|
Samoa
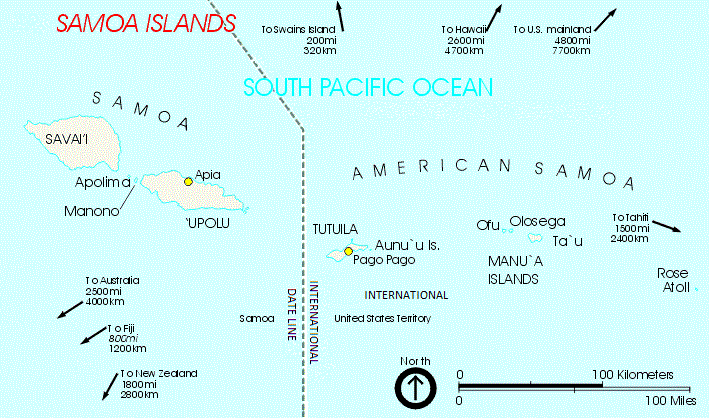
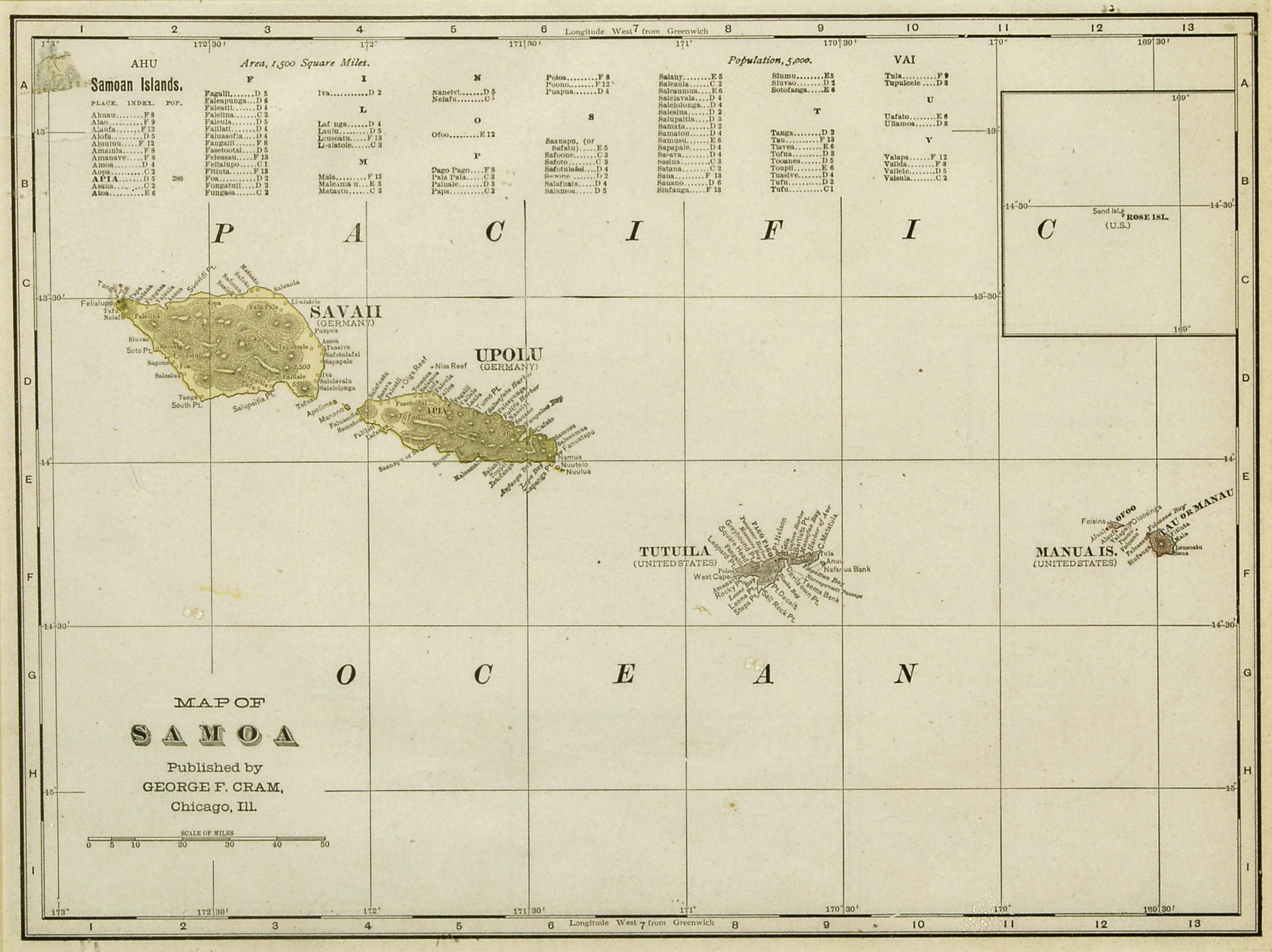
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa (), is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); and several smaller, uninhabited islands, including the Aleipata Islands ( Nu'utele, Nu'ulua, Fanuatapu and Namua). Samoa is located west of American Samoa, northeast of Tonga, northeast of Fiji, east of Wallis and Futuna, southeast of Tuvalu, south of Tokelau, southwest of Hawaii, and northwest of Niue. The capital and largest city is Apia. The Lapita people discovered and settled the Samoan Islands around 3,500 years ago. They developed a Samoan language and Samoan cultural identity. Samoa is a unitary parliamentary democracy with 11 administrative divisions. It is a sovereign state and a member of the Commonwealth of Nations. Western Samoa was admitted to the United Nations on 15 December 1976. Because of the Samoans' se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samoan Language
Samoan ( or ; ) is a Polynesian language spoken by Samoans of the Samoan Islands. Administratively, the islands are split between the sovereign country of Samoa and the United States territory of American Samoa. It is an official language, alongside English, in both jurisdictions. It is widely spoken across the Pacific region, heavily so in New Zealand and also in Australia and the United States. Among the Polynesian languages, Samoan is the most widely spoken by number of native speakers. Samoan is spoken by approximately 260,000 people in the archipelago and with many Samoans living in diaspora in a number of countries, the total number of speakers worldwide was estimated at 510,000 in 2015. It is the third-most widely spoken language in New Zealand, where 2.2% of the population, 101,900 people, were able to speak it as of 2018. The language is notable for the phonological differences between formal and informal speech as well as a ceremonial form used in Samoan oratory. Cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samoa National Anthem
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands (Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands (Manono Island, Manono and Apolima); and several smaller, uninhabited islands, including the Aleipata Islands (Nu'utele, Nu'ulua, Fanuatapu and Namua). Samoa is located west of American Samoa, northeast of Tonga (closest foreign country), northeast of Fiji, east of Wallis and Futuna, southeast of Tuvalu, south of Tokelau, southwest of Hawaii, and northwest of Niue. The capital city is Apia. The Lapita culture, Lapita people discovered and settled the Samoan Islands around 3,500 years ago. They developed a Samoan language and Samoan culture, Samoan cultural identity. Samoa is a Unitary state, unitary Parliamentary system, parliamentary democracy with 11 Administrative divisions of Samoa, administrative divisions. It is a sovereign state and a member of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Minister Of Samoa
The prime minister of the Independent State of Samoa ( sm, Palemia o le Malo Tuto’atasi o Sāmoa) is the head of government of Samoa. The prime minister is a member of the Legislative Assembly, and is appointed by the O le Ao o le Malo (Head of State) for a five-year term. Since independence in 1962, a total of seven individuals have served as prime minister. The incumbent was disputed due to the 2021 constitutional crisis, when Tuila'epa Sa'ilele Malielegaoi refused to accept the results of the 2021 general election. On 23 July 2021, the Samoan Court of Appeal ruled that the Faʻatuatua i le Atua Samoa ua Tasi (FAST) party had been in government since 24 May. Tuila'epa then conceded defeat, resulting in FAST party leader Fiamē Naomi Mataʻafa becoming prime minister. History of the office Colonial period The first prime minister during the colonial period was Albert Barnes Steinberger, who originally represented the American government in the Samoan Islands but w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atua
Atua are the gods and spirits of the Polynesian peoples such as the Māori mythology, Māori or the Hawaiian religion, Hawaiians (see also ); the Polynesian languages, Polynesian word literally means "power" or "strength" and so the concept is similar to that of ''mana''. Today, it is also used for the monotheistic conception of God. Especially powerful atua included: * ''Rongo, Rongo-mā-Tāne'' – god of agriculture and peace * ''Tāne, Tāne Mahuta'' – creator of all living things such as animals, birds and trees * ''Tangaroa'' – god of the sea * ''Tūmatauenga'' – a god of war * ''Whiro'' – god of darkness and evil In Samoa, where means "god" in the Samoan language, traditional pe'a, tattooing was based on the doctrine of tutelary spirits. There is also a district on the island of Upolu in Samoa called Atua (district), Atua. Atua or gods were also the center of Māori mythology, Māori religion. In Māori mythology, Māori's belief, there was no such word as "reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuimalealiʻifano Vaʻaletoʻa Sualauvi II
Afioga Tuimalealiʻifano Vaʻaletoʻa Eti Sualauvi II (born 29 April 1947) is a Samoan politician who is the current O le Ao o le Malo (head of state) of Samoa, in office since 2017. He was appointed to the Tama-a-ʻaiga title of Tuimalealiʻifano in July 1977, one of four paramount titles of Samoa. Biography Tuimalealiʻifano Vaʻaletoʻa Eti Sualauvi II is a member of the Tuimalealiʻifano family, a cadet branch of the Sā Tupua state dynasty and one of the four paramount titles of Samoa. He is married to Masiofo Faʻamausili Leinafo Tuimalealiʻifano. He is the great-grandson of one of the Mau movement leaders, Tuimaleali'ifano Fa'aoloi'i Si'ua'ana I, and grand-nephew of the sole Member of the Council of Deputies (1962–1974), Tui Aʻana Tuiaana Tuimaleali'ifano Suatipatipa II. Early career He worked as a policeman, lawyer and previously was a Samoan Police Chief Inspector and a secondary school teacher. He was a police officer in New Zealand for three years. He al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations. It is the world's largest and most familiar international organization. The UN is headquarters of the United Nations, headquartered on extraterritoriality, international territory in New York City, and has other main offices in United Nations Office at Geneva, Geneva, United Nations Office at Nairobi, Nairobi, United Nations Office at Vienna, Vienna, and Peace Palace, The Hague (home to the International Court of Justice). The UN was established after World War II with Dumbarton Oaks Conference, the aim of preventing future world wars, succeeding the League of Nations, which was characterized as ineffective. On 25 April 1945, 50 governments met in San Francisco for United Nations Conference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations Security Council Resolution 399
United Nations Security Council Resolution 399, adopted unanimously on December 1, 1976, after examining the application of the Western Samoa for membership in the United Nations, the Council recommended to the General Assembly that Samoa be admitted. See also * List of United Nations member states * List of United Nations Security Council Resolutions 301 to 400 This is a list of United Nations Security Council Resolutions 301 to 400 adopted between 20 October 1971 and 7 December 1976. See also * Lists of United Nations Security Council resolutions * List of United Nations Security Council Resoluti ... (1971–1976) ReferencesText of the Resolution at undocs.org External links * {{UNSCR 1976 0399 0399 0399 December 1976 events 1976 in Samoa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Samoa Trust Territory
Western Samoa Mandate, then Western Samoa Trust Territory, officially Territory of Western Samoa was the name of Western Samoa during its civil administration by New Zealand between 1920 and Samoan independence in 1962. Six years earlier, German Samoa was captured by the British shortly after the outbreak of World War I, but it would not be formally annexed by the British Empire until then. History Occupation of German Samoa in World War I At the outbreak of World War I German Samoa was a German colony. On 7 August 1914, the British government indicated to New Zealand (which was at this time a British dominion), that the seizure of a wireless station near Apia, the colony's capital which was used by the German East Asia Squadron, would be a "great and urgent Imperial service". This was followed by the first action of New Zealand in the war, the sailing of a Samoa Expeditionary Force on 15 August, which landed at Apia two weeks later. Although Germany refused to officiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Samoa
German Samoa (german: Deutsch-Samoa) was a German protectorate from 1900 to 1920, consisting of the islands of Upolu, Savai'i, Apolima and Manono, now wholly within the independent state of Samoa, formerly ''Western Samoa''. Samoa was the last German colonial acquisition in the Pacific basin, received following the Tripartite Convention signed at Washington on 2 December 1899 with ratifications exchanged on 16 February 1900.Ryden, George Herbert. ''The Foreign Policy of the United States in Relation to Samoa''. New York: Octagon Books, 1975. (Reprint by special arrangement with Yale University Press. Originally published at New Haven: Yale University Press, 1928), p. 574; the Tripartite Convention (United States, Germany, Great Britain) was signed at Washington on 2 December 1899 with ratifications exchanged on 16 February 1900 It was the only German colony in the Pacific, aside from the Kiautschou Bay concession in China, that was administered separately from German New Guine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tripartite Convention
The Tripartite Convention of 1899 concluded the Second Samoan Civil War, resulting in the formal partition of the Samoan archipelago into a German colony and a United States territory. Forerunners to the Tripartite Convention of 1899 were the Washington Conference of 1887, the Treaty of Berlin of 1889, and the Anglo-German Agreement on Samoa of 1899. Politics prior to the convention By the 1870s modern economic conditions were well established and accepted by the Samoans, who had just enough of a government that could be manipulated at will by the foreign business interests in Samoa. After the United States concluded a friendship treaty with Samoa in 1878, Germany negotiated her own Favorite Nation Treaty in 1879 with the same Samoan faction as the U.S., while later in 1879 the Anglo-Samoan treaty was completed with a rival faction. Contentions among the whites in Samoa, plus native factional strife led to side-choosing that became deadly warring with the introduction of mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Berlin (1889)
The Treaty of Berlin (1889) (also known as the Samoan Treaty) was the concluding document of the conference at Berlin in 1889 on Samoa. The conference was proposed by German foreign minister Count Herbert von Bismarck (son of chancellor Otto von Bismarck) to reconvene the adjourned Washington conference on Samoa of 1887. Herbert von Bismarck invited delegations from the United States and the British Empire to Berlin in April 1889. The treaty launched the condominium in Samoa between the United States, Germany and Great Britain. It was designed to guarantee the preservation of rights of the three powers as secured in separate treaties with the Samoan régime in 1878 and 1879. Further, the independence and neutrality of the Samoan government was ensured, public finance was reorganized and the Samoan king elected in 1881 was restored. The treaty established a court and the position of a "Chief Justice of Samoa" who would be appointed by all three powers. If they could not reach a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |