|
Antiphagocytic
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell (biology), cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a Multicellular organism, multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. History Phagocytosis was first noted by Canadian physician William Osler (1876), and later studied and named by Élie Metchnikoff (1880, 1883). In immune system Phagocytosis is one main mechanisms of the Innate immune system, innate immune defense. It is one of the first processes responding to infection, and is also one of the initia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0309 Phagocytosis
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. The Indian digits spread to the Caliphate in the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Immune System
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies found in vertebrates (the other being the innate immune system). Like the innate system, the adaptive immune system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components and destroys invading pathogens. Unlike the innate immune system, which is pre-programmed to react to common broad categories of pathogen, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to each particular pathogen the body has encountered. Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, and leads to an enhanced response to future encounters with that pathogen. Antibodies are a critical part of the adaptive immune system. Adaptive immunity can provide l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactoferrin
Lactoferrin (LF), also known as lactotransferrin (LTF), is a multifunctional protein of the transferrin family. Lactoferrin is a globular glycoprotein with a molecular mass of about 80 kDa that is widely represented in various secretory fluids, such as milk, saliva, tears, and nasal secretions. Lactoferrin is also present in secondary granules of PMNs and is secreted by some acinar cells. Lactoferrin can be purified from milk or produced recombinantly. Human colostrum (''"first milk"'') has the highest concentration, followed by human milk, then cow milk (150 mg/L). Lactoferrin is one of the components of the immune system of the body; it has antimicrobial activity (bacteriocide, fungicide) and is part of the innate defense, mainly at mucoses. In particular, lactoferrin provides antibacterial activity to human infants. Lactoferrin interacts with DNA and RNA, polysaccharides and heparin, and shows some of its biological functions in complexes with these ligands. Lactoferri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myeloperoxidase
Myeloperoxidase (MPO) is a peroxidase enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MPO'' gene on chromosome 17. MPO is most abundantly expressed in neutrophil granulocytes (a subtype of white blood cells), and produces hypohalous acids to carry out their antimicrobial activity, including hypochlorous acid, the sodium salt of which is the chemical in bleach. It is a lysosomal protein stored in azurophilic granules of the neutrophil and released into the extracellular space during degranulation. Neutrophil myeloperoxidase has a heme pigment, which causes its green color in secretions rich in neutrophils, such as mucus and sputum. The green color contributed to its outdated name verdoperoxidase. Structure The 150-kDa MPO protein is a cationic heterotetramer consisting of two 15-kDa light chains and two variable-weight glycosylated heavy chains bound to a prosthetic heme group complex with calcium ions, arranged as a homodimer of heterodimers. The light chains are glycosylated a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine Protease
Serine proteases (or serine endopeptidases) are enzymes that cleave peptide bonds in proteins. Serine serves as the nucleophilic amino acid at the (enzyme's) active site. They are found ubiquitously in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Serine proteases fall into two broad categories based on their structure: chymotrypsin-like (trypsin-like) or subtilisin-like. Classification The MEROPS protease classification system counts 16 superfamilies (as of 2013) each containing many families. Each superfamily uses the catalytic triad or dyad in a different protein fold and so represent convergent evolution of the catalytic mechanism. The majority belong to the S1 family of the PA clan (superfamily) of proteases. For superfamilies, P: superfamily, containing a mixture of nucleophile class families, S: purely serine proteases. superfamily. Within each superfamily, families are designated by their catalytic nucleophile, (S: serine proteases). Substrate specificity Serine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelatinase
Gelatinases are enzymes capable of degrading gelatin. Gelatinases are expressed in several bacteria including ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' and ''Serratia marcescens''. In humans, the gelatinases are matrix metalloproteinases MMP2 and MMP9 Matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP-9), also known as 92 kDa type IV collagenase, 92 kDa gelatinase or gelatinase B (GELB), is a matrixin, a class of enzymes that belong to the zinc-metalloproteinases family involved in the degradation of the extrace .... References EC 3.4.24 {{enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagenase
Collagenases are enzymes that break the peptide bonds in collagen. They assist in destroying extracellular structures in the pathogenesis of bacteria such as ''Clostridium''. They are considered a virulence factor, facilitating the spread of gas gangrene. They normally target the connective tissue in muscle cells and other body organs. Collagen, a key component of the animal extracellular matrix, is made through cleavage of pro-collagen by collagenase once it has been secreted from the cell. This stops large structures from forming inside the cell itself. In addition to being produced by some bacteria, collagenase can be made by the body as part of its normal immune response. This production is induced by cytokines, which stimulate cells such as fibroblasts and osteoblasts, and can cause indirect tissue damage. Therapeutic uses Collagenases have been approved for medical uses for: * treatment of Dupuytren's contracture and Peyronie's disease (Xiaflex). * wound healing (Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eosinophil
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells (WBCs) and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along with mast cells and basophils, they also control mechanisms associated with allergy and asthma. They are granulocytes that develop during hematopoiesis in the bone marrow before migrating into blood, after which they are terminally differentiated and do not multiply. They form about 2 to 3% of WBCs. These cells are eosinophilic or "acid-loving" due to their large acidophilic cytoplasmic granules, which show their affinity for acids by their affinity to coal tar dyes: Normally transparent, it is this affinity that causes them to appear brick-red after staining with eosin, a red dye, using the Romanowsky method. The staining is concentrated in small granules within the cellular cytoplasm, which contain many chemical mediators, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoclast
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated protein and mineral at a molecular level by secreting acid and a collagenase, a process known as ''bone resorption''. This process also helps regulate the level of blood calcium. Osteoclasts are found on those surfaces of bone that are undergoing resorption. On such surfaces, the osteoclasts are seen to be located in shallow depressions called ''resorption bays (Howship's lacunae)''. The resorption bays are created by the erosive action of osteoclasts on the underlying bone. The border of the lower part of an osteoclast exhibits finger-like processes due to the presence of deep infoldings of the cell membrane; this border is called ''ruffled border''. The ruffled border lies in contact with the bone surface within a resorption bay. The periph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
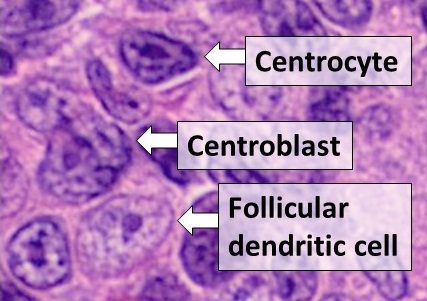
Dendritic Cell
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. They act as messengers between the innate and the adaptive immune systems. Dendritic cells are present in those tissues that are in contact with the external environment, such as the skin (where there is a specialized dendritic cell type called the Langerhans cell) and the inner lining of the nose, lungs, stomach and intestines. They can also be found in an immature state in the blood. Once activated, they migrate to the lymph nodes where they interact with T cells and B cells to initiate and shape the adaptive immune response. At certain development stages they grow branched projections, the ''dendrites'' that give the cell its name (δένδρον or déndron being Greek for 'tree'). While similar in appearance, these are structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocyte
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and conventional dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also influence adaptive immune responses and exert tissue repair functions. There are at least three subclasses of monocytes in human blood based on their phenotypic receptors. Structure Monocytes are amoeboid in appearance, and have nongranulated cytoplasm. Thus they are classified as agranulocytes, although they might occasionally display some azurophil granules and/or vacuoles. With a diameter of 15–22 μm, monocytes are the largest cell type in peripheral blood. Monocytes are mononuclear cells and the ellipsoidal nucleus is often lobulated/indented, causing a bean-shaped or kidney-shaped appearance. Monocytes compose 2% to 10% of all leukocytes in the human body. Development Monocytes are produced by the bone marrow from precursors ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)
