|
Zygomycosis
Zygomycosis is the broadest term to refer to infections caused by ''bread mold fungi'' of the zygomycota phylum. However, because zygomycota has been identified as polyphyletic, and is not included in modern fungal classification systems, the diseases that zygomycosis can refer to are better called by their specific names: mucormycosis (after Mucorales), phycomycosis (after Phycomycetes) and basidiobolomycosis (after Basidiobolus). These rare yet serious and potentially life-threatening fungal infections usually affect the face or oropharyngeal (nose and mouth) cavity. Zygomycosis type infections are most often caused by common fungi found in soil and decaying vegetation. While most individuals are exposed to the fungi on a regular basis, those with immune disorders (immunocompromised) are more prone to fungal infection. These types of infections are also common after natural disasters, such as tornadoes or earthquakes, where people have open wounds that have become filled with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basidiobolus
''Basidiobolus ranarum'' is a filamentous fungus with worldwide distribution. The fungus was first isolated by Eidam in 1886. It can saprophytically live in the intestines of mainly cold-blooded vertebrates and on decaying fruits and soil. The fungus prefers glucose as a carbon source and grows rapidly at room temperature. ''Basidiobolus ranarum'' is also known as a cause of subcutaneous zygomycosis, usually causing granulomatous infections on a host's limbs. Infections are generally geographically limited to tropical and subtropical regions such as East and West Africa. Subcutaneous zygomycosis caused by ''B. ranarum'' is a rare disease and predominantly affects children and males. Common subcutaneous zygomycosis shows characteristic features and is relatively easy to be diagnosed; while, certain rare cases might show non-specific clinical features that might pose a difficulty on its identification. Although disease caused by this fungus is known to resolve spontaneously on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomycosis
Zygomycosis is the broadest term to refer to infections caused by ''bread mold fungi'' of the zygomycota phylum. However, because zygomycota has been identified as polyphyletic, and is not included in modern fungal classification systems, the diseases that zygomycosis can refer to are better called by their specific names: mucormycosis (after Mucorales), phycomycosis (after Phycomycetes) and basidiobolomycosis (after Basidiobolus). These rare yet serious and potentially life-threatening fungal infections usually affect the face or oropharyngeal (nose and mouth) cavity. Zygomycosis type infections are most often caused by common fungi found in soil and decaying vegetation. While most individuals are exposed to the fungi on a regular basis, those with immune disorders (immunocompromised) are more prone to fungal infection. These types of infections are also common after natural disasters, such as tornadoes or earthquakes, where people have open wounds that have become filled with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
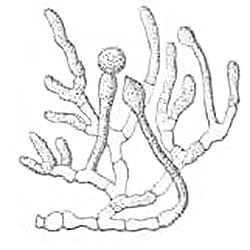
Apophysomyces
''Apophysomyces'' is a genus of filamentous fungi that are commonly found in soil and decaying vegetation. Species normally grow in tropical to subtropical regions. The genus ''Apophysomyces'' historically was monospecific, containing only the type species ''Apophysomyces elegans''. In 2010, three new species were described: ''variabilis'', ''trapeziformis'', and ''ossiformis''. Characteristics Among the other members of zygomycetes, ''Apophysomyces elegans'' mostly resembles those from genus ''Absidia''. However, its bell-shaped (although not conical) apophyses (outgrowth), the existence of its foot-cell like hyphal segment, rhizoids produced opposite to the sporangiophores upon cultivation on plain agar, the darker and thicker subapical segment, and inability to sporulate on routine culture media help in distinguishing ''Apophysomyces elegans''.Davise H. Larone, "Medically Important Fungi - A Guide to Identification", 3rd ed. (1995). (ASM Press, Washington, D.C.). (ISBN is fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
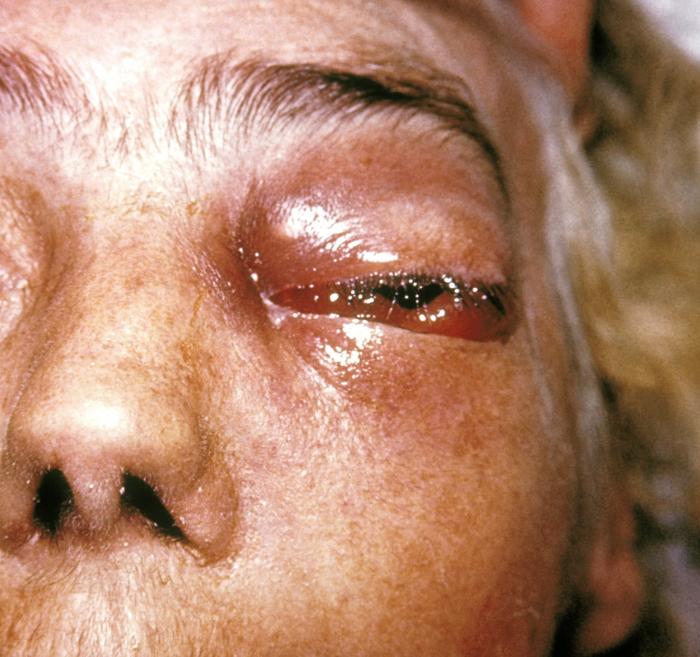
Mucormycosis
Mucormycosis, also known as black fungus, is a serious fungal infection that comes under fulminant fungal sinusitis, usually in people who are immunocompromised. It is curable only when diagnosed early. Symptoms depend on where in the body the infection occurs. It most commonly infects the nose, sinuses, eye, and brain resulting in a runny nose, one-sided facial swelling and pain, headache, fever, blurred vision, bulging or displacement of the eye (proptosis), and tissue death. Other forms of disease may infect the lungs, stomach and intestines, and skin. It is spread by spores of molds of the order Mucorales, most often through inhalation, contaminated food, or contamination of open wounds. These fungi are common in soils, decomposing organic matter (such as rotting fruit and vegetables), and animal manure, but usually do not affect people. It is not transmitted between people. Risk factors include diabetes with persistently high blood sugar levels or diabetic ketoacido ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phycomycosis
Phycomycosis is an uncommon condition of the gastrointestinal tract and skin most commonly found in dogs and horses. The condition is caused by a variety of molds and fungi, and individual forms include pythiosis, zygomycosis, and lagenidiosis. Pythiosis is the most common type and is caused by ''Pythium'', a type of water mould. Zygomycosis can also be caused by two types of zygomycetes, ''Entomophthorales'' (such as '' Basidiobolus'' and ''Conidiobolus'') and ''Mucorales'' (such as ''Mucor'', ''Mortierella'', ''Absidia'', ''Rhizopus'', ''Rhizomucor'', and ''Saksenaea''). The latter type of zygomycosis is also referred to as mucormycosis. Lagenidiosis is caused by a ''Lagenidium'' species, which like ''Pythium'' is a water mould. Since both pythiosis and lagenidiosis are caused by organisms from the class Oomycetes, they are sometimes collectively referred to as oomycosis. Pythiosis Pythiosis is caused by ''Pythium insidiosum'' and occurs most commonly in dogs and horses, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apophysomyces Trapeziformis
''Apophysomyces'' is a genus of filamentous fungi that are commonly found in soil and decaying vegetation. Species normally grow in tropical to subtropical regions. The genus ''Apophysomyces'' historically was monospecific, containing only the type species ''Apophysomyces elegans''. In 2010, three new species were described: ''variabilis'', ''trapeziformis'', and ''ossiformis''. Characteristics Among the other members of zygomycetes, ''Apophysomyces elegans'' mostly resembles those from genus ''Absidia''. However, its bell-shaped (although not conical) apophyses (outgrowth), the existence of its foot-cell like hyphal segment, rhizoids produced opposite to the sporangiophores upon cultivation on plain agar, the darker and thicker subapical segment, and inability to sporulate on routine culture media help in distinguishing ''Apophysomyces elegans''.Davise H. Larone, "Medically Important Fungi - A Guide to Identification", 3rd ed. (1995). (ASM Press, Washington, D.C.). (ISBN is fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apophysomyces Elegans
''Apophysomyces'' is a genus of filamentous fungi that are commonly found in soil and decaying vegetation. Species normally grow in tropical to subtropical regions. The genus ''Apophysomyces'' historically was monospecific, containing only the type species ''Apophysomyces elegans''. In 2010, three new species were described: ''variabilis'', ''trapeziformis'', and ''ossiformis''. Characteristics Among the other members of zygomycetes, ''Apophysomyces elegans'' mostly resembles those from genus ''Absidia''. However, its bell-shaped (although not conical) apophyses (outgrowth), the existence of its foot-cell like hyphal segment, rhizoids produced opposite to the sporangiophores upon cultivation on plain agar, the darker and thicker subapical segment, and inability to sporulate on routine culture media help in distinguishing ''Apophysomyces elegans''.Davise H. Larone, "Medically Important Fungi - A Guide to Identification", 3rd ed. (1995). (ASM Press, Washington, D.C.). (ISBN is fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizomucor Pusillus
''Rhizomucor pusillus'' is a species of ''Rhizomucor''. It can cause disease in humans. ''R. pusillus'' is a grey mycelium fungi most commonly found in compost piles. Yellow-brown spores grow on a stalk to reproduce more fungal cells. Biology ''Rhizomucor pusillus'' is a thermophilic fungus that lives in hot environments. Its growth optimum is between 50 and 70 degrees Celsius. It is a good producer of amylase. It is homothallic and can cause infections in humans and animals. ''R. pusillus'' cells have stolons, rhizoids, and branched sporangiophores. Because of the high temperatures required for this microorganism, it is difficult to study in laboratory environments. The ability to utilize different carbon sources can be used differentiate this fungus from other species: it is unable to assimilate sucrose, glycine, phenylalanine, and B-alanine. Diversity There are three species in the genus ''Rhizomucor''. ''R. pusillus'', '' R. miehei'', and ''R.hizomucor variabilis''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antifungal Drug
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually yes obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). Types of antifungal There are two types of antifungals: local and systemic. Local antifungals are usually administered topically or vaginally, depending on the condition being treated. Systemic antifungals are administered orally or intravenously. Of the clinically employed azole antifungals, only a handful are used systemically. These include ketoconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole, fosfluconazole, voriconazole, posaconazole, and isavuconazole. Examples of non-azole systemic antifungals include griseofulvin and terbinafine. Classes Polyenes A polyene is a molecule with multiple conjugated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucorales
The Mucorales is the largest and best studied order of zygomycete fungi. Members of this order are sometimes called pin molds. The term mucormycosis is now preferred for infections caused by molds belonging to the order Mucorales. Systematics The order includes: 11 families, 56 genera, and approximately 300 species. Mucoralean classification has traditionally been based on morphological, developmental, and ecological characteristics. Recently, molecular data has revealed, that some aspects of traditional classification are quite artificial. For example, the Mucoraceae is believed to be polyphyletic, as are the Thamnidiaceae, Chaetocladiaceae and Radiomycetaceae. Some of the genera, (including ''Mucor'', ''Absidia'' and ''Backusella'') appear to be polyphyletic. Today, the traditional system is still largely in use, as further studies are needed to reconcile morphological and molecular concepts of families and genera. Families The order consists of the following families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absidia Corymbifera
''Lichtheimia corymbifera'' is a thermophilic fungus in the phylum Zygomycota. It normally lives as a saprotrophic mold, but can also be an opportunistic pathogen known to cause pulmonary, CNS, rhinocerebral, or cutaneous infections in animals and humans with impaired immunity. Appearance ''Lichtheimia corymbifera'' was originally described as ''Mucor corymbifer'' in 1884 by Lichtheim from clinical isolations in Wrocław, Poland. At the time of the description, the species epithet, "corymbifer" was attributed to Cohn. In 1903, the fungus was transferred to the mucoralean genus ''Lichtheimia'' (honoring Lichtheim) by Jules Vuillemin as ''L. corymbifera''. In 1912 the species was again transferred by Saccardo and Trotter to the genus ''Absidia'' as ''A. corymbifera'' where it remained for most of the 20th century. Alastruey-Izquierdo and colleagues in 1991 transferred the species to the genus ''Mycocladus'', described originally by Beauverie in 1900. The type of ''Mycocladus'' ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucoraceae
The Mucoraceae are a family of fungi of the order Mucorales, characterized by having the thallus not segmented or ramified. Pathogenic genera include ''Absidia'', ''Apophysomyces'', ''Mucor'', ''Rhizomucor'', and ''Rhizopus''. According to a 2008 estimate, the family contains 25 genera and 129 species. Genera The family consists of the following genera: * '' Actinomucor'' * ''Apophysomyces'' * '' Benjaminiella'' * '' Chaetocladium'' * ''Circinella'' * ''Cokeromyces'' * ''Dicranophora'' * '' Ellisomyces'' * ''Helicostylum'' * '' Hyphomucor'' * '' Kirkomyces'' * ''Mucor'' * '' Parasitella'' * ''Pilaira'' * '' Pilophora'' * '' Pirella'' * ''Rhizomucor'' * '' Rhizopodopsis'' * ''Rhizopus'' * '' Sporodiniella'' * '' Syzygites'' * ''Thamnidium ''Thamnidium'' is a genus of fungi belonging to the family Mucoraceae. The genus was circumscribed in 1809 by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link. ''Thamnidium'' molds are key participants in the aging process for dry aged beef, producing prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |