|
Atom Optics
Atom optics (or atomic optics) "refers to techniques to manipulate the trajectories and exploit the wave properties of neutral atoms". Typical experiments employ beams of cold, slowly moving neutral atoms, as a special case of a particle beam. Like an optical beam, the atomic beam may exhibit diffraction and interference, and can be focused with a Fresnel zone plate or a concave atomic mirror. For comprehensive overviews of atom optics, see the 1994 review by Adams, Sigel, and Mlynek or the 2009 review by Cronin, Jörg, and Pritchard. More bibliography about Atom Optics can be found in the 2017 Resource Letter in the American Journal of Physics. For quantum atom optics see the 2018 review by Pezzè et al. History Interference of atom matter waves was first observed by Esterman and Stern in 1930, when a Na beam was diffracted off a surface of NaCl. The short de Broglie wavelength of atoms prevented progress for many years until two technological breakthroughs revived interes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matter Wave
Matter waves are a central part of the theory of quantum mechanics, being half of wave–particle duality. At all scales where measurements have been practical, matter exhibits wave-like behavior. For example, a beam of electrons can be diffracted just like a beam of light or a water wave. The concept that matter behaves like a wave was proposed by French physicist Louis de Broglie () in 1924, and so matter waves are also known as de Broglie waves. The ''de Broglie wavelength'' is the wavelength, , associated with a particle with momentum through the Planck constant, : \lambda = \frac. Wave-like behavior of matter has been experimentally demonstrated, first for electrons in 1927 and for other elementary particles, neutral atoms and molecules in the years since. Matter waves have more complex velocity relations than solid objects and they also differ from electromagnetic waves (light). Collective matter waves are used to model phenomena in solid state physics; standing matte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Cooling
Laser cooling includes several techniques where atoms, molecules, and small mechanical systems are cooled with laser light. The directed energy of lasers is often associated with heating materials, e.g. laser cutting, so it can be counterintuitive that laser cooling often results in sample temperatures approaching absolute zero. It is a routinely used in atomic physics experiments where the laser-cooled atoms are manipulated and measured, or in technologies, such as atom-based quantum computing architectures. Laser cooling reduces the random motion of particles or the random vibrations of mechanical systems. For atoms and molecules this reduces Doppler shifts in spectroscopy, allowing for high precision measurements and instruments such as optical clocks. The reduction in thermal energy also allows for efficient loading of atoms and molecules into traps where they can be used in experiments or atom-based devices for longer periods of time. Laser cooling relies on the momen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ridged Mirror
In atomic physics, a ridged mirror (or ridged atomic mirror, or Fresnel diffraction mirror) is a kind of atomic mirror, designed for the specular reflection of neutral particles (atoms) coming at a grazing incidence angle. In order to reduce the mean attraction of particles to the surface and increase the reflectivity, this surface has narrow ridges. Reflectivity of ridged atomic mirrors Various estimates for the efficiency of quantum reflection of waves from ridged mirror were discussed in the literature. All the estimates explicitly use the de Broglie theory about wave properties of reflected atoms. Scaling of the van der Waals force The ridges enhance the quantum reflection from the surface, reducing the effective constant ~C~ of the van der Waals attraction of atoms to the surface. Such interpretation leads to the estimate of the reflectivity : \displaystyle r \approx r_0\!\left( \frac \ell L C,\!~K\sin(\theta)\right), where ~\ell~ is width of the ridges, ~L~ is distan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optics And Photonics News
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible light, visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Light is a type of electromagnetic radiation, and other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the Classical electromagnetism, classical electromagnetic description of light, however complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of Ray (optics), rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evanescent Field
In electromagnetics, an evanescent field, or evanescent wave, is an oscillating electric and/or magnetic field that does not propagate as an electromagnetic wave but whose energy is spatially concentrated in the vicinity of the source (oscillating charges and currents). Even when there is a propagating electromagnetic wave produced (e.g., by a transmitting Antenna (radio), antenna), one can still identify as an evanescent field the component of the electric or magnetic field that cannot be attributed to the propagating wave observed at a distance of many wavelengths (such as the far field of a transmitting antenna). A hallmark of an evanescent field is that there is no net energy flow in that region. Since the net flow of electromagnetic energy is given by the average Poynting vector, this means that the Poynting vector in these regions, as averaged over a complete oscillation cycle, is zero. Use of the term In many cases one cannot simply say that a field is or is not "evane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Tweezers
Optical tweezers (originally called single-beam gradient force trap) are scientific instruments that use a highly focused laser beam to hold and move microscopic and sub-microscopic objects like atoms, nanoparticles and droplets, in a manner similar to tweezers. If the object is held in air or vacuum without additional support, it can be called optical levitation. The laser light provides an attractive or repulsive force (typically on the order of piconewtons), depending on the relative refractive index between particle and surrounding medium. Levitation is possible if the force of the light counters the force of gravity. The trapped particles are usually micron-sized, or even smaller. Dielectric and absorbing particles can be trapped, too. Optical tweezers are used in biology and medicine (for example to grab and hold a single bacterium, a cell like a sperm cell or a blood cell, or a molecule like DNA), nanoengineering and nanochemistry (to study and build materials from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magneto-optical Trap
In atomic, molecular, and optical physics, a magneto-optical trap (MOT) is an apparatus which uses laser cooling and a spatially varying magnetic field to create a Magnetic trap (atoms), trap which can produce samples of Ultracold atom, cold neutral atoms. Temperatures achieved in a MOT can be as low as several microkelvins, depending on the atomic species, which is two or three times below the Recoil temperature, photon-recoil limit. However, for atoms with an unresolved hyperfine structure, such as , the temperature achieved in a MOT will be higher than the Doppler cooling limit. A MOT is formed from the intersection of the zero of a weak Quadrupole magnet, quadrupolar magnetic field and six Circular polarization, circularly polarized Laser detuning, red-detuned optical molasses beams. Counterpropagating beams have opposite handed polarization. As atoms travel away from the zero field at the center of the trap, the spatially varying Zeeman effect, Zeeman shift brings an atomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Trap (atoms)
In experimental physics, a magnetic trap is an apparatus which uses a magnetic field gradient to trap neutral particles with magnetic moments. Although such traps have been employed for many purposes in physics research, they are best known as the last stage in cooling atoms to achieve Bose–Einstein condensation. The magnetic trap (as a way of trapping very cold atoms) was first proposed by David E. Pritchard. Operating principle Many atoms have a magnetic moment; their energy shifts in a magnetic field according to the formula :\Delta E = - \vec \cdot \vec. According to the principles of quantum mechanics the magnetic moment of an atom will be quantized; that is, it will take on one of certain discrete values. If the atom is placed in a strong magnetic field, its magnetic moment will be aligned with the field. If a number of atoms are placed in the same field, they will be distributed over the various allowed values of magnetic quantum number for that atom. If a magneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultracold Atom
In condensed matter physics, an ultracold atom is an atom with a temperature near absolute zero. At such temperatures, an atom's quantum-mechanical properties become important, especially through what's known as a "superfluid", such as Superfluid Helium 4. To reach such low temperatures, a combination of several techniques typically has to be used. First, atoms are trapped and pre-cooled via laser cooling in a magneto-optical trap. To reach the lowest possible temperature, further cooling is performed using evaporative cooling in a magnetic or optical trap. Several Nobel prizes in physics are related to the development of the techniques to manipulate quantum properties of individual atoms (e.g. 1989, 1996, 1997, 2001, 2005, 2012, 2018). Experiments with ultracold atoms study a variety of phenomena, including quantum phase transitions, Bose–Einstein condensation (BEC), bosonic superfluidity, quantum magnetism, many-body spin dynamics, Efimov states, Bardeen–Cooper� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
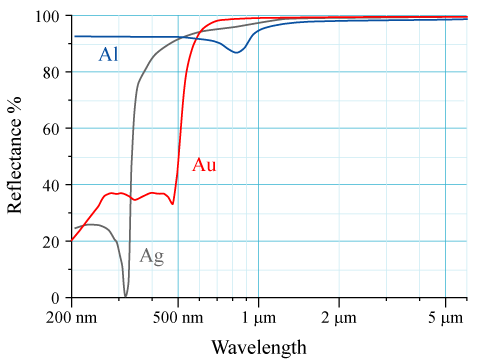
Reflectivity
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in Reflection (physics), reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the response of the electronic structure of the material to the electromagnetic field of light, and is in general a function of the frequency, or wavelength, of the light, its polarization, and the angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence. The dependence of reflectance on the wavelength is called a ''reflectance spectrum'' or ''spectral reflectance curve''. Mathematical definitions Hemispherical reflectance The ''hemispherical reflectance'' of a surface, denoted , is defined as R = \frac, where is the radiant flux ''reflected'' by that surface and is the radiant flux ''received'' by that surface. Spectral hemispherical reflectance The ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in frequency'' and ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in wavelength ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Of Incidence (optics)
The angle of incidence, in geometric optics, is the angle between a ray incident on a surface and the line perpendicular (at 90 degree angle) to the surface at the point of incidence, called the normal. The ray can be formed by any waves, such as optical, acoustic, microwave, and X-ray. In the figure below, the line representing a ray makes an angle θ with the normal (dotted line). The angle of incidence at which light is first totally internally reflected is known as the critical angle. The angle of reflection and angle of refraction are other angles related to beams. In computer graphics and geography, the angle of incidence is also known as the illumination angle of a surface with a light source, such as the Earth's surface and the Sun. It can also be equivalently described as the angle between the tangent plane of the surface and another plane at right angles to the light rays. This means that the illumination angle of a certain point on Earth's surface is 0° if the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numerical Aperture
In optics, the numerical aperture (NA) of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one material to another, provided there is no refractive power at the interface (e.g., a flat interface). The exact definition of the term varies slightly between different areas of optics. Numerical aperture is commonly used in microscopy to describe the acceptance cone of an Objective (optics), objective (and hence its light-gathering ability and Optical resolution, resolution), and in fiber optics, in which it describes the range of angles within which light that is incident on the fiber will be transmitted along it. General optics In most areas of optics, and especially in microscopy, the numerical aperture of an optical system such as an objective lens is defined by \mathrm = n \sin \t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |