|
Acute Viral Nasopharyngitis
The common cold or the cold is a viral infectious disease of the upper respiratory tract that primarily affects the respiratory mucosa of the nose, throat, sinuses, and larynx. Signs and symptoms may appear fewer than two days after exposure to the virus. These may include coughing, sore throat, runny nose, sneezing, headache, and fever. People usually recover in seven to ten days, but some symptoms may last up to three weeks. Occasionally, those with other health problems may develop pneumonia. Well over 200 virus strains are implicated in causing the common cold, with rhinoviruses, coronaviruses, adenoviruses and enteroviruses being the most common. They spread through the air during close contact with infected people or indirectly through contact with objects in the environment, followed by transfer to the mouth or nose. Risk factors include going to child care facilities, not sleeping well, and psychological stress. The symptoms are mostly due to the bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinovirus
The rhinovirus (from the grc, ῥίς, rhis "nose", , romanized: "of the nose", and the la, vīrus) is the most common viral infectious agent in humans and is the predominant cause of the common cold. Rhinovirus infection proliferates in temperatures of 33–35 °C (91–95 °F), the temperatures found in the nose. Rhinoviruses belong to the genus ''Enterovirus'' in the family ''Picornaviridae''. The three species of rhinovirus (A, B, and C) include around 160 recognized types (called serotypes) of human rhinovirus that differ according to their surface antigens. They are lytic in nature and are among the smallest viruses, with diameters of about 30 nanometers. By comparison, other viruses, such as smallpox and vaccinia, are around ten times larger at about 300 nanometers, while flu viruses are around 80–120 nm. History In 1953, when a cluster of nurses developed a mild respiratory illness, Winston Price, from the Johns Hopkins University, took nasal pas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
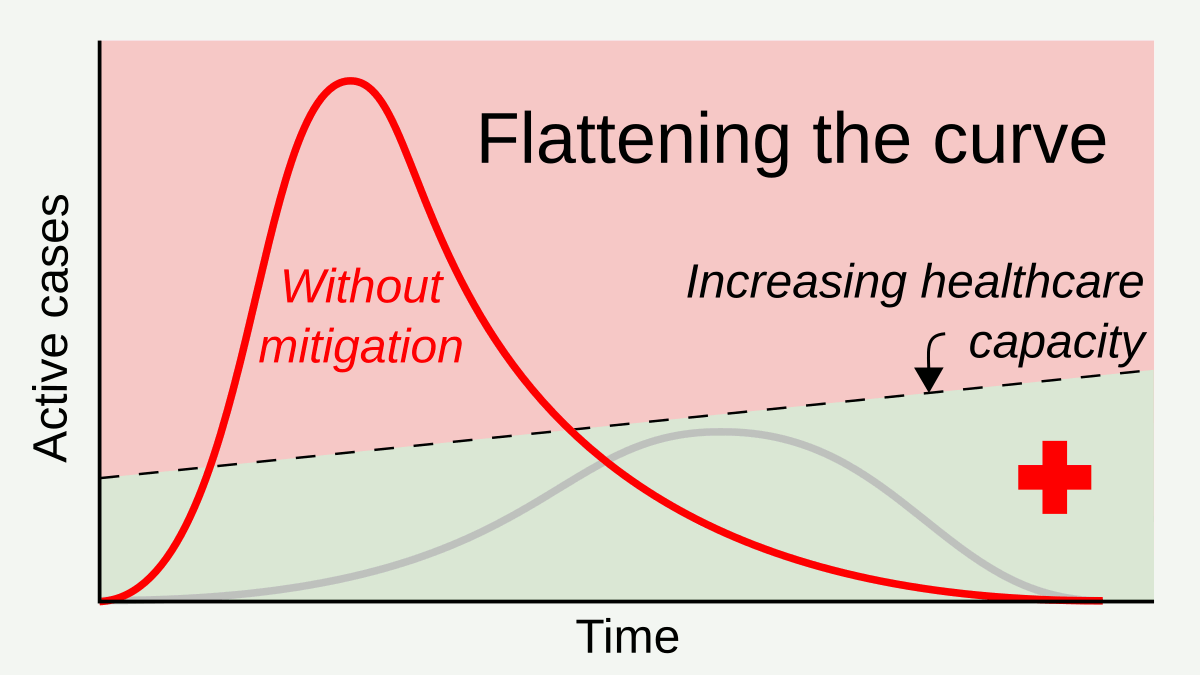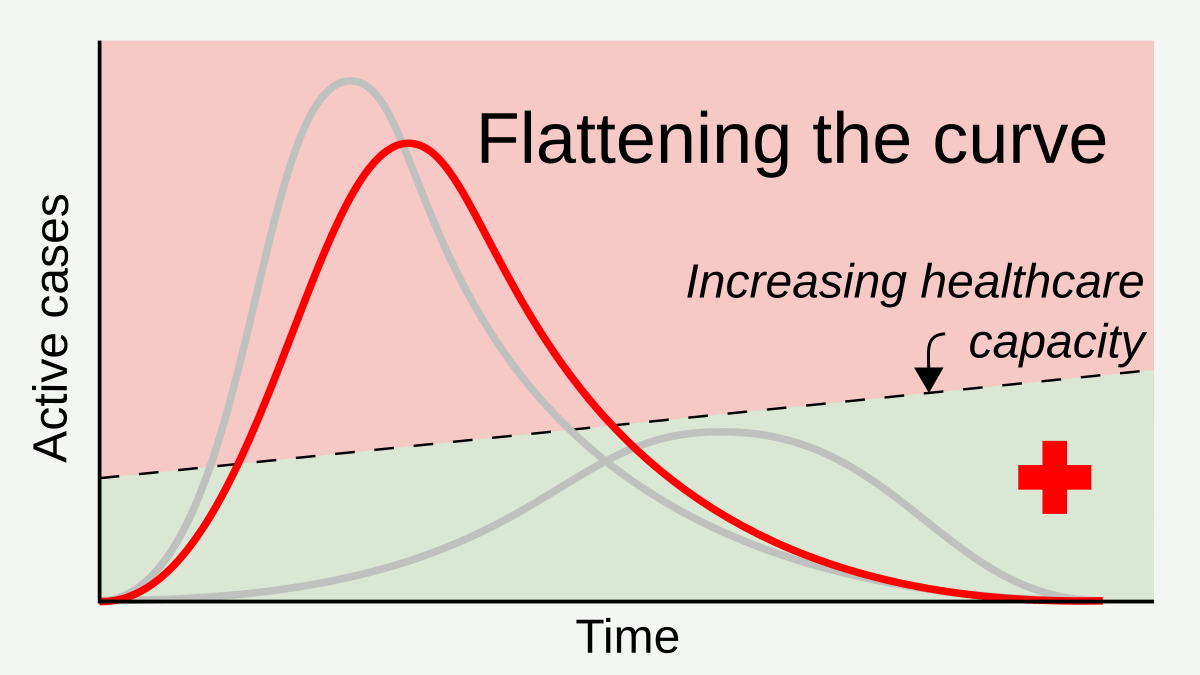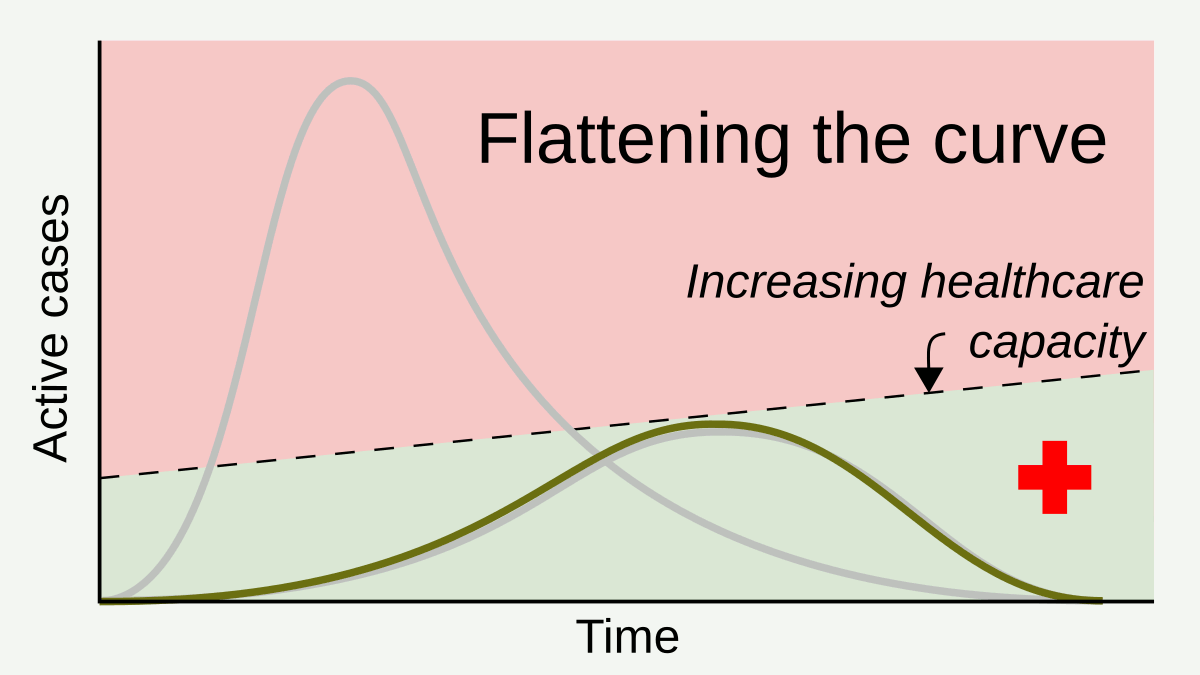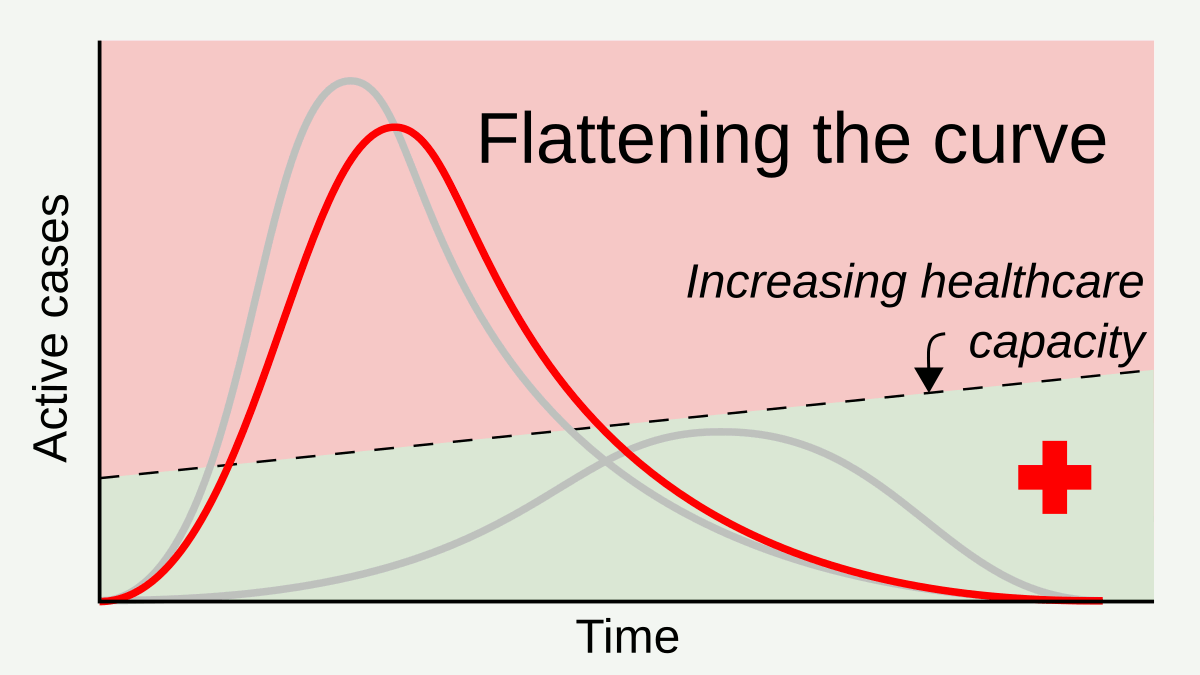
Social Distancing
In public health, social distancing, also called physical distancing, (NB. Regula Venske is president of the PEN Centre Germany.) is a set of non-pharmaceutical interventions or measures intended to prevent the spread of a contagious disease by maintaining a physical distance between people and reducing the number of times people come into close contact with each other. It usually involves keeping a certain distance from others (the distance specified differs from country to country and can change with time) and avoiding gathering together in large groups. By minimising the probability that a given uninfected person will come into physical contact with an infected person, the disease transmission can be suppressed, resulting in fewer deaths. The measures may be used in combination with others, such as good respiratory hygiene, face masks and hand washing. To slow down the spread of infectious diseases and avoid overburdening healthcare systems, particularly during a pand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinorrhea
Rhinorrhea, rhinorrhoea, or informally runny nose is the free discharge of a thin mucus fluid from the nose; it is a common condition. It is a common symptom of allergies ( hay fever) or certain viral infections, such as the common cold or COVID-19. It can be a side effect of crying, exposure to cold temperatures, cocaine abuse, or drug withdrawal, such as from methadone or other opioids. Treatment for rhinorrhea is not usually undertaken, but there are a number of medical treatments and preventive techniques. The term was coined in 1866 from the Ancient Greek, Greek ''rhino-'' ("of the nose") and ''-rhoia'' ("discharge" or "flow"). Signs and symptoms Rhinorrhea is characterized by an excess amount of mucus produced by the mucous membranes that line the nasal cavities. The membranes create mucus faster than it can be processed, causing a backup of mucus in the nasal cavities. As the cavity fills up, it blocks off the air passageway, causing difficulty breathing through the nose. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages that can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three phases: an inhalation, a forced exhalation against a closed glottis, and a violent release of air from the lungs following opening of the glottis, usually accompanied by a distinctive sound. Frequent coughing usually indicates the presence of a disease. Many viruses and bacteria benefit, from an evolutionary perspective, by causing the host to cough, which helps to spread the disease to new hosts. Most of the time, irregular coughing is caused by a respiratory tract infection but can also be triggered by choking, smoking, air pollution, asthma, gastroesophageal reflux disease, post-nasal drip, chronic bronchitis, lung tumors, heart failure and medications such as angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors). Treatment should t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about 4–5 centimeters in diameter. The larynx houses the vocal cords, and manipulates pitch and volume, which is essential for phonation. It is situated just below where the tract of the pharynx splits into the trachea and the esophagus. The word ʻlarynxʼ (plural ʻlaryngesʼ) comes from the Ancient Greek word ''lárunx'' ʻlarynx, gullet, throat.ʼ Structure The triangle-shaped larynx consists largely of cartilages that are attached to one another, and to surrounding structures, by muscles or by fibrous and elastic tissue components. The larynx is lined by a ciliated columnar epithelium except for the vocal folds. The cavity of the larynx extends from its triangle-shaped inlet, to the epiglottis, and to the circular outlet at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paranasal Sinuses
Paranasal sinuses are a group of four paired air-filled spaces that surround the nasal cavity. The maxillary sinuses are located under the eyes; the frontal sinuses are above the eyes; the ethmoidal sinuses are between the eyes and the sphenoidal sinuses are behind the eyes. The sinuses are named for the facial bones in which they are located. Structure Humans possess four pairs of paranasal sinuses, divided into subgroups that are named according to the bones within which the sinuses lie. They are all innervated by branches of the trigeminal nerve (CN V). * The maxillary sinuses, the largest of the paranasal sinuses, are under the eyes, in the maxillary bones (open in the back of the semilunar hiatus of the nose). They are innervated by the maxillary nerve (CN V2). * The frontal sinuses, superior to the eyes, in the frontal bone, which forms the hard part of the forehead. They are innervated by the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1). * The ethmoidal sinuses, which are formed from sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Throat
In vertebrate anatomy, the throat is the front part of the neck, internally positioned in front of the vertebrae. It contains the pharynx and larynx. An important section of it is the epiglottis, separating the esophagus from the trachea (windpipe), preventing food and drinks being inhaled into the lungs. The throat contains various blood vessels, pharyngeal muscles, the nasopharyngeal tonsil, the tonsils, the palatine uvula, the trachea, the esophagus, and the vocal cords. Mammal throats consist of two bones, the hyoid bone and the clavicle. The "throat" is sometimes thought to be synonymous for the fauces. It works with the mouth, ears and nose, as well as a number of other parts of the body. Its pharynx is connected to the mouth, allowing speech to occur, and food and liquid to pass down the throat. It is joined to the nose by the nasopharynx at the top of the throat, and to the ear by its Eustachian tube. The throat's trachea carries inhaled air to the bronchi of the lungs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Nose
The human nose is the most protruding part of the face. It bears the nostrils and is the first organ of the respiratory system. It is also the principal organ in the olfactory system. The shape of the nose is determined by the nasal bones and the nasal cartilages, including the nasal septum which separates the nostrils and divides the nasal cavity into two. On average the nose of a male is larger than that of a female. The nose has an important function in breathing. The nasal mucosa lining the nasal cavity and the paranasal sinuses carries out the necessary conditioning of inhaled air by warming and moistening it. Nasal conchae, shell-like bones in the walls of the cavities, play a major part in this process. Filtering of the air by nasal hair in the nostrils prevents large particles from entering the lungs. Sneezing is a reflex to expel unwanted particles from the nose that irritate the mucosal lining. Sneezing can transmit infections, because aerosols are created in w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
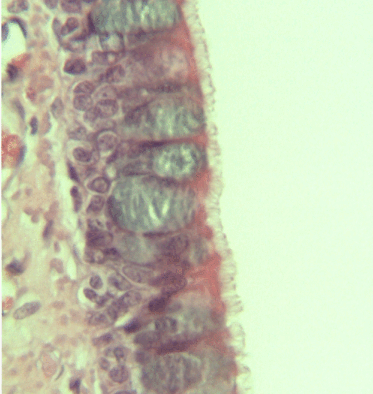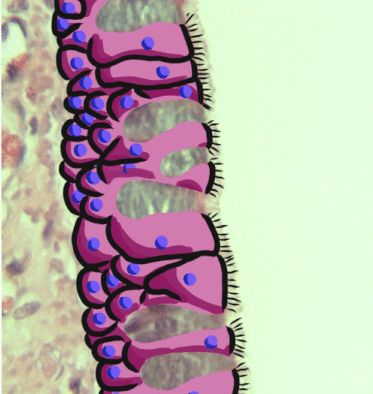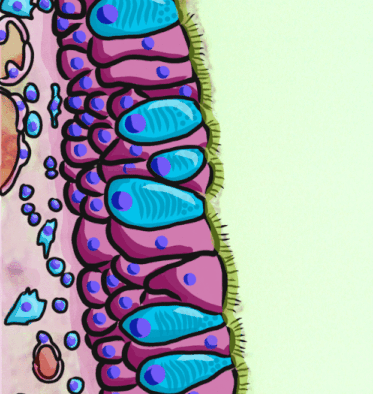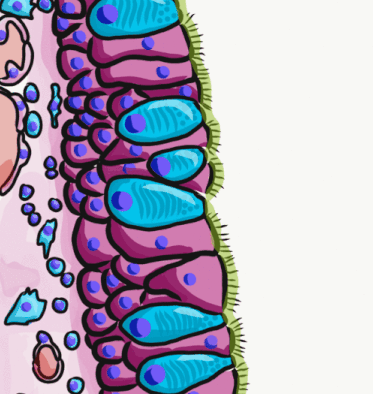
Respiratory Epithelium
Respiratory epithelium, or airway epithelium, is a type of ciliated columnar epithelium found lining most of the respiratory tract as respiratory mucosa, where it serves to moisten and protect the airways. It is not present in the vocal cords of the larynx, or the oropharynx and laryngopharynx, where instead the epithelium is stratified squamous. It also functions as a barrier to potential pathogens and foreign particles, preventing infection and tissue injury by the secretion of mucus and the action of mucociliary clearance. Structure The respiratory epithelium lining the upper respiratory airways is classified as ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium. This designation is due to the arrangement of the multiple cell types composing the respiratory epithelium. While all cells make contact with the basement membrane and are, therefore, a single layer of cells, their nuclei are not aligned in the same plane. Hence, it appears as though several layers of cells are presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Respiratory Tract
The respiratory tract is the subdivision of the respiratory system involved with the process of respiration in mammals. The respiratory tract is lined with respiratory epithelium as respiratory mucosa. Air is breathed in through the nose to the nasal cavity, where a layer of nasal mucosa acts as a filter and traps pollutants and other harmful substances found in the air. Next, air moves into the pharynx, a passage that contains the intersection between the oesophagus and the larynx. The opening of the larynx has a special flap of cartilage, the epiglottis, that opens to allow air to pass through but closes to prevent food from moving into the airway. From the larynx, air moves into the trachea and down to the intersection known as the carina that branches to form the right and left primary (main) bronchi. Each of these bronchi branches into a secondary (lobar) bronchus that branches into tertiary (segmental) bronchi, that branch into smaller airways called bronchioles that ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infectious Disease
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic material, i. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |