|
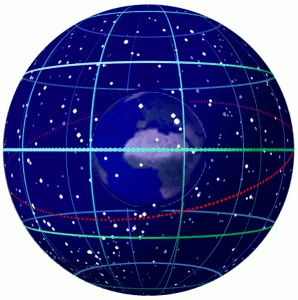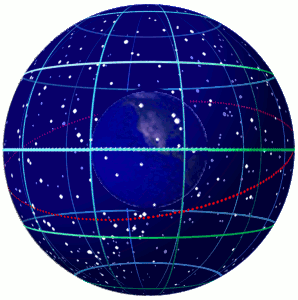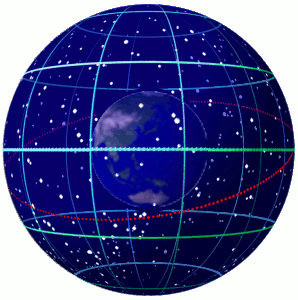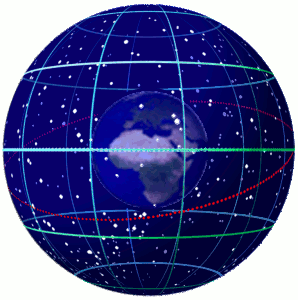
Astronomical Coordinate System
Astronomical coordinate systems are organized arrangements for specifying positions of satellites, planets, stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects relative to physical reference points available to a situated observer (e.g. the true horizon and north cardinal direction to an observer situated on the Earth's surface). Coordinate systems in astronomy can specify an object's position in three-dimensional space or plot merely its direction on a celestial sphere, if the object's distance is unknown or trivial. Spherical coordinates, projected on the celestial sphere, are analogous to the geographic coordinate system used on the surface of Earth. These differ in their choice of fundamental plane, which divides the celestial sphere into two equal hemispheres along a great circle. Rectangular coordinates, in appropriate units, have the same fundamental () plane and primary (-axis) direction, such as a rotation axis. Each coordinate system is named after its choice of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecliptic Equator Galactic Anim
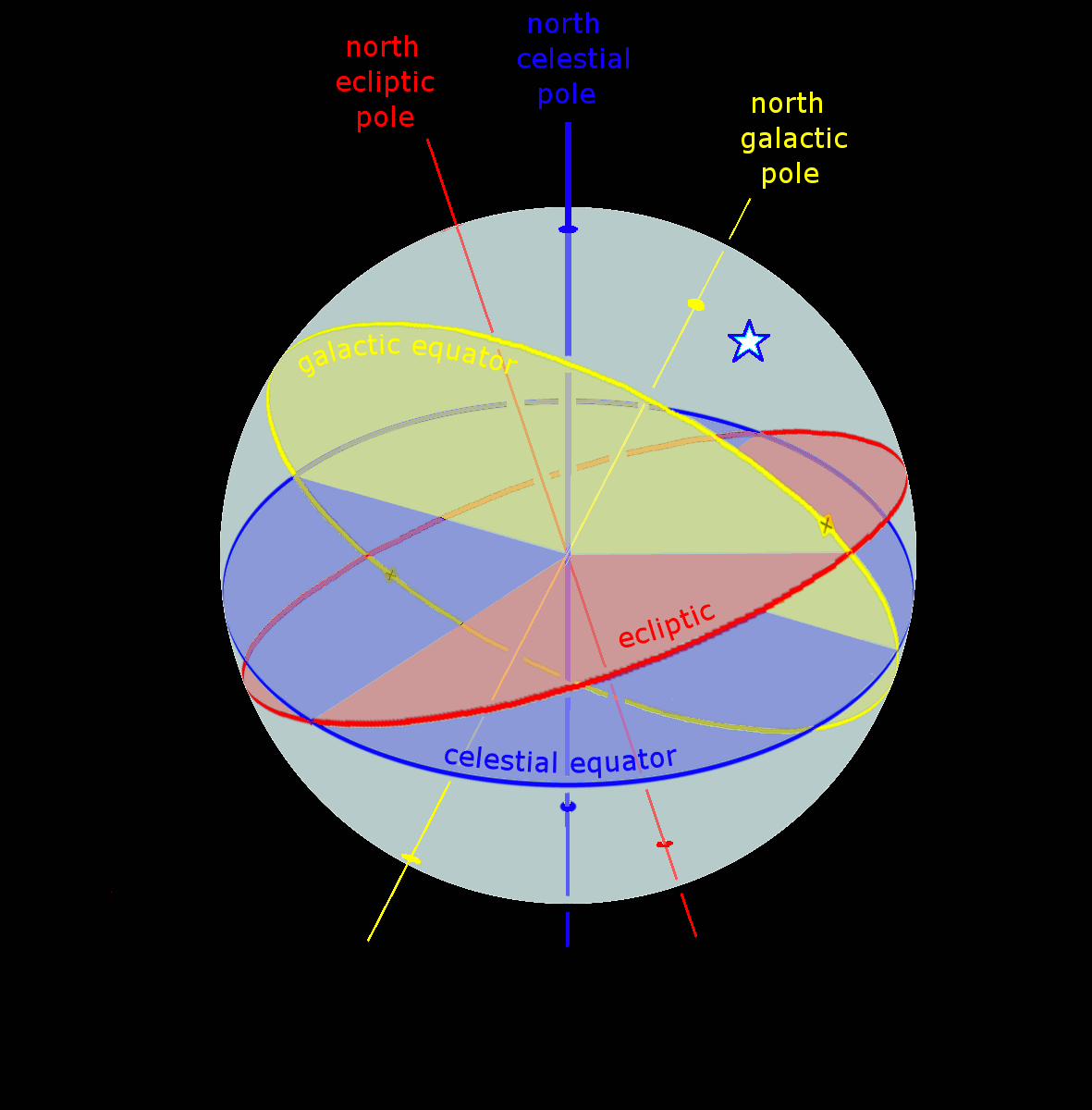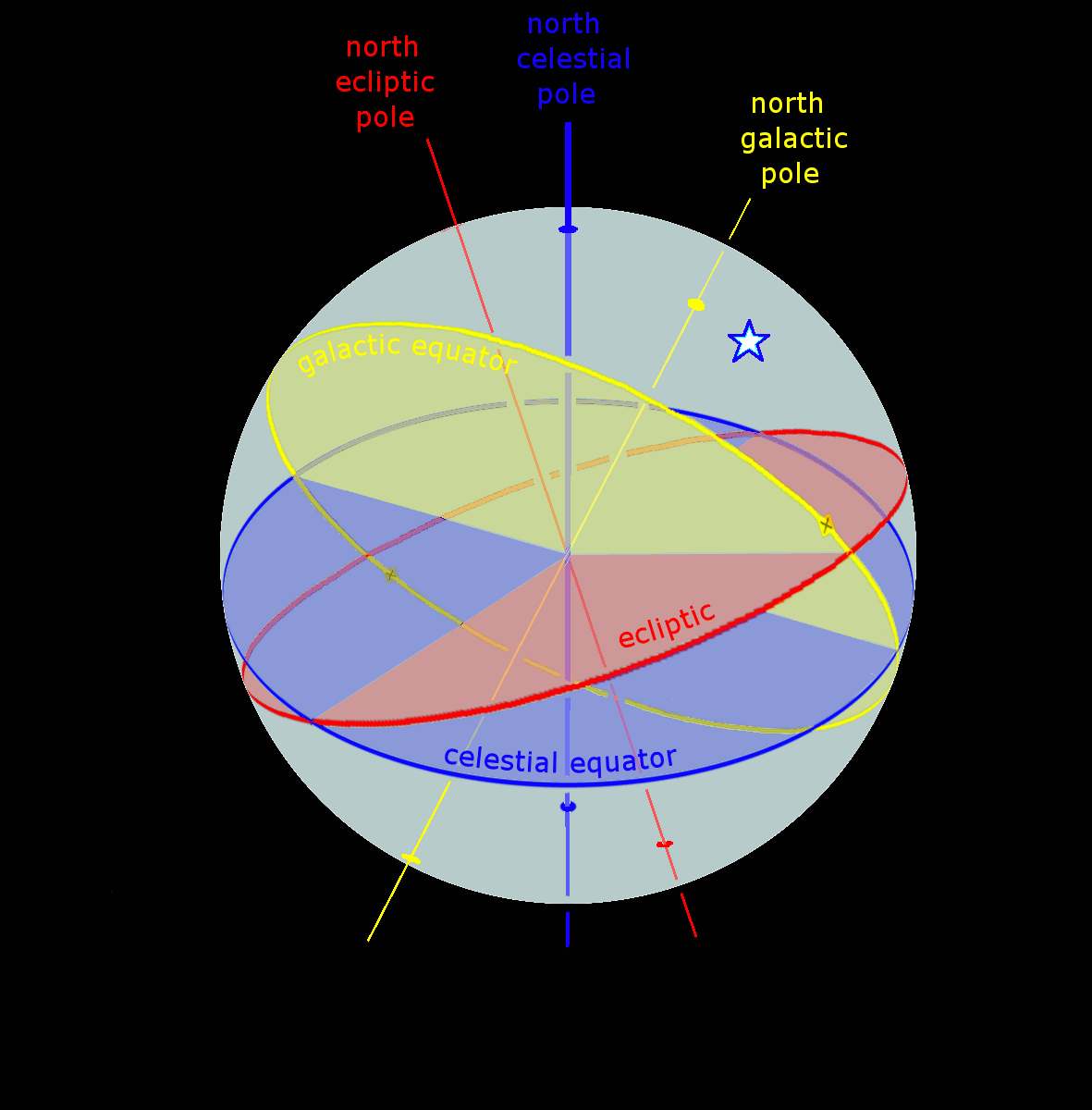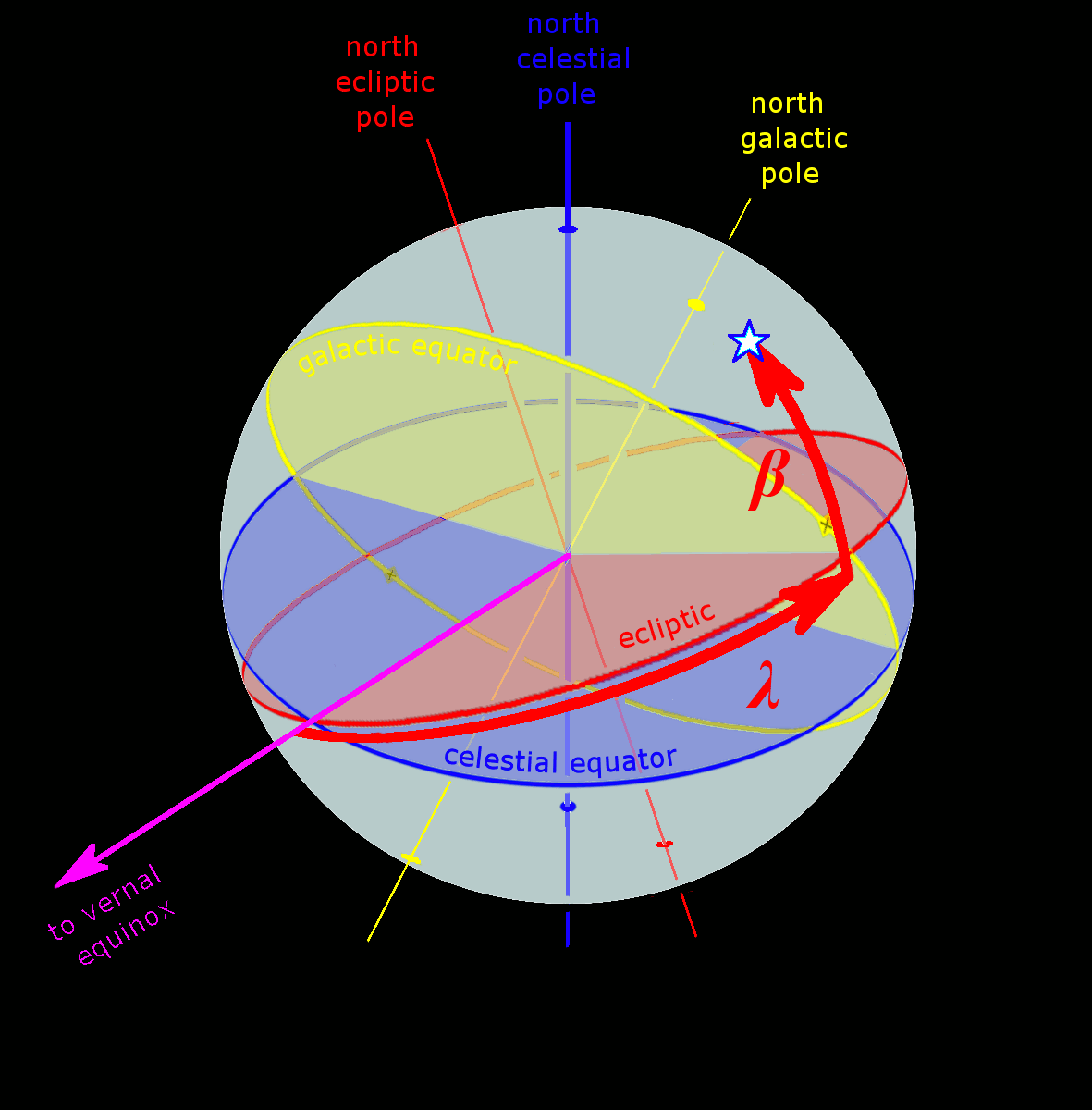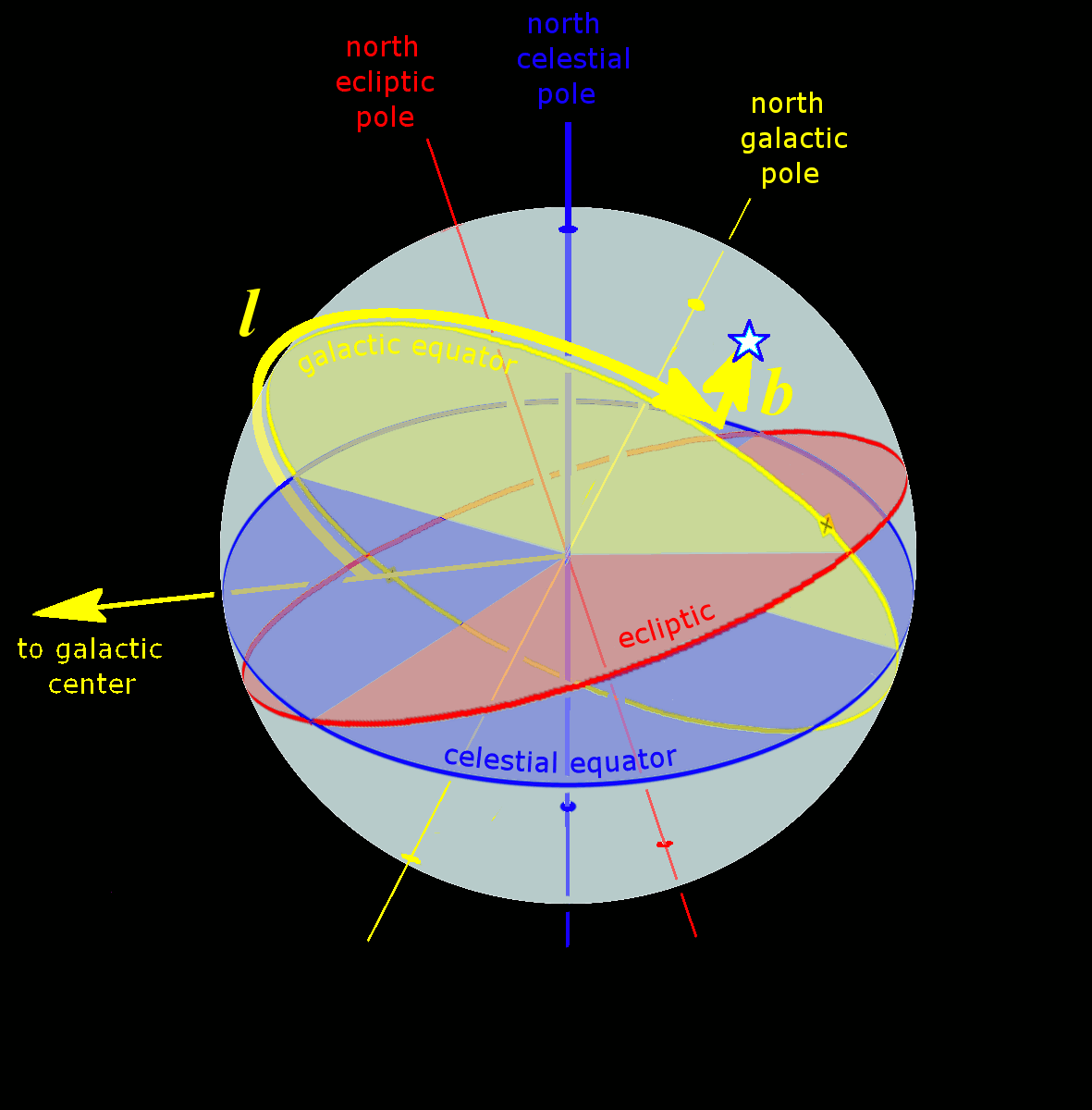
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the background of stars. The ecliptic is an important reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system. Sun's apparent motion The ecliptic is the apparent path of the Sun throughout the course of a year. Because Earth takes one year to orbit the Sun, the apparent position of the Sun takes one year to make a complete circuit of the ecliptic. With slightly more than 365 days in one year, the Sun moves a little less than 1° eastward every day. This small difference in the Sun's position against the stars causes any particular spot on Earth's surface to catch up with (and stand directly north or south of) the Sun about four minutes later each day than it would if Earth did not orbit; a day on Earth is therefore 24 hours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Coordinates
In mathematics, a spherical coordinate system is a coordinate system for three-dimensional space where the position of a point is specified by three numbers: the ''radial distance'' of that point from a fixed origin, its ''polar angle'' measured from a fixed zenith direction, and the ''azimuthal angle'' of its orthogonal projection on a reference plane that passes through the origin and is orthogonal to the zenith, measured from a fixed reference direction on that plane. It can be seen as the three-dimensional version of the polar coordinate system. The radial distance is also called the ''radius'' or ''radial coordinate''. The polar angle may be called '' colatitude'', '' zenith angle'', '' normal angle'', or ''inclination angle''. When radius is fixed, the two angular coordinates make a coordinate system on the sphere sometimes called spherical polar coordinates. The use of symbols and the order of the coordinates differs among sources and disciplines. This article wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizontal Coordinate System
The horizontal coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system that uses the observer's local horizon as the fundamental plane to define two angles: altitude and azimuth. Therefore, the horizontal coordinate system is sometimes called as the az/el system, the alt/az system, or the alt-azimuth system, among others. In an altazimuth mount of a telescope, the instrument's two axes follow altitude and azimuth. Definition This celestial coordinate system divides the sky into two hemispheres: The upper hemisphere, where objects are above the horizon and are visible, and the lower hemisphere, where objects are below the horizon and cannot be seen, since the Earth obstructs views of them. The great circle separating the hemispheres is called the celestial horizon, which is defined as the great circle on the celestial sphere whose plane is normal to the local gravity vector. In practice, the horizon can be defined as the plane tangent to a quiet, liquid surface, such as a pool of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can also be used for any other celestial body that is roughly spherical. In spatial (3D) geometry, as applied in astronomy, the equator of a rotating spheroid (such as a planet) is the parallel (circle of latitude) at which latitude is defined to be 0°. It is an imaginary line on the spheroid, equidistant from its poles, dividing it into northern and southern hemispheres. In other words, it is the intersection of the spheroid with the plane perpendicular to its axis of rotation and midway between its geographical poles. On and near the equator (on Earth), noontime sunlight appears almost directly overhead (no more than about 23° from the zenith) every day, year-round. Consequently, the equator has a rather stable daytime temperature throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, which may be centered on Earth or the observer. If centered on the observer, half of the sphere would resemble a hemispherical screen over the observing location. The celestial sphere is a conceptual tool used in spherical astronomy to specify the position of an object in the sky without consideration of its linear distance from the observer. The celestial equator divides the celestial sphere into northern and southern hemispheres. Introduction Because astronomical objects are at such remote distances, casual observation of the sky offers no information on their actual distances. All celestial objects seem equally far away, as if fixed onto the inside of a sphere with a large but unknown radius, which appears to rotate westward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundamental Plane (spherical Coordinates)
The fundamental plane in a spherical coordinate system is a plane of reference that divides the sphere into two hemispheres. The geocentric latitude of a point is then the angle between the fundamental plane and the line joining the point to the centre of the sphere. For a geographic coordinate system of the Earth, the fundamental plane is the Equator. Astronomical coordinate systems have varying fundamental planes: * The horizontal coordinate system uses the observer's horizon. * The Besselian coordinate system uses Earth's terminator (day/night boundary). This is a Cartesian coordinate system (''x'', ''y'', ''z''). * The equatorial coordinate system uses the celestial equator. * The ecliptic coordinate system uses the ecliptic. * The galactic coordinate system uses the Milky Way The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotation Axis
Rotation around a fixed axis is a special case of rotational motion. The fixed-axis hypothesis excludes the possibility of an axis changing its orientation and cannot describe such phenomena as wobbling or precession. According to Euler's rotation theorem, simultaneous rotation along a number of stationary axes at the same time is impossible; if two rotations are forced at the same time, a new axis of rotation will appear. This article assumes that the rotation is also stable, such that no torque is required to keep it going. The kinematics and dynamics of rotation around a fixed axis of a rigid body are mathematically much simpler than those for free rotation of a rigid body; they are entirely analogous to those of linear motion along a single fixed direction, which is not true for ''free rotation of a rigid body''. The expressions for the kinetic energy of the object, and for the forces on the parts of the object, are also simpler for rotation around a fixed axis, than f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Direction
Primary direction is a term in astronomy for the reference meridian used in a celestial coordinate system for that system's longitude. See also * Celestial coordinate system Astronomical coordinate systems are organized arrangements for specifying positions of satellites, planets, stars, galaxies, and other celestial objects relative to physical reference points available to a situated observer (e.g. the true hor ... * Geographic coordinate system Astronomical coordinate systems Astronomy Navigation Cartography {{astronomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Units Of Measurement
A unit of measurement is a definite magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other quantity of that kind can be expressed as a multiple of the unit of measurement. For example, a length is a physical quantity. The metre (symbol m) is a unit of length that represents a definite predetermined length. For instance, when referencing "10 metres" (or 10 m), what is actually meant is 10 times the definite predetermined length called "metre". The definition, agreement, and practical use of units of measurement have played a crucial role in human endeavour from early ages up to the present. A multitude of systems of units used to be very common. Now there is a global standard, the International System of Units (SI), the modern form of the metric system. In trade, weights and measures is often a subject of governmental regulation, to ensure fairness and transparency. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectangular Coordinates
A Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely by a pair of numerical coordinates, which are the signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, measured in the same unit of length. Each reference coordinate line is called a ''coordinate axis'' or just ''axis'' (plural ''axes'') of the system, and the point where they meet is its ''origin'', at ordered pair . The coordinates can also be defined as the positions of the perpendicular projections of the point onto the two axes, expressed as signed distances from the origin. One can use the same principle to specify the position of any point in three-dimensional space by three Cartesian coordinates, its signed distances to three mutually perpendicular planes (or, equivalently, by its perpendicular projection onto three mutually perpendicular lines). In general, ''n'' Cartesian coordinates (an element of real ''n''-space) specify the point in an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Circle
In mathematics, a great circle or orthodrome is the circular intersection of a sphere and a plane passing through the sphere's center point. Any arc of a great circle is a geodesic of the sphere, so that great circles in spherical geometry are the natural analog of straight lines in Euclidean space. For any pair of distinct non- antipodal points on the sphere, there is a unique great circle passing through both. (Every great circle through any point also passes through its antipodal point, so there are infinitely many great circles through two antipodal points.) The shorter of the two great-circle arcs between two distinct points on the sphere is called the ''minor arc'', and is the shortest surface-path between them. Its arc length is the great-circle distance between the points (the intrinsic distance on a sphere), and is proportional to the measure of the central angle formed by the two points and the center of the sphere. A great circle is the largest circle that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere
A sphere () is a geometrical object that is a three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres roll smoothly in any direction, so most balls used in sports and toys are spherical, as are ball bearings. Basic terminology As mentioned earlier is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |