environment as yellow, black, and brown. Richard Dawkins in 1978 and then again in his 1982 book '' The Extended Phenotype'' suggested that one can regard bird nests and other built structures such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 4
Chromosome 4 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 4 spans more than 186 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 6 and 6.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. Genomics The chromosome is ~191 megabases in length. In a 2012 paper, 775 protein-encoding genes were identified on this chromosome.Chen LC, Liu MY, Hsiao YC, Choong WK, Wu HY, Hsu WL, Liao PC, Sung TY, Tsai SF, Yu JS, Chen YJ (2012) Decoding the disease-associated proteins encoded in the human chromosome 4. J Proteome Res 211 (27.9%) of these coding sequences did not have any experimental evidence at the protein level, in 2012. 271 appear to be membrane proteins. 54 have been classified as cancer-associated proteins. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 4. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicase
Helicases are a class of enzymes thought to be vital to all organisms. Their main function is to unpack an organism's genetic material. Helicases are motor proteins that move directionally along a nucleic acid phosphodiester backbone, separating two hybridized nucleic acid strands (hence '' helic- + -ase''), using energy from ATP hydrolysis. There are many helicases, representing the great variety of processes in which strand separation must be catalyzed. Approximately 1% of eukaryotic genes code for helicases. The human genome codes for 95 non-redundant helicases: 64 RNA helicases and 31 DNA helicases. Many cellular processes, such as DNA replication, transcription, translation, recombination, DNA repair, and ribosome biogenesis involve the separation of nucleic acid strands that necessitates the use of helicases. Some specialized helicases are also involved in sensing of viral nucleic acids during infection and fulfill a immunological function. Function Helicases are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
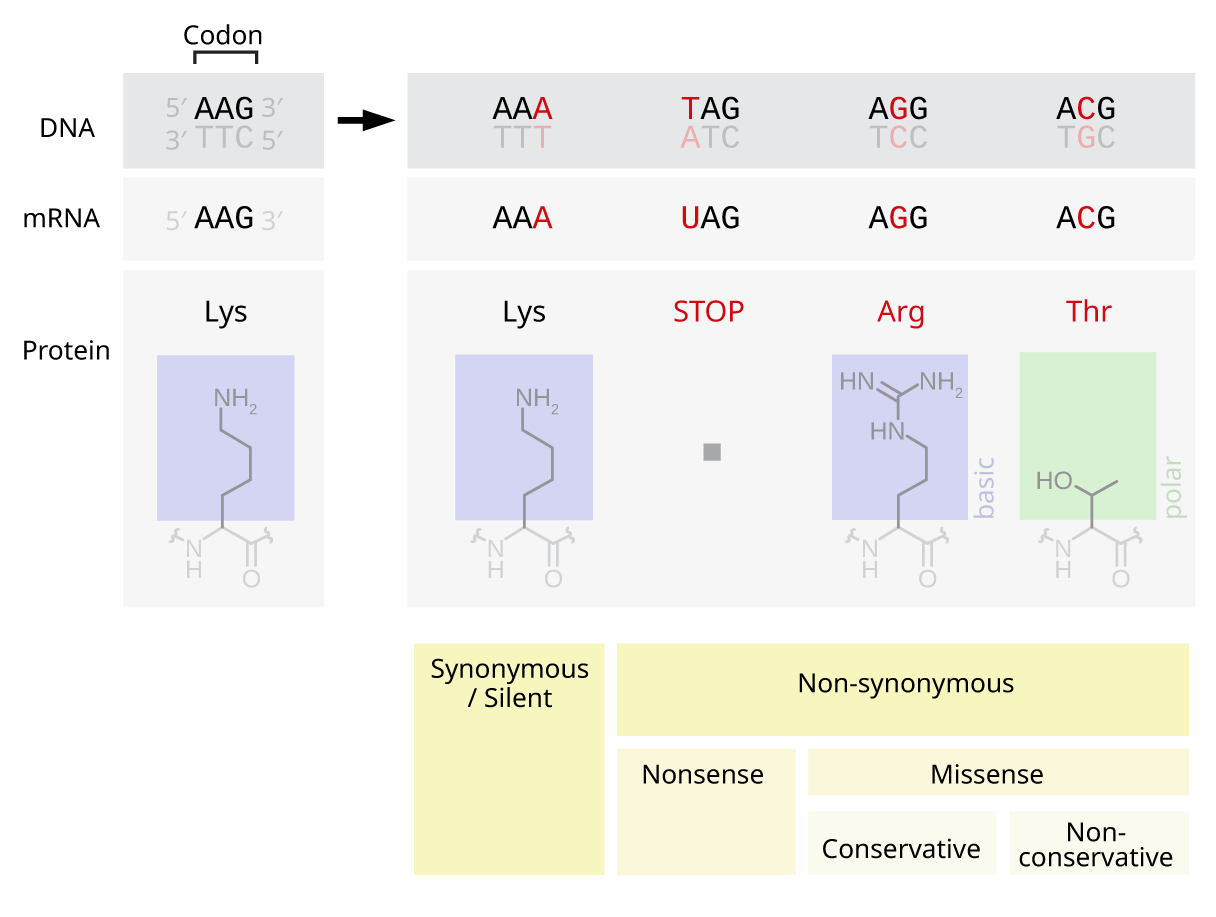
Point Mutation
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences that are moderately predictable based upon the specifics of the mutation. These consequences can range from no effect (e.g. synonymous mutations) to deleterious effects (e.g. frameshift mutations), with regard to protein production, composition, and function. Causes Point mutations usually take place during DNA replication. DNA replication occurs when one double-stranded DNA molecule creates two single strands of DNA, each of which is a template for the creation of the complementary strand. A single point mutation can change the whole DNA sequence. Changing one purine or pyrimidine may change the amino acid that the nucleotides code for. Point mutations may arise from spontaneous mutations that occur during DNA replication. The rate o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism. Most eukaryotes have two matching sets of chromosomes; that is, they are diploid. Diploid organisms have the same loci on each of their two sets of homologous chromosomes except that the sequences at these loci may differ between the two chromosomes in a matching pair and that a few chromosomes may be mismatched as part of a chromosomal sex-determination system. If both alleles of a diploid organism are the same, the organism is homozygous at that locus. If they are different, the organism is heterozygous at that locus. If one allele is missing, it is hemizygous, and, if both alleles are missing, it is nullizygous. The DNA sequence of a gene often varies from one individual to another. These gene variants are called alleles. While so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of DNA repair#DNA damage, damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (DNA repair#Translesion synthesis, translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from Insertion (genetics), insertion or Deletion (genetics), deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes (autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |