|
Alismatid
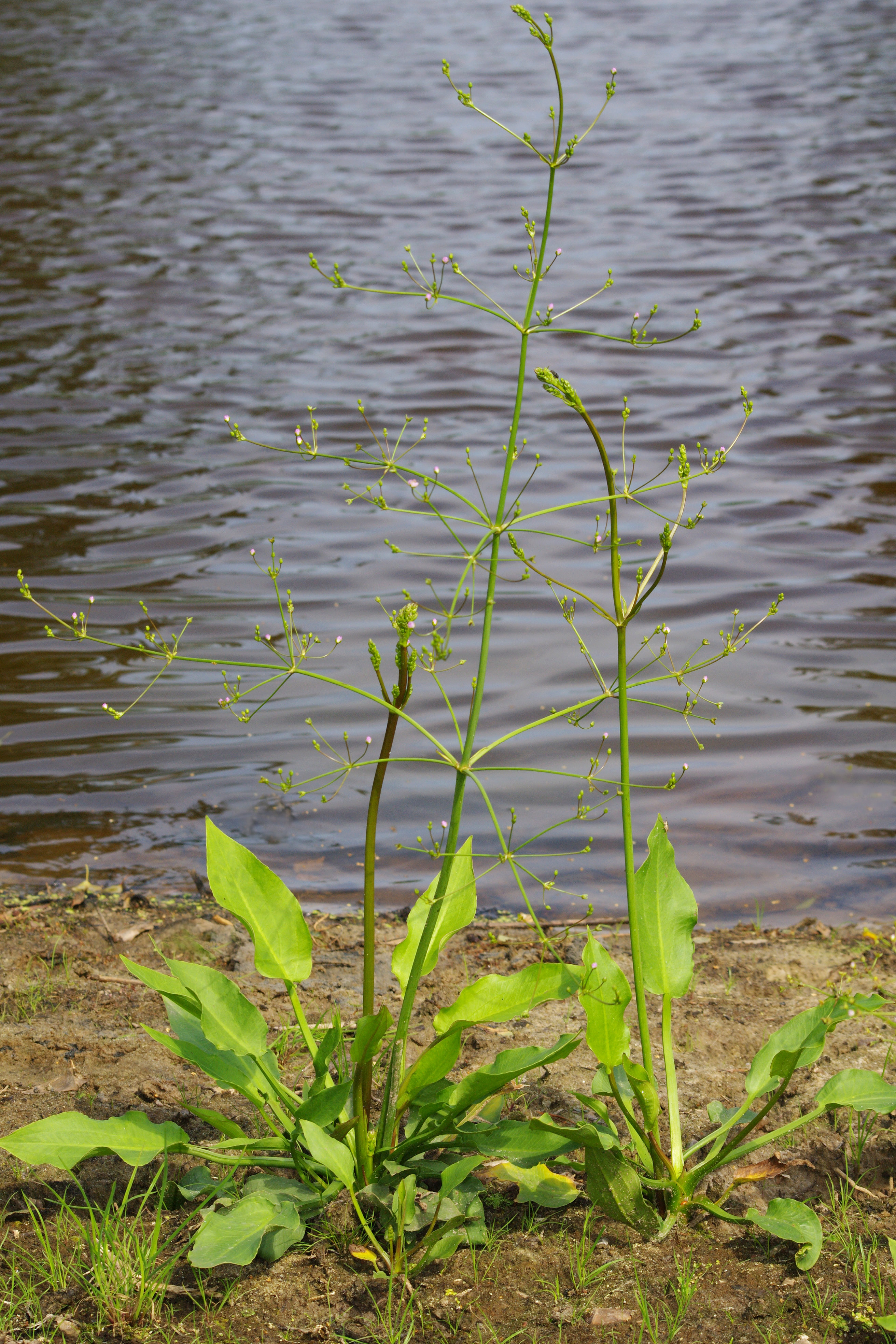
Alismatid monocots (alismatids, basal monocots) is an informal name for a group of early branching (hence basal) monocots, consisting of two orders, the Acorales and Alismatales. The name has also been used to refer to the Alismatales alone. Monocots are frequently treated as three informal groupings based on their branching from ancestral monocots and shared characteristics: alismatid monocots, lilioid monocots (the five other non-commelinid monocots) and commelinid monocots. Research at the Royal Botanical Gardens, Kew is organised into two teams I: Alismatids and Lilioids and II: Commelinids. A similar approach is taken by Judd in his ''Plant systematics''. Phylogeny Cladogram showing the orders of monocots (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) based on molecular phylogenetic evidence according to the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group IV (APG IV). Subdivision Of the two orders, the Acorales is monotypic, consisting of a single family, the Acoraceae, which in turn has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alismatales
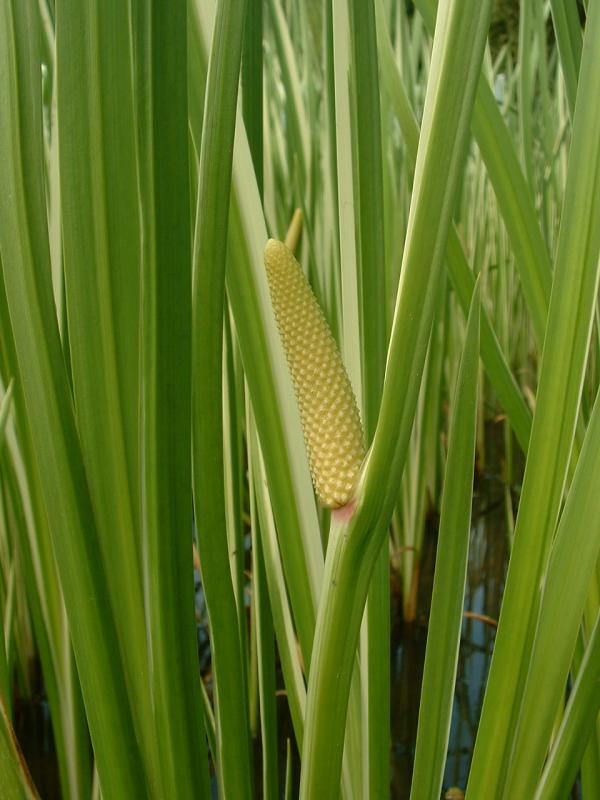
The Alismatales (alismatids) are an order of flowering plants including about 4,500 species. Plants assigned to this order are mostly tropical or aquatic. Some grow in fresh water, some in marine habitats. Description The Alismatales comprise herbaceous flowering plants of often aquatic and marshy habitats, and the only monocots known to have green embryos other than the Amaryllidaceae. They also include the only marine angiosperms growing completely submerged, the seagrasses. The flowers are usually arranged in inflorescences, and the mature seeds lack endosperm. Both marine and freshwater forms include those with staminate flowers that detach from the parent plant and float to the surface. There they can pollinate carpellate flowers floating on the surface via long pedicels. In others, pollination occurs underwater, where pollen may form elongated strands, increasing chance of success. Most aquatic species have a totally submerged juvenile phase, and flowers are either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lilioid Monocots
Lilioid monocots (lilioids, liliid monocots, petaloid monocots, petaloid lilioid monocots) is an informal name used for a grade (grouping of taxa with common characteristics) of five monocot orders (Petrosaviales, Dioscoreales, Pandanales, Liliales and Asparagales) in which the majority of species have flowers with relatively large, coloured tepals. This characteristic is similar to that found in lilies ("lily-like"). Petaloid monocots refers to the flowers having tepals which all resemble petals (petaloid). The taxonomic terms Lilianae or Liliiflorae have also been applied to this assemblage at various times. From the early nineteenth century many of the species in this group of plants were put into a very broadly defined family, Liliaceae ''sensu lato'' or ''s.l.'' (lily family). These classification systems are still found in many books and other sources. Within the monocots the Liliaceae ''s.l.'' were distinguished from the Glumaceae. The development of molecular phyloge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asparagales
Asparagales (asparagoid lilies) is an order (biology), order of plants in modern classification systems such as the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (APG) and the Angiosperm Phylogeny Web. The order takes its name from the type (biology), type family (biology), family Asparagaceae and is placed in the monocots amongst the lilioid monocots. The order has only recently been recognized in classification systems. It was first put forward by herbert Huber (botanist), Huber in 1977 and later taken up in the Dahlgren system of 1985 and then the APG in 1998, 2003 and 2009. Before this, many of its families were assigned to the old order Liliales, a very large order containing almost all monocots with colorful tepals and lacking starch in their endosperm. DNA sequencing, DNA sequence analysis indicated that many of the taxa previously included in Liliales should actually be redistributed over three orders, Liliales, Asparagales, and Dioscoreales. The boundaries of the Asparagales and of its fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commelinid Monocots
In plant taxonomy, commelinids (originally commelinoids) (plural, not capitalised) is a clade of flowering plants within the monocots, distinguished by having cell walls containing ferulic acid. The commelinids are the only clade that the APG IV system has informally named within the monocots. The remaining monocots are a paraphyletic unit. Also known as the commelinid monocots it forms one of three groupings within the monocots, and the final branch; the other two groups are the alismatid monocots and the lilioid monocots. Description Members of the commelinid clade have cell walls containing UV-fluorescent ferulic acid. Taxonomy The commelinids were first recognized as a formal group in 1967 by Armen Takhtajan, who named them the Commelinidae and assigned them to a subclass of Liliopsida (monocots). The name was also used in the 1981 Cronquist system. However, by the release of his 1980 system of classification, Takhtajan had merged this subclass into a larger one, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lilianae
Lilianae (also known as Liliiflorae) is a botanical name for a superorder (that is, a rank higher than that of order) of flowering plants. Such a superorder of necessity includes the type family Liliaceae (and usually the type order Liliales). Terminations at the rank of superorder are not standardized by the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN), although the suffix ''-anae'' has been proposed. Lilianae, introduced in 1966 as a name for a superorder, progressively replaced the older term Liliiflorae, introduced in 1825 as a name for an order. Taxonomy History Early history - Liliiflorae Liliiflorae was a term introduced by Carl Adolph Agardh in 1825 as a higher order to include the Liliaceae (which he called Coronariae) and related families. Argadh, together with De Candolle developed the concept of ordered botanical ranks, in this case grouping together De Jussieu's (1789) recently defined collections of genera (families) into high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocots
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of the major groups into which the flowering plants have traditionally been divided; the rest of the flowering plants have two cotyledons and are classified as dicotyledons, or dicots. Monocotyledons have almost always been recognized as a group, but with various taxonomic ranks and under several different names. The APG III system of 2009 recognises a clade called "monocots" but does not assign it to a taxonomic rank. The monocotyledons include about 60,000 species, about a quarter of all angiosperms. The largest family in this group (and in the flowering plants as a whole) by number of species are the orchids (family Orchidaceae), with more than 20,000 species. About half as many species belong to the true grasses (Poaceae), which are ec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew
Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew is a non-departmental public body in the United Kingdom sponsored by the Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs. An internationally important botanical research and education institution, it employs 1,100 staff. Its board of trustees is chaired by Dame Amelia Fawcett. The organisation manages botanic gardens at Kew in Richmond upon Thames in south-west London, and at Wakehurst, a National Trust property in Sussex which is home to the internationally important Millennium Seed Bank, whose scientists work with partner organisations in more than 95 countries. Kew, jointly with the Forestry Commission, founded Bedgebury National Pinetum in Kent in 1923, specialising in growing conifers. In 1994, the Castle Howard Arboretum Trust, which runs the Yorkshire Arboretum, was formed as a partnership between Kew and the Castle Howard Estate. In 2019, the organisation had 2,316,699 public visitors at Kew, and 312,813 at Wakehurst. Its site at Kew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botanical Journal Of The Linnean Society
The ''Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society'' is a scientific journal publishing original papers relating to the taxonomy of all plant groups and fungi, including anatomy, biosystematics, cytology, ecology, ethnobotany, electron microscopy, morphogenesis, palaeobotany, palynology and phytochemistry.Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society The journal is published by the and is available in both print and searchable online formats. Like the '' |
Acorus
''Acorus'' is a genus of monocot flowering plants. This genus was once placed within the family Araceae (aroids), but more recent classifications place it in its own family Acoraceae and order Acorales, of which it is the sole genus of the oldest surviving line of monocots. Some older studies indicated that it was placed in a lineage (the order Alismatales), that also includes aroids (Araceae), Tofieldiaceae, and several families of aquatic monocots (e.g., Alismataceae, Posidoniaceae). However, modern phylogenetic studies demonstrate that ''Acorus'' is sister to all other monocots. Common names include calamus and sweet flag. The genus is native to North America and northern and eastern Asia, and naturalised in southern Asia and Europe from ancient cultivation. The known wild populations are diploid except for some tetraploids in eastern Asia, while the cultivated plants are sterile triploids, probably of hybrid origin between the diploid and tetraploid forms. Characteristics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Taxon
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, '' Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commelinales
Commelinales is an order of flowering plants. It comprises five families: Commelinaceae, Haemodoraceae, Hanguanaceae, Philydraceae, and Pontederiaceae. All the families combined contain over 885 species in about 70 genera; the majority of species are in the Commelinaceae. Plants in the order share a number of synapomorphies that tie them together, such as a lack of mycorrhizal associations and tapetal raphides. Estimates differ as to when the Commelinales evolved, but most suggest an origin and diversification sometime during the mid- to late Cretaceous. Depending on the methods used, studies suggest a range of origin between 123 and 73 million years, with diversification occurring within the group 110 to 66 million years ago. The order's closest relatives are in the Zingiberales, which includes ginger, bananas, cardamom, and others.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, November 2011. Taxonomy According to the most recent classification scheme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |