|
Alveolo-palatal Lateral Approximant
The voiced palatal lateral approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , a rotated lowercase letter , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is L. Many languages that were previously thought to have a palatal lateral approximant actually have a lateral approximant that is, broadly, alveolo-palatal; that is to say, it is articulated at a place in-between the alveolar ridge and the hard palate (excluded), and it may be variously described as alveolo-palatal, lamino-postalveolar,, citing or postalveolo-prepalatal. None of the 13 languages investigated by , many of them Romance, has a 'true' palatal. That is likely the case for several other languages listed here. Some languages, like Portuguese and Catalan, have a lateral approximant that varies between alveolar and alveolo-palatal. There is no dedicated symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents the alveol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract, except for the h sound, which is pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Examples are and [b], pronounced with the lips; and [d], pronounced with the front of the tongue; and [g], pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced throughout the vocal tract; , [v], , and [z] pronounced by forcing air through a narrow channel (fricatives); and and , which have air flowing through the nose (nasal consonant, nasals). Most consonants are Pulmonic consonant, pulmonic, using air pressure from the lungs to generate a sound. Very few natural languages are non-pulmonic, making use of Ejective consonant, ejectives, Implosive consonant, implosives, and Click consonant, clicks. Contrasting with consonants are vowels. Since the number of speech sounds in the world's languages is much greater than the number of letters in any one alphabet, Linguis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arvanitika
Arvanitika (; Arvanitika: , ; Greek: , ), also known as Arvanitic, is the variety of Albanian traditionally spoken by the Arvanites, a population group in Greece. Arvanitika was brought to Southern Greece during the late Middle Ages by Albanian settlers who moved south from their homeland in present-day Albania in several waves. The dialect preserves elements of medieval Albanian, while also being significantly influenced by the Greek language. Arvanitika is today endangered, as its speakers have been shifting to the use of Greek and most younger members of the community no longer speak it. Name The name ''Arvanítika'' and its native equivalent Arbërisht are derived from the ethnonym ''Arvanites'', which in turn comes from the toponym Arbën or Arbër (Greek: Άρβανον), which in the Middle Ages referred to a region in modern Albania. Its native equivalents (''Arbërorë, Arbëreshë'' and others) used to be the self-designation of Albanians in general. In the past ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Alphabet
The Bulgarian Cyrillic alphabet () is used to write the Bulgarian language. The Cyrillic alphabet was originally developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 9th – 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School. It has been used in Bulgaria (with modifications and exclusion of certain archaic letters via spelling reforms) continuously since then, superseding the previously used Glagolitic alphabet, which was also invented and used there before the Cyrillic script overtook its use as a written script for the Bulgarian language. The Cyrillic alphabet was used in the then much bigger territory of Bulgaria (including most of today's Serbia), North Macedonia, Kosovo, Albania, Northern Greece (Macedonia region), Romania and Moldova, officially from 893. It was also transferred from Bulgaria and adopted by the East Slavic languages in Kievan Rus' and evolved into the Belarusian, Russian and Ukrainian alphabets and the alphabets of many other Slavic (and later non-Slavic) lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Language
Bulgarian (; , ) is an Eastern South Slavic, Eastern South Slavic language spoken in Southeast Europe, primarily in Bulgaria. It is the language of the Bulgarians. Along with the closely related Macedonian language (collectively forming the East South Slavic languages), it is a member of the Balkan sprachbund and South Slavic languages, South Slavic dialect continuum of the Indo-European language family. The two languages have several characteristics that set them apart from all other Slavic languages, including the elimination of grammatical case, case declension, the development of a suffixed definite article, and the lack of a verb infinitive. They retain and have further developed the Proto-Slavic language, Proto-Slavic verb system (albeit analytically). One such major development is the innovation of evidentiality, evidential verb forms to encode for the source of information: witnessed, inferred, or reported. It is the official Languages of Bulgaria, language of Bulgar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breton Language
Breton (, , ; or in Morbihan) is a Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic languages, Celtic language group spoken in Brittany, part of modern-day France. It is the only Celtic language still widely in use on the European mainland, albeit as a member of the Insular Celtic languages, insular branch instead of the extinct Continental Celtic languages, continental grouping. Breton was brought from Great Britain to Armorica (the ancient name for the coastal region that includes the Brittany peninsula) by migrating Britons (Celtic people), Britons during the Early Middle Ages, making it an Insular Celtic language. Breton is most closely related to Cornish language, Cornish, another Southwestern Brittonic language. Welsh language, Welsh and the extinct Cumbric language, Cumbric, both Western Brittonic languages, are more distantly related, and the Goidelic languages (Irish language, Irish, Manx language, Manx, Scottish Gaelic) have a slight connection due to both of their origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basque Alphabet
The Basque alphabet is a Latin alphabet used to write the Basque language. It consists of 27 letters. List of letters The letters of the Basque alphabet are the 26 letters of the ISO basic Latin alphabet plus . The letter is officially not considered a separate letter, but a variant of . This is the whole list, EuskaltzaindiaRule no. 17 for the Standard Basque, ''Names of the letters in the Basque alphabet'' Rule passed on 25 November 1994. Retrieved 2010-10-22. plus their corresponding phonemes in IPA: All letters and digraphs represent unique phonemes. The main exception is if are preceded by ; most dialects palatalize the sound into , and even if that is not written. is silent in most regions but is pronounced in much of the Northeast, which is the main reason for its existence in the Basque alphabet. It doesn't even represent syllable breaks in the other dialects, although it can stop the aforementioned palatalization from taking place in some words, for exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basque Language
Basque ( ; ) is a language spoken by Basques and other residents of the Basque Country (greater region), Basque Country, a region that straddles the westernmost Pyrenees in adjacent parts of northern Spain and southwestern France. Basque is classified as a language isolate (unrelated to any other known languages), the only one in Europe. The Basques are indigenous to and primarily inhabit the Basque Country. The Basque language is spoken by 806,000 Basques in all territories. Of them, 93.7% (756,000) are in the Spanish area of the Basque Country and the remaining 6.3% (50,000) are in the French portion. Native speakers live in a contiguous area that includes parts of four Spanish provinces and the French Basque Country, three "ancient provinces" in France. Gipuzkoa, most of Biscay, a few municipalities on the northern border of Álava and the northern area of Navarre formed the core of the remaining Basque-speaking area before measures were introduced in the 1980s to stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aymara Language
Aymara (; also ) is an Aymaran languages, Aymaran language spoken by the Aymara people of the Bolivian Andes. It is one of only a handful of Indigenous languages of the Americas, Native American languages with over one million speakers.The other native American languages with more than one million speakers are Nahuatl, Quechua languages, and Guarani language, Guaraní. Aymara, along with Spanish language, Spanish and Quechua language, Quechua, is an official language in Bolivia and Peru. It is also spoken, to a much lesser extent, by some communities in northern Chile, where it is a Minority language, recognized minority language. Some linguists have claimed that Aymara is related to its more widely spoken neighbor, Quechua languages, Quechua. That claim, however, is disputed. Although there are indeed similarities, like the nearly identical phonologies, the majority position among linguists today is that the similarities are better explained as areal feature (linguistics), areal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mirandese Language
Mirandese ( ) is an Asturleonese language, Asturleonese language or variety that is sparsely spoken in a small area of northeastern Portugal in eastern Terra de Miranda, Tierra de Miranda (made up of the municipalities of Miranda do Douro, Miranda de l Douro, Mogadouro and Vimioso, Bumioso, being extinct in Mogadouro and present in Bumioso only in some eastern villages, like Angueira). The Assembly of the Republic (Portugal), Assembly of the Republic granted it official recognition alongside Portuguese language, Portuguese for local matters with Law 7/99 of 29 January 1999. In 2001, Mirandese was officially recognised by the European Bureau for Lesser-Used Languages, which aims to promote the survival of the least spoken European languages. Mirandese has a distinct phonology, Morphology (linguistics), morphology and syntax. It has its roots in the local Vulgar Latin spoken in the northern Iberian Peninsula. Mirandese is a descendant of the Astur-Leonese variety spoken in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonese Dialect
Leonese (''llionés, ḷḷionés, lionés'') is a set of vernacular Romance language varieties spoken in northern and western portions of the historical region of León in Spain (the modern provinces of León, Zamora, and Salamanca), the village of Riudenore (in both Spain and Portugal) and Guadramil in Portugal, sometimes considered another language. In the past, it was spoken in a wider area, including most of the historical region of Leon. The current number of Leonese speakers is estimated at 20,000 to 50,000. Spanish is now the predominant language in the area. Leonese forms part of the Asturleonese linguistic group along with dialects of Asturian. The division between Asturian and Leonese is extra-linguistic, as the main divisions within the Asturleonese complex are between eastern and western varieties, rather than between varieties spoken in Asturias and Leon. Name Menéndez Pidal used "Leonese" for the entire linguistic area, including Asturias. This desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
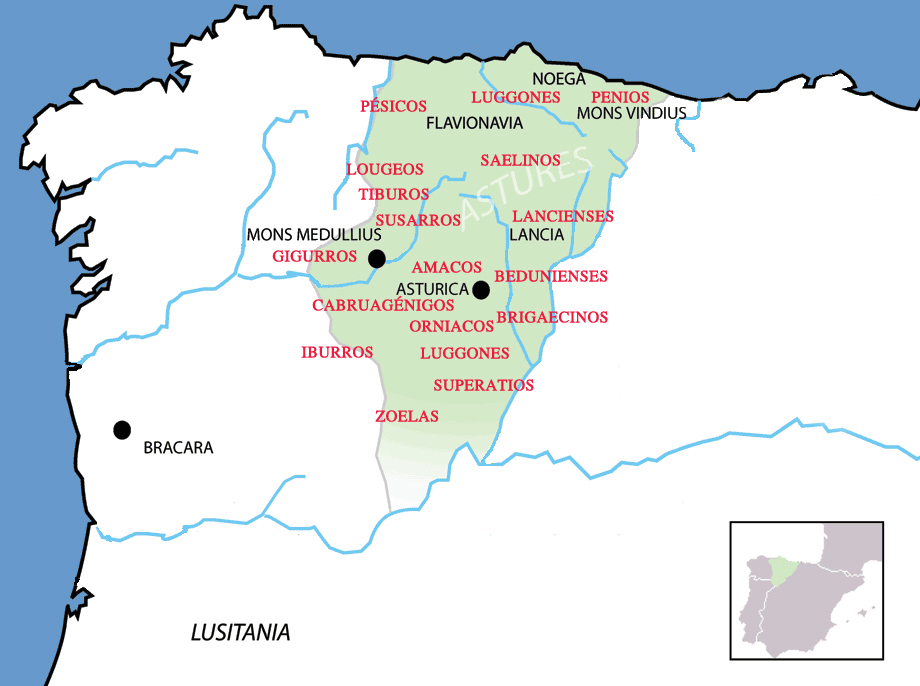
Asturian Language
Asturian (; )Art. 1 de lLey 1/1998, de 23 de marzo, de uso y promoción del bable/asturiano [Law 1/93, of March 23, on the Use and Promotion of the Asturian Language/nowiki>] is a West Iberian languages, West Iberian Romance languages, Romance language spoken in the Principality of Asturias, Spain. Asturian is part of a wider linguistic group, the Asturleonese languages. The number of speakers is estimated at 100,000 (native) and 450,000 (second language). The dialects of the Astur-Leonese language family are traditionally classified in three groups: Western, Central, and Eastern. For historical and demographic reasons, the Standard language, standard is based on #Dialects, Central Asturian. Asturian has a distinct grammar, dictionary, and orthography. It is regulated by the Academy of the Asturian Language. Although it is not an official language of Spain, it is protected under the Statute of Autonomy of Asturias and is an elective language in schools. For much of its history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |