|
Auctioneer
An auction is usually a process of buying and selling goods or services by offering them up for bids, taking bids, and then selling the item to the highest bidder or buying the item from the lowest bidder. Some exceptions to this definition exist and are described in the section about different types. The branch of economic theory dealing with auction types and participants' behavior in auctions is called auction theory. The open ascending price auction is arguably the most common form of auction and has been used throughout history. Participants bid openly against one another, with each subsequent bid being higher than the previous bid. An auctioneer may announce prices, while bidders submit bids vocally or electronically. Auctions are applied for trade in diverse contexts. These contexts include antiques, paintings, rare collectibles, expensive wines, commodities, livestock, radio spectrum, used cars, real estate, online advertising, vacation packages, emission t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bidding
Bidding is an offer (often competitive) to set a price tag by an individual or business for a product or service ''or'' a demand that something be done. Bidding is used to determine the cost or value of something. Bidding can be performed by a person under influence of a product or service based on the context of the situation. In the context of auctions, stock exchange, or real estate, the price offer a business or individual is willing to pay is called a bid. In the context of corporate or government procurement initiatives, in Business and Law school students actively bid for high demand elective courses that have a maximum seat capacity though a course bidding process using pre allocated bidding points or e-bidding currency on course bidding systems. The price offer a business or individual is willing to sell is also called a bid. The term "bidding" is also used when placing a bet in card games. Bidding is used by various economic niches for determining the demand and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrum Auction
A spectrum auction is a process whereby a government uses an auction system to sell the rights to transmit signals over specific bands of the electromagnetic spectrum and to assign scarce spectrum resources. Depending on the specific auction format used, a spectrum auction can last from a single day to several months from the opening bid to the final winning bid. With a well-designed auction, resources are allocated efficiently to the parties that value them the most, the government securing revenue in the process. Spectrum auctions are a step toward market-based spectrum management and privatization of public airwaves, and are a way for governments to allocate scarce resources. Alternatives to auctions include administrative licensing, such as the comparative hearings conducted historically (sometimes referred to as "beauty contests"), or lotteries. Innovation In the past decade, telecommunications has turned into a highly competitive industry where companies are competing to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auction Theory
Auction theory is an applied branch of economics which deals with how bidders act in auction markets and researches how the features of auction markets incentivise predictable outcomes. Auction theory is a tool used to inform the design of real-world auctions. Sellers use auction theory to raise higher revenues while allowing buyers to procure at a lower cost. The conference of the price between the buyer and seller is an economic equilibrium. Auction theorists design rules for auctions to address issues which can lead to market failure. The design of these rulesets encourages optimal bidding strategies among a variety of informational settings. The 2020 Nobel Prize for Economics was awarded to Paul R. Milgrom and Robert B. Wilson “for improvements to auction theory and inventions of new auction formats.” Introduction Auctions facilitate transactions by enforcing a specific set of rules regarding the resource allocations of a group of bidders. Theorists consider auctions t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wine Auction
A wine auction may also auction other alcoholic beverages than wine. There are two basic types of wine auctions: ''first hand wine auctions'', where wineries sell their own wines, and ''second hand wine auctions'', arranged by auction houses or other auctioneers to make it possible for any owners of wine to trade it. In most cases, the wines traded at wine auctions are collectible "fine wines" typically suitable for extended cellaring. Second-hand buyers may be looking for mature wines which are no longer available first-hand. In all types of auction the auctioneer charges commission to both buyers and sellers. First hand auctions First hand wine auctions are usually arranged by wine industry organisations, and fill promotional or charitable purposes, or are used to gauge the market. The wines sold at such auctions are usually special lot wines, or back vintages stored by the producers. An example of such auctions is the annual wine auction held by Hospices de Beaune in Burgundy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auto Auction
Auto auctions are a method of selling vehicles based on an auction system. Auto auctions can be found in most countries and are usually exclusive to licensed automobile dealers. In a few countries, such as Japan, auto auctions are well known and used by most residents. Country specific Japan Auto auctions are the most popular method to sell used vehicles in Japan. Most customers are Japanese seeking a cheap vehicle to start with or replace their older vehicle. There are many also trying to sell their vehicles. Individuals though cannot directly use auto auctions, but must go through those holding auction membership. In Japanese law, only dealerships may become members to auto auctions. The system allows people to have access to information, but keeps the auctions orderly with only professionals actually able to bid. A small percentage of the dealers that are members of Japanese auto auctions are also used vehicle exporters that most often use the auto auctions as their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P214
P, or p, is the sixteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''pee'' (pronounced ), plural ''pees''. History The Semitic Pê (mouth), as well as the Greek Π or π ( Pi), and the Etruscan and Latin letters that developed from the former alphabet, all symbolized , a voiceless bilabial plosive. Use in writing systems In English orthography and most other European languages, represents the sound . A common digraph in English is , which represents the sound , and can be used to transliterate ''phi'' in loanwords from Greek. In German, the digraph is common, representing a labial affricate . Most English words beginning with are of foreign origin, primarily French, Latin and Greek; these languages preserve Proto-Indo-European initial *p. Native English cognates of such words often start with , since English is a Germanic language and thus has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
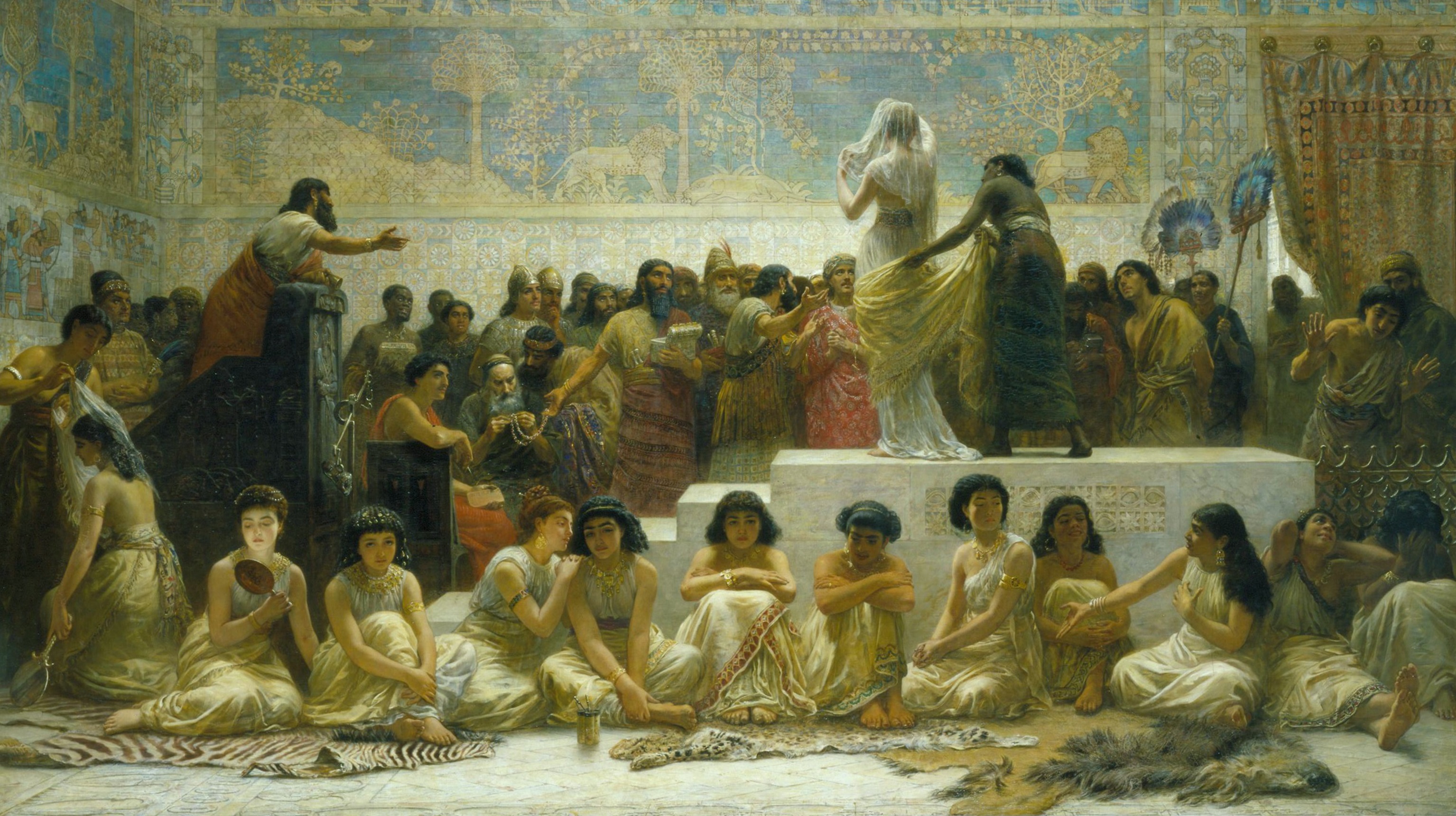
Babylonian Marriage Market
Babylonian may refer to: * Babylon, a Semitic Akkadian city/state of ancient Mesopotamia founded in 1894 BC * Babylonia, an ancient Akkadian-speaking Semitic nation-state and cultural region based in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq) * Babylonian language, a dialect of the Akkadian language See also * Babylonia (other) * Babylonian astronomy * Babylonian calendar * Babylonian captivity or Babylonian exile, a period in Jewish history * Babylonian Jews, Jews of the area of modern-day Iraq and north Syria * Babylonian literature * Babylonian mathematics, also known as Assyro-Babylonian mathematics * Babylonian religion * First Babylonian dynasty, the first dynasty of Babylonia * Neo-Babylonian Empire The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the List of kings of Babylon, King of B ... (626–539 BC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria ( Italy). He is known for having written the ''Histories'' – a detailed account of the Greco-Persian Wars. Herodotus was the first writer to perform systematic investigation of historical events. He is referred to as " The Father of History", a title conferred on him by the ancient Roman orator Cicero. The ''Histories'' primarily cover the lives of prominent kings and famous battles such as Marathon, Thermopylae, Artemisium, Salamis, Plataea, and Mycale. His work deviates from the main topics to provide a cultural, ethnographical, geographical, and historiographical background that forms an essential part of the narrative and provides readers with a wellspring of additional information. Herodotus has been criticized for his inclusion of "legends and fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
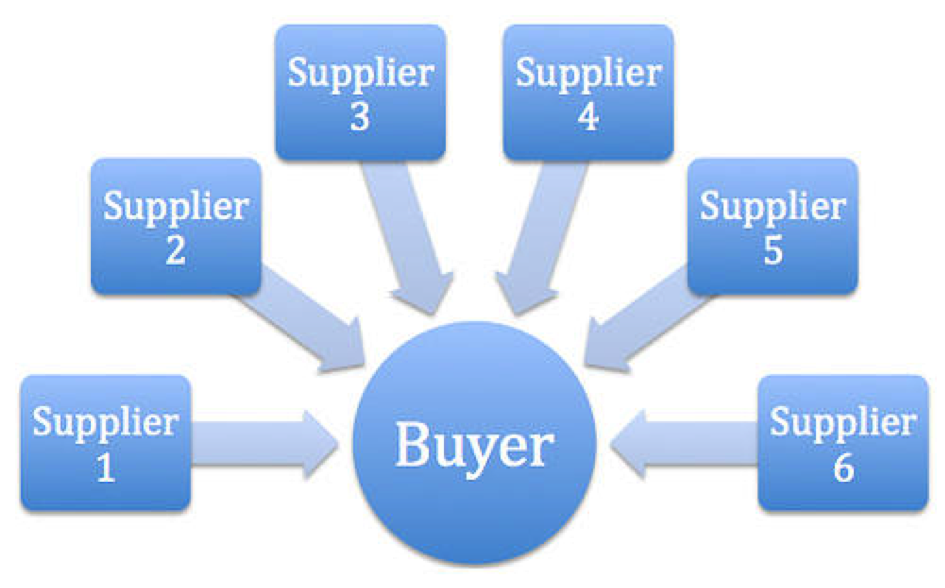
Reverse Auction
A reverse auction (also known as buyer-determined auction or procurement auction) is a type of auction in which the traditional roles of buyer and seller are reversed. Thus, there is one buyer and many potential sellers. In an ordinary auction also known as a forward auction, buyers compete to obtain goods or services by offering increasingly higher prices. In contrast, in a reverse auction, the sellers compete to obtain business from the buyer and prices will typically decrease as the sellers underbid each other. A reverse auction is similar to a unique bid auction because the basic principle remains the same; however, a unique bid auction follows the traditional auction format more closely as each bid is kept confidential and one clear winner is defined after the auction finishes. For business auctions, the term refers to a specific type of auction process (also called e-auction, sourcing event, e-sourcing or eRA, eRFP, e-RFO, e-procurement, B2B Auction). Open procurement proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forward Auction
Forward is a relative direction, the opposite of backward. Forward may also refer to: People *Forward (surname) Sports * Forward (association football) * Forward (basketball), including: ** Point forward ** Power forward (basketball) ** Small forward * Forward (ice hockey) ** Power forward (ice hockey) * In rugby football: ** Forwards (rugby league), in rugby league football ** Forwards (rugby union), in rugby union football * Forward Sports, a Pakistan sportswear brand * BK Forward, a Swedish club for association football and bandy Politics * Avante (political party) (Portuguese for ''forward''), a political party in Brazil * Forward (Belgium), a political party in Belgium * Forward (Denmark), a political party in Denmark * Forward (Greenland), a political party in Greenland * Forward Party (United States), a centrist American political party * Kadima (Hebrew for ''forward''), a political party in Israel * La République En Marche! (sometimes translated as ''Forw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacation
A vacation (American English) or holiday (British English) is either a leave of absence from a regular job or an instance of leisure travel away from home. People often take a vacation during specific holiday observances or for specific festivals or celebrations. Vacations are often spent with friends or family. Vacations may include a specific trip or journey, usually for the purpose of recreation or tourism. A person may take a longer break from work, such as a sabbatical, gap year, or career break. The concept of taking a vacation is a recent invention, and has developed through the last two centuries. Historically, the idea of travel for recreation was a luxury that only wealthy people could afford (see Grand Tour). In the Puritan culture of early America, taking a break from work for reasons other than weekly observance of the Sabbath was frowned upon. However, the modern concept of vacation was led by a later religious movement encouraging spiritual retreat and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |