|
Sparta
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon ( grc, , Lakedaímōn, label=none), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas (river), Eurotas River in the Evrotas Valley, Eurotas valley of Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant Military, military land-power in ancient Greece. Given its military pre-eminence, Sparta was recognized as the leading force of the unified Greek military during the Greco-Persian Wars, in rivalry with the rising naval power of Classical Athens, Athens. Sparta was the principal enemy of History of Athens, Athens during the Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), from which it emerged victorious after the Battle of Aegospotami. The decisive Battle of Leuctra against Thebes, Greece, Thebes in 371 BC ended the Spartan hegemony, although the city-state maintained its Independence, political independen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Thermopylae
The Battle of Thermopylae ( ; grc, Μάχη τῶν Θερμοπυλῶν, label=Greek, ) was fought in 480 BC between the Achaemenid Persian Empire under Xerxes I and an alliance of Greek city-states led by Sparta under Leonidas I. Lasting over the course of three days, it was one of the most prominent battles of both the second Persian invasion of Greece and the wider Greco-Persian Wars. The engagement at Thermopylae occurred simultaneously with the Battle of Artemisium: between July and September 480 BC. The second Persian invasion under Xerxes I was a delayed response to the failure of the first Persian invasion, which had been initiated by Darius I and ended in 490 BC by an Athenian-led Greek victory at the Battle of Marathon. By 480 BC, a decade after the Persian defeat at Marathon, Xerxes had amassed a massive land and naval force, and subsequently set out to conquer all of Greece. In response, the Athenian politician and general Themistocles proposed that the allie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evrotas Valley
The Evrotas Valley is an 82 km elongated valley between Taygetus and Parnon which traverses Laconia, Greece. Homer called the valley Kili Lakedemon, while Sparta, Mystras and Gytheio are the main cities within the valley. It is one of the largest valleys in Greece. The valley is predominantly an agricultural region that contains many citrus groves, olive groves, and pasture lands. It is the location of the largest orange production in the Peloponnese and probably in all of Greece. ''Lakonia'', a brand of orange juice, is based in Amykles. The Evrotas Valley records the highest summer mean maximum temperatures in Greece. Geography The Evrotas River is the main river traversing the valley. The valley runs until the delta of the river in the Laconian Gulf. Modern day Sparta, the capital of the prefecture of Laconia, lies on the eastern foothills of Mount Taygetos. The city has been built upon the site of ancient Sparta, whose Acropolis lies north of the modern city. The Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurotas (river)
The Eurotas ( grc, Εὐρώτας) or Evrotas (modern Greek: ) is the main river of Laconia and one of the major rivers of the Peloponnese, in Greece. The river's springs are located just northwest of the border between Laconia and Arcadia (regional unit), Arcadia, at Skortsinos. The river is also fed by underwater springs at Pellana and by tributaries coursing down from Taygetos, Mt. Taygetos and Parnon, Mt. Parnon, which flank the Eurotas valley to the west and east, respectively. The river is long, flowing in a north-south direction and emptying into the Laconian Gulf. Its drainage basin is . Etymology The classical Eurotas was changed to Iri in the Middle Ages and only changed back to Eurotas in recent times. Eurotas, however, is not the most ancient name of the river. It does not appear in the works of Homer, which purport to recount the stories and geography of Mycenaean Greece. In that legendary time, the Dorians are not known to have been present in the Eurotas Valley. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
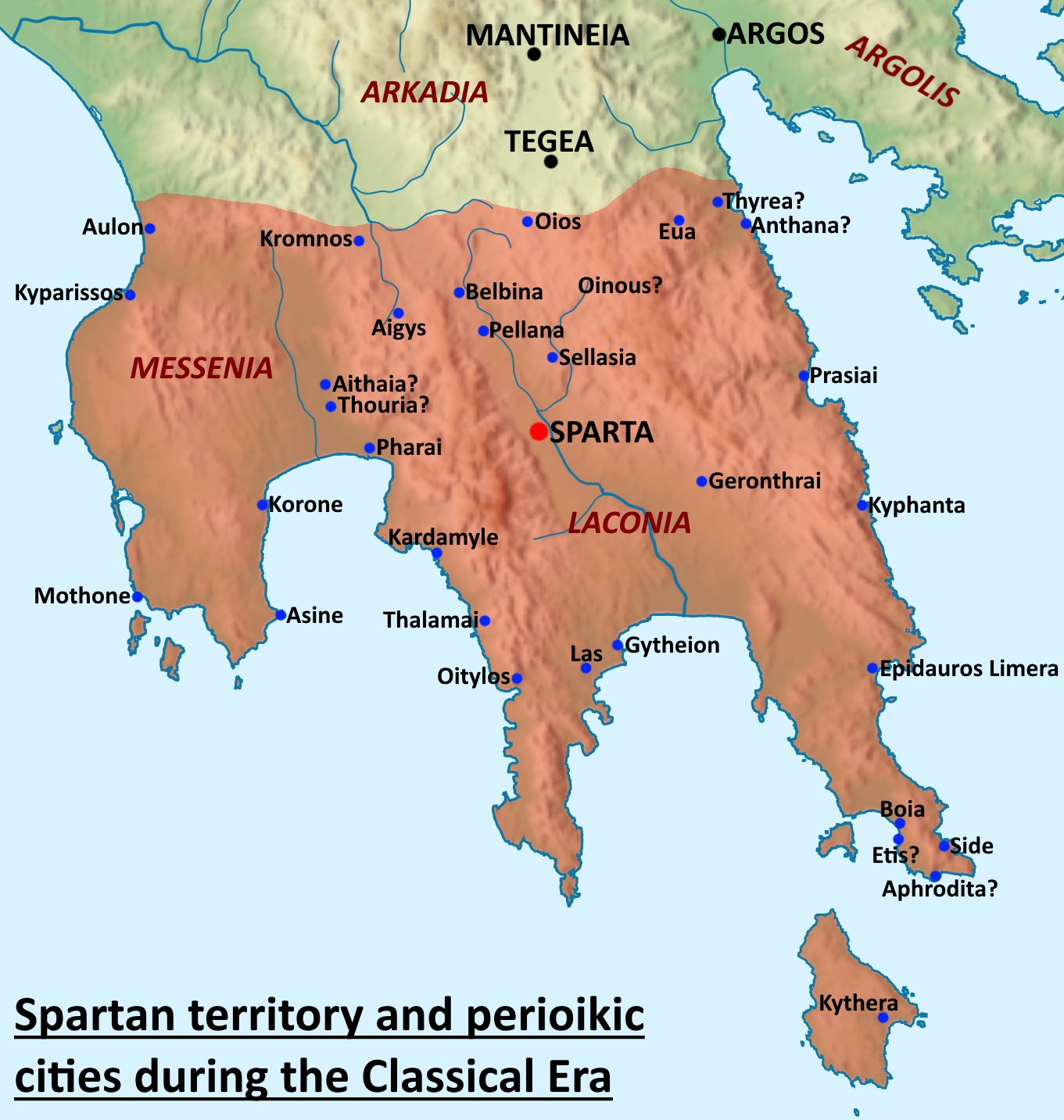
Perioeci
The Perioeci or Perioikoi (, ) were the second-tier citizens of the ''polis'' of Sparta until 200 BC. They lived in several dozen cities within Spartan territories (mostly Laconia and Messenia), which were dependent on Sparta. The ''perioeci'' only had political rights in their own city, while the course of the Spartan state exclusively belonged to Spartan citizens, or Spartiates. The name ''perioeci'' roughly means "those dwelling around/nearby", deriving from , ''peri'', "around", and , ''oîkos'', "dwelling, house". ''Perioeci'' and Spartans were collectively called the ''Lakedaimonians''. They had a central role in the Spartan economy, controlling commerce and business, as well as being responsible for crafts and manufacturing, including producing the weapons and armour of the Spartan army, as the higher-ranking Spartan citizens considered all commercial and money-making activities to be unworthy of them. The ''perioeci'' were also the only people allowed to freely travel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as Rome, Athens, Sparta, Carthage, and the Italian city-states during the Middle Ages and Renaissance, such as Florence, Venice, Genoa and Milan. With the rise of nation states worldwide, only a few modern sovereign city-states exist, with some disagreement as to which qualify; Monaco, Singapore and Vatican City are most commonly accepted as such. Singapore is the clearest example, with full self-governance, its own currency, a robust military and a population of 5.5 million. Several non-sovereign cities enjoy a high degree of autonomy and are sometimes considered city-states. Hong Kong, Macau, and members of the United Arab Emirates—most notably Dubai and Abu Dhabi—are often cited as such. Historical background Ancient and medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spartan Hegemony
The polis ''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, πόλις, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means "city" in Greek. In Ancient Greece, it originally referred to an administrative and religious city center, as distinct from the rest of the city. Later, it also ... of Sparta was the greatest Spartan army, military land power of classical Ancient Greece, Greek antiquity. During the classical Greece, Classical period, Sparta governed, dominated or influenced the entire Peloponnese. Additionally, the defeat of the Athenians and the Delian League in the Peloponnesian War in 431–404 BC resulted in a short-lived Spartan dominance of the southern Greek world from 404 to 371 BC.Jones, Nicholas F. ''Politics and Society in Ancient Greece.'' Westport, CT: Prager, 2008 Due to their mistrust of others, Spartans discouraged the creation of records about their internal affairs. The only histories of Sparta are from the writings of Xenophon, Thucydides, Herodotus and Plutarch, none of whom were Spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebes, Greece
Thebes (; ell, Θήβα, ''Thíva'' ; grc, Θῆβαι, ''Thêbai'' .) is a city in Boeotia, Central Greece. It played an important role in Greek myths, as the site of the stories of Cadmus, Oedipus, Dionysus, Heracles and others. Archaeological excavations in and around Thebes have revealed a Mycenaean settlement and clay tablets written in the Linear B script, indicating the importance of the site in the Bronze Age. Thebes was the largest city of the ancient region of Boeotia and was the leader of the Boeotian confederacy. It was a major rival of ancient Athens, and sided with the Persians during the 480 BC invasion under Xerxes I. Theban forces under the command of Epaminondas ended Spartan hegemony at the Battle of Leuctra in 371 BC, with the Sacred Band of Thebes, an elite military unit of male lovers celebrated as instrumental there. Macedonia would rise in power at the Battle of Chaeronea in 338 BC, bringing decisive victory to Philip II over an alliance of Thebes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Leuctra
The Battle of Leuctra ( grc-gre, Λεῦκτρα, ) was a battle fought on 6 July 371 BC between the Boeotians led by the Thebans, and the Spartans along with their allies amidst the post-Corinthian War conflict. The battle took place in the vicinity of Leuctra, a village in Boeotia in the territory of Thespiae. The Theban victory shattered Sparta's immense influence over the Greek peninsula, which Sparta had gained with its victory in the Peloponnesian War a generation earlier. Prelude In 371 BC, the newly established democracy of Thebes had elected four Boeotarchs, the traditional title of the generals of the Boeotian League, and so proclaimed their intention of reconstituting the aforementioned league that Sparta had disbanded.Tritle 1987, p. 80 During this period, Thebes had an ally in Athens, but Athens was far from happy with the treatment Plataea had received. When it came to swearing an oath to respect the treaty, Sparta swore on behalf of itself and its allies. When Ep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Aegospotami
The Battle of Aegospotami was a naval confrontation that took place in 405 BC and was the last major battle of the Peloponnesian War. In the battle, a Spartan fleet under Lysander destroyed the Athenian navy. This effectively ended the war, since Athens could not import grain or communicate with its empire without control of the sea. Prelude Lysander's campaigns In 405 BC, following the severe Spartan defeat at the Battle of Arginusae, Lysander, the commander who had been responsible for the first Spartan naval successes, was reinstated in command. Since the Spartan constitution prohibited any commander from holding the office of navarch more than once, he was appointed as a vice-admiral instead, with the clear understanding that this was a mere legal fiction. One of Lysander's advantages as a commander was his close relationship with the Persian prince Cyrus. Using this connection, he quickly raised the money to begin rebuilding the Spartan fleet. When Cyrus was recalled to Sus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Athens
Athens is one of the oldest named cities in the world, having been continuously inhabited for perhaps 5,000 years. Situated in southern Europe, Athens became the leading city of Ancient Greece in the first millennium BC, and its cultural achievements during the 5th century BC laid the foundations of Western civilization. During the early Middle Ages, the city experienced a decline, then recovered under the later Byzantine Empire and was relatively prosperous during the period of the Crusades (12th and 13th centuries), benefiting from Italian trade. Following a period of sharp decline under the rule of the Ottoman Empire, Athens in the 19th century as the capital of the independent and self-governing Greek state. Name The name of Athens, connected to the name of its patron goddess Athena, originates from an earlier Pre-Greek language. The origin myth explaining how Athens acquired this name through the legendary contest between Poseidon and Athena was described by Herodotus,H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Athens
The city of Athens ( grc, Ἀθῆναι, ''Athênai'' .tʰɛ̂ː.nai̯ Modern Greek: Αθήναι, ''Athine'' or, more commonly and in singular, Αθήνα, ''Athina'' .'θi.na during the classical period of ancient Greece (480–323 BC) was the major urban centre of the notable ''polis'' (city-state) of the same name, located in Attica, Greece, leading the Delian League in the Peloponnesian War against Sparta and the Peloponnesian League. Athenian democracy was established in 508 BC under Cleisthenes following the tyranny of Isagoras. This system remained remarkably stable, and with a few brief interruptions remained in place for 180 years, until 322 BC (aftermath of Lamian War). The peak of Athenian hegemony was achieved in the 440s to 430s BC, known as the Age of Pericles. In the classical period, Athens was a centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum, Athens was also the birthplace of Socrates, Plato, Pericles, Ari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greco-Persian Wars
The Greco-Persian Wars (also often called the Persian Wars) were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the Greeks and the enormous empire of the Persians began when Cyrus the Great conquered the Greek-inhabited region of Ionia in 547 BC. Struggling to control the independent-minded cities of Ionia, the Persians appointed tyrants to rule each of them. This would prove to be the source of much trouble for the Greeks and Persians alike. In 499 BC, the tyrant of Miletus, Aristagoras, embarked on an expedition to conquer the island of Naxos, with Persian support; however, the expedition was a debacle and, preempting his dismissal, Aristagoras incited all of Hellenic Asia Minor into rebellion against the Persians. This was the beginning of the Ionian Revolt, which would last until 493 BC, progressively drawing more regions of Asia Minor into the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |