|
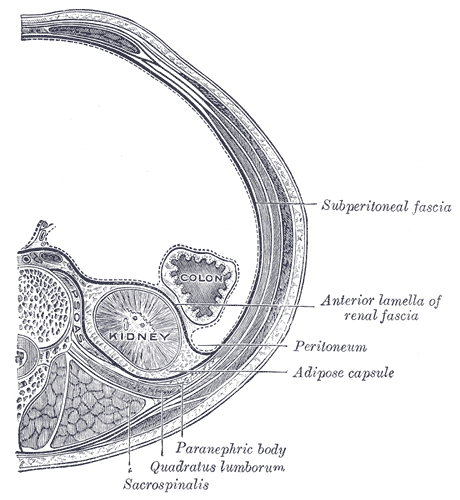
Adipose Capsule Of Kidney
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their anterior side only. Structures that are not suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity and that lie between the parietal peritoneum and abdominal wall are classified as retroperitoneal. This is different from organs that are not retroperitoneal, which have peritoneum on their posterior side and are suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity. The retroperitoneum can be further subdivided into the following: *Perirenal (or perinephric) space *Anterior pararenal (or paranephric) space *Posterior pararenal (or paranephric) space Retroperitoneal structures Structures that lie behind the peritoneum are termed "retroperitoneal". Organs that were once suspended within the abdominal cavity by mesentery but migrated posterior to the per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizontal Plane
Horizontal may refer to: *Horizontal plane, in astronomy, geography, geometry and other sciences and contexts *Horizontal coordinate system, in astronomy *Horizontalism, in monetary circuit theory *Horizontalidad, Horizontalism, in sociology *Horizontal market, in microeconomics *Horizontal (album), ''Horizontal'' (album), a 1968 album by the Bee Gees **Horizontal (song), "Horizontal" (song)" is a 1968 song by the Bee Gees See also *Horizontal and vertical *Horizontal and vertical (other) *Horizontal fissure (other), anatomical features *Horizontal bar, an apparatus used by male gymnasts in artistic gymnastics *Vertical (other) * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Fascia
The renal fascia is a dense, elastic connective tissue envelope enclosing the kidney and adrenal gland, together with the layer of perirenal fat surrounding these two. The renal fascia separates the adipose capsule of kidney from the overlying pararenal fat. The deeper layers deep to the renal fascia are, in order, the adipose capsule (or perirenal fat), the renal capsule and finally the parenchyma of the renal cortex. At the renal hilum, the renal capsule extends into the renal sinus The renal sinus is a cavity within the kidney which is occupied by the renal pelvis, renal calyces, blood vessels, nerves and fat. The renal hilum extends into a large cavity within the kidney occupied by the renal vessels, minor renal calyces, .... The renal fascia was originally described as consisting of two distinct structures: the anterior renal fascia (Gerota's fascia), and posterior renal fascia (Zuckerkandl's fascia); these two fasciae were said to fuse laterally to form the lateroco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retroperitoneal Lymph Node Dissection
Retroperitoneal lymph node dissection (RPLND) is a surgical procedure to remove abdominal lymph nodes. It is used to treat testicular cancer, as well as to help establish the exact stage and type of the cancer. Indications Testicular cancer metastasizes in a predictable pattern, and lymph nodes in the retroperitoneum are typically the first place it lands. By examining the removed lymphatic tissue, a pathologist can determine whether the disease has spread. If no malignant tissue is found, the cancer can be labeled Stage I, limited to the testicle. The procedure is common in the treatment of Stage I and II non-seminomatous germ cell tumors. In seminomas, another form of testicular cancer, radiation therapy is generally preferred to the invasive RPLND procedure. Whether RPLND is needed after orchiectomy depends on the type of tumor and its stage. RPLND may be performed to remove tumor remnants that persist after chemotherapy, because these remnants might otherwise spread and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retroperitoneal Fibrosis
Retroperitoneal fibrosis or Ormond's disease is a disease featuring the proliferation of fibrous tissue (fibrosis) in the retroperitoneum, the compartment of the body containing the kidneys, aorta, renal tract, and various other structures. It may present with lower back pain, kidney failure, hypertension, deep vein thrombosis, and other obstructive symptoms. It is named after John Kelso Ormond, who rediscovered the condition in 1948. Causes The association of idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis with various immune-related conditions and response to immunosuppression led to a search for an autoimmune cause of idiopathic RPF. Many of these previously idiopathic cases can now be attributed to IgG4-related disease, an autoimmune disorder proposed in 2003. Otherwise, one-third of cases are secondary to malignancy, medication ( methysergide, hydralazine, beta blockers), prior radiotherapy, or certain infections. However, emerging evidence suggests that occupational exposure to asbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retroperitoneal Hemorrhage
Retroperitoneal bleeding is an accumulation of blood in the retroperitoneal space. Signs and Symptom, symptoms may include abdominal or upper leg pain, hematuria, and Shock (circulatory), shock. It can be caused by major trauma or by non-traumatic mechanisms. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms may include: * abdominal pain. * upper leg pain. * hematuria. * Shock (circulatory), shock. Causes Retroperitoneal bleeds are most often caused by major trauma, such as from a Traffic collision, traffic collisions or a Falls in older adults, fall. Less common non-traumatic causes including: * anticoagulation. * a ruptured aortic aneurysm. * a ruptured renal aneurysm. * acute pancreatitis. * malignancy. Retroperitoneal bleeds may also be Iatrogenesis, iatrogenic, caused accidentally during medical procedures. Such procedures include cannulating the femoral artery for cardiac catheterization or for interventional radiology, and the administration of a psoas compartment nerve block. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadratus Lumborum Muscle
The quadratus lumborum muscle, informally called the ''QL'', is a paired muscle of the left and right posterior abdominal wall. It is the deepest abdominal muscle, and commonly referred to as a back muscle. Each muscle of the pair is an irregular quadrilateral in shape, hence the name. The quadratus lumborum muscles originate from the wings of the ilium; their insertions are on the transverse processes of the upper four lumbar vertebrae Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal ... plus the lower posterior border of the twelfth rib. Contraction of one of the pair of muscles causes lateral flexion of the Lumbar vertebrae, lumbar spine, ''elevation'' of the pelvis, or both. Contraction of both causes ''extension'' of the lumbar spine. A disorder of the quadratus lumborum mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliopsoas Muscle
The iliopsoas muscle (; ) refers to the joined psoas major muscle, psoas major and the iliacus muscles. The two muscles are separate in the abdomen, but usually merge in the thigh. They are usually given the common name ''iliopsoas''. The iliopsoas muscle joins to the femur at the lesser trochanter. It acts as the strongest :wikt:flexion, flexor of the hip. The iliopsoas muscle is supplied by the lumbar spinal nerves Lumbar spinal nerve 1, L1–Lumbar spinal nerve 3, L3 (psoas) and parts of the femoral nerve (iliacus). Structure The iliopsoas muscle is a composite muscle formed from the psoas major muscle, and the iliacus muscle. The psoas major originates along the outer surfaces of the Body of vertebra, vertebral bodies of Thoracic spinal nerve 12, T12 and Lumbar spinal nerve 1, L1–Lumbar spinal nerve 3, L3 and their associated intervertebral discs. The iliacus originates in the iliac fossa of the pelvis. The psoas major unites with the iliacus at the level of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliac Fossa
The iliac fossa is a large, smooth, concave surface on the internal surface of the Ilium (bone), ilium (part of the three fused bones making the hip bone). Structure The iliac fossa is bounded above by the iliac crest, and below by the Arcuate line (ilium), arcuate line. It is bordered in front and behind by the anterior and posterior borders of the Ilium (bone), ilium. The iliac fossa gives origin to the iliacus muscle. The obturator nerve passes around the iliac fossa. It is perforated at its inner part by a nutrient canal. Below it there is a smooth, rounded border, the arcuate line (ilium), arcuate line, which runs anterior, inferior, and medial. When the "left" or "right" adjective is used (e.g. "right iliac fossa"), the iliac fossa usually means one of the groin, inguinal regions of the Quadrants and regions of abdomen, nine regions of the abdomen. Additional images File:Anterior Hip Muscles 2.PNG, The iliacus and nearby muscles File:Slide5AA.JPG, Iliac fossa File:Slid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In mammals, it may be the principal site for iron absorption. The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest part of the small intestine. In humans, the duodenum is a hollow jointed tube about long connecting the stomach to the jejunum, the middle part of the small intestine. It begins with the duodenal bulb, and ends at the duodenojejunal flexure marked by the suspensory muscle of duodenum. The duodenum can be divided into four parts: the first (superior), the second (descending), the third (transverse) and the fourth (ascending) parts. Overview The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms ''anterior intestine'' or ''proximal intestine'' may be used instead of duodenum. In mammals the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreas
The pancreas (plural pancreases, or pancreata) is an Organ (anatomy), organ of the Digestion, digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdominal cavity, abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e., it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. Ninety-nine percent of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins and lipids, fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach. Inflammation of the pancreas is kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perirenal Fat
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their anterior side only. Structures that are not suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity and that lie between the parietal peritoneum and abdominal wall are classified as retroperitoneal. This is different from organs that are not retroperitoneal, which have peritoneum on their posterior side and are suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity. The retroperitoneum can be further subdivided into the following: *Perirenal (or perinephric) space *Anterior pararenal (or paranephric) space *Posterior pararenal (or paranephric) space Retroperitoneal structures Structures that lie behind the peritoneum are termed "retroperitoneal". Organs that were once suspended within the abdominal cavity by mesentery but migrated posterior to the peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |