|
Rebellion (video Game)
Rebellion is a violent uprising against one's government. A rebel is a person who engages in a rebellion. A rebel group is a consciously coordinated group that seeks to gain political control over an entire state or a portion of a state. Classification An insurrection is an armed rebellion. A revolt is a rebellion with an aim to replace a government, authority figure, law, or policy. If a government does not recognize rebels as ''belligerents'' then they are ''insurgents'' and the revolt is an insurgency. In a larger conflict the ''rebels'' may be recognized as ''belligerents'' without their government being recognized by the established government, in which case the conflict becomes a '' civil war''. Civil resistance movements have often aimed at, and brought about, the fall of a government or head of state, and in these cases could be considered a form of ''rebellion''. In many of these cases, the opposition movement saw itself not only as nonviolent, but also as uph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prise De La Bastille
The Storming of the Bastille (french: Prise de la Bastille ) occurred in Paris, France, on 14 July 1789, when revolutionary insurgents stormed and seized control of the medieval armoury, fortress, and political prison known as the Bastille. At the time, the Bastille represented royal authority in the centre of Paris. The prison contained only seven inmates at the time of its storming, but was seen by the revolutionaries as a symbol of the monarchy's abuse of power; its fall was the flashpoint of the French Revolution. In France, 14 July is a national holiday, usually called Bastille Day in English. However, the expression Bastille Day is properly incorrect, as the event celebrated during the national holiday is the Fête de la Fédération of 1790, which was itself the 1st anniversary of the Bastille Day. Background During the reign of Louis XVI France faced a major economic crisis. This crisis was caused in part by the cost of intervening in the American Revolution and exacerb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Violence
Political violence is violence which is perpetrated in order to achieve political goals. It can include violence which is used by a state against other states ( war), violence which is used by a state against civilians and non-state actors ( forced disappearance, psychological warfare, police brutality, state terrorism, targeted assassinations, torture, ethnic cleansing, or genocide), and violence which is used by violent non-state actors against states and civilians (kidnappings, targeted assassinations, terrorist attacks, torture, psychological and/or guerrilla warfare). It can also describe politically-motivated violence which is used by violent non-state actors against a state (rebellion, rioting, treason, or coup d'etat) or it can describe violence which is used against other non-state actors and/or civilians. Non-action on the part of a government can also be characterized as a form of political violence, such as refusing to alleviate famine or otherwise denying resour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smallholding
A smallholding or smallholder is a small farm operating under a small-scale agriculture model. Definitions vary widely for what constitutes a smallholder or small-scale farm, including factors such as size, food production technique or technology, involvement of family in labor and economic impact. Smallholdings are usually farms supporting a single family with a mixture of cash crops and subsistence farming. As a country becomes more affluent, smallholdings may not be self-sufficient, but may be valued for the rural lifestyle. As the sustainable food and local food movements grow in affluent countries, some of these smallholdings are gaining increased economic viability. There are an estimated 500 million smallholder farms in developing countries of the world alone, supporting almost two billion people. Small-scale agriculture is often in tension with industrial agriculture, which finds efficiencies by increasing outputs, monoculture, consolidating land under big agri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Rider Problem
In the social sciences, the free-rider problem is a type of market failure that occurs when those who benefit from resources, public goods (such as public roads or public library), or services of a communal nature do not pay for them or under-pay. Free riders are a problem because while not paying for the good (either directly through fees or tolls or indirectly through taxes), they may continue to access or consume it. Thus, the good may be under-produced, overused or degraded. Additionally, it has been shown that despite evidence that people tend to be cooperative by nature, the presence of free-riders cause this prosocial behaviour to deteriorate, perpetuating the free-rider problem. The free-rider problem in social science is the question of how to limit free riding and its negative effects in these situations. Such an example is the free-rider problem of when property rights are not clearly defined and imposed. The free-rider problem is common with public goods which are no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collective Action Theory
The collective action theory was first published by Mancur Olson in 1965. Olson argues that any group of individuals attempting to provide a public good has difficulty doing so efficiently. On the one hand individuals have incentives to " free-ride" on the efforts of others in certain groups and on the other hand the size of a group is of high importance and difficult to optimally determine. Basic theory of groups Purpose of organizations The primary function of an organization is the furtherance of common interests of groups of individuals. In general, an organization will fail if it does not further the common interest of its members. If such a common interest exists, any unorganized action by an individual will either fail in advancing the common interest at all or will not be able to advance the interest in a suitable way. However, each member of the organization has his or her own individual interests which differ from the interests of other members. Public goods Pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Good (economics)
In economics Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analy ..., a public good (also referred to as a social good or collective good)Oakland, W. H. (1987). Theory of public goods. In Handbook of public economics (Vol. 2, pp. 485-535). Elsevier. is a Good (economics), good that is both excludable, non-excludable and rivalry (economics), non-rivalrous. For such goods, users cannot be barred from accessing or using them for failing to pay for them. Also, use by one person neither prevents access of other people nor does it reduce availability to others. Therefore, the good can be used simultaneously by more than one person. This is in contrast to a Common good (economics), common good, such as wild fish stocks in the ocean, which is non-excludable but rivalrous to a certain degree. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tragedy Of The Commons
Tragedy (from the grc-gre, τραγῳδία, ''tragōidia'', ''tragōidia'') is a genre of drama based on human suffering and, mainly, the terrible or sorrowful events that befall a main character. Traditionally, the intention of tragedy is to invoke an accompanying catharsis, or a "pain hatawakens pleasure", for the audience. While many cultures have developed forms that provoke this paradoxical response, the term ''tragedy'' often refers to a specific tradition of drama that has played a unique and important role historically in the self-definition of Western civilization. That tradition has been multiple and discontinuous, yet the term has often been used to invoke a powerful effect of cultural identity and historical continuity—"the Greeks and the Elizabethans, in one cultural form; Hellenes and Christians, in a common activity," as Raymond Williams puts it. From its origins in the theatre of ancient Greece 2500 years ago, from which there survives only a frac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Logic Of Collective Action
''The Logic of Collective Action: Public Goods and the Theory of Groups'' is a book by Mancur Olson Jr. published in 1965. It develops a theory of political science and economics of concentrated benefits versus diffuse costs. Its central argument is that concentrated minor interests will be overrepresented and diffuse majority interests trumped, due to a free-rider problem that is stronger when a group becomes larger. Overview The book challenged accepted wisdom in Olson's day that: # if everyone in a group (of any size) has interests in common, then they will act collectively to achieve them; and # in a democracy, the greatest concern is that the majority will tyrannize and exploit the minority. The book argues instead that individuals in any group attempting collective action will have incentives to " free ride" on the efforts of others if the group is working to provide public goods. Individuals will not "free ride" in groups that provide benefits only to active participants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mancur Olson
Mançur Lloyd Olson Jr. (; January 22, 1932 – February 19, 1998) was an American economist and political scientist who taught at the University of Maryland, College Park. His most influential contributions were in institutional economics, and in the role which private property, taxation, public goods, collective action, and contract rights play in economic development. Early life and education Olson was born on January 22, 1932, in Grand Forks, North Dakota, to a family of Norwegian immigrants. He grew up on a farm near Buxton, North Dakota, next to the state border with Climax, Minnesota. Olson claimed that his given name, Mançur, was common throughout Scandinavian-immigrant communities in North America and was a variation of the Arabic name Mansoor. Olson graduated from North Dakota State University in 1954 and was a Rhodes Scholar at University College, Oxford until 1956, before earning a PhD in economics from Harvard in 1963. He also served in the U.S. Air Force for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
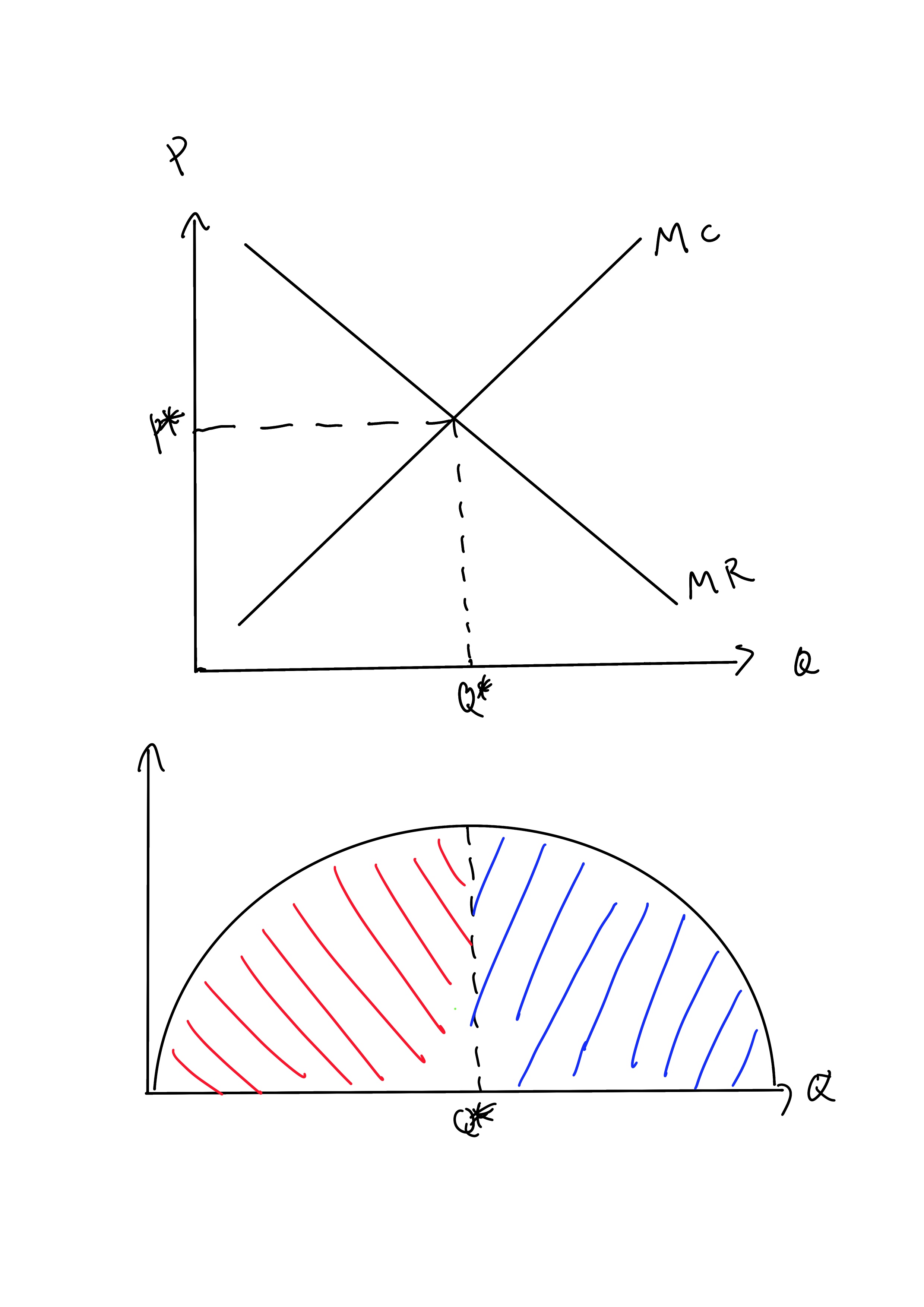
Profit Maximization
In economics, profit maximization is the short run or long run process by which a firm may determine the price, input and output levels that will lead to the highest possible total profit (or just profit in short). In neoclassical economics, which is currently the mainstream approach to microeconomics, the firm is assumed to be a " rational agent" (whether operating in a perfectly competitive market or otherwise) which wants to maximize its total profit, which is the difference between its total revenue and its total cost. Measuring the total cost and total revenue is often impractical, as the firms do not have the necessary reliable information to determine costs at all levels of production. Instead, they take a more practical approach by examining how small changes in production influence revenues and costs. When a firm produces an extra unit of product, the additional revenue gained from selling it is called the marginal revenue (\text), and the additional cost to pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Tilly
Charles Tilly (May 27, 1929 – April 29, 2008) was an American sociologist, political scientist, and historian who wrote on the relationship between politics and society. He was a professor of history, sociology, and social science at the University of Michigan from 1969 to 1984 before becoming the Joseph L. Buttenwieser Professor of Social Science at Columbia University. He has been described as "the founding father of 21st-century sociology" and "one of the world's preeminent sociologists and historians." He published widely across topics such as urban sociology, state formation, democracy, social movements, labor, and inequality. He was an influential proponent of large-scale historical social science research. The title of Tilly's 1984 book ''Big Structures, Large Processes, Huge Comparisons'' is characteristic of his particular approach to social science research. Early life and education Tilly was born in Lombard, Illinois (near Chicago). His parents were Naneth and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Deprivation Thesis
Relative deprivation is the lack of resources to sustain the diet, lifestyle, activities and amenities that an individual or group are accustomed to or that are widely encouraged or approved in the society to which they belong. Peter Townsend, ''Poverty in the United Kingdom : A Survey of household resources and standards of living'', Penguin Books, 1979,/ref> Measuring relative deprivation allows an objective comparison between the situation of the individual or group compared to the rest of society. Relative deprivation may also emphasise the individual experience of discontent when being deprived of something to which one believes oneself to be entitled, however emphasizing the perspective of the individual makes objective measurement problematic. Iain Walker, Heather J. Smith, ''Relative Deprivation: Specification, Development, and Integration'', Cambridge University Press, 2001, Google Books/ref> It is a term used in social sciences to describe feelings or measures of economic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |