|
Zhou–Chu War
The Zhou–Chu War was a military conflict between the Zhou dynasty under King Zhao and the state of Chu from 961 to 957 BC. King Zhao personally led at least two major campaigns against Chu and other states and tribes of the middle Yangtze region, initially conquering the lands north of the Yangtze and the Han River valley. Eventually, however, the Zhou forces suffered a crushing defeat, with half of their armed forces as well as King Zhao killed, subsequently losing control of much conquered territory. The war ended the era of Western Zhou's early expansion and forced it into the defense against foreign aggressors. On the other side, Chu consolidated its de facto independence and would continue to grow into one of the most powerful states of China. Background The middle Yangtze area The war took place in the middle Yangtze region, which was dominated by marshes, swamps, and mountains, but still very fertile and extremely rich in ores like gold, copper and tin. As r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubei
Hubei (; ; alternately Hupeh) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, and is part of the Central China region. The name of the province means "north of the lake", referring to its position north of Dongting Lake. The provincial capital, Wuhan, serves as a major transportation hub and the political, cultural, and economic hub of central China. Hubei's name is officially abbreviated to "" (), an ancient name associated with the eastern part of the province since the State of E of the Western Zhou dynasty of –771 BCE; a popular name for Hubei is "" () (suggested by that of the powerful State of Chu, which existed in the area during the Eastern Zhou dynasty of 770 – 256 BCE). Hubei borders the provinces of Henan to the north, Anhui to the east, Jiangxi to the southeast, Hunan to the south, Chongqing to the west, and Shaanxi to the northwest. The high-profile Three Gorges Dam is located at Yichang, in the west of the province. Hubei is the 7th-largest p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marsh
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found at the edges of lakes and streams, where they form a transition between the aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. They are often dominated by grasses, rushes or reeds. If woody plants are present they tend to be low-growing shrubs, and the marsh is sometimes called a carr. This form of vegetation is what differentiates marshes from other types of wetland such as swamps, which are dominated by trees, and mires, which are wetlands that have accumulated deposits of acidic peat. Marshes provide habitats for many kinds of invertebrates, fish, amphibians, waterfowl and aquatic mammals. This biological productivity means that marshes contain 0.1% of global sequestered terrestrial carbon. Moreover, they have an outsized influence on climate resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
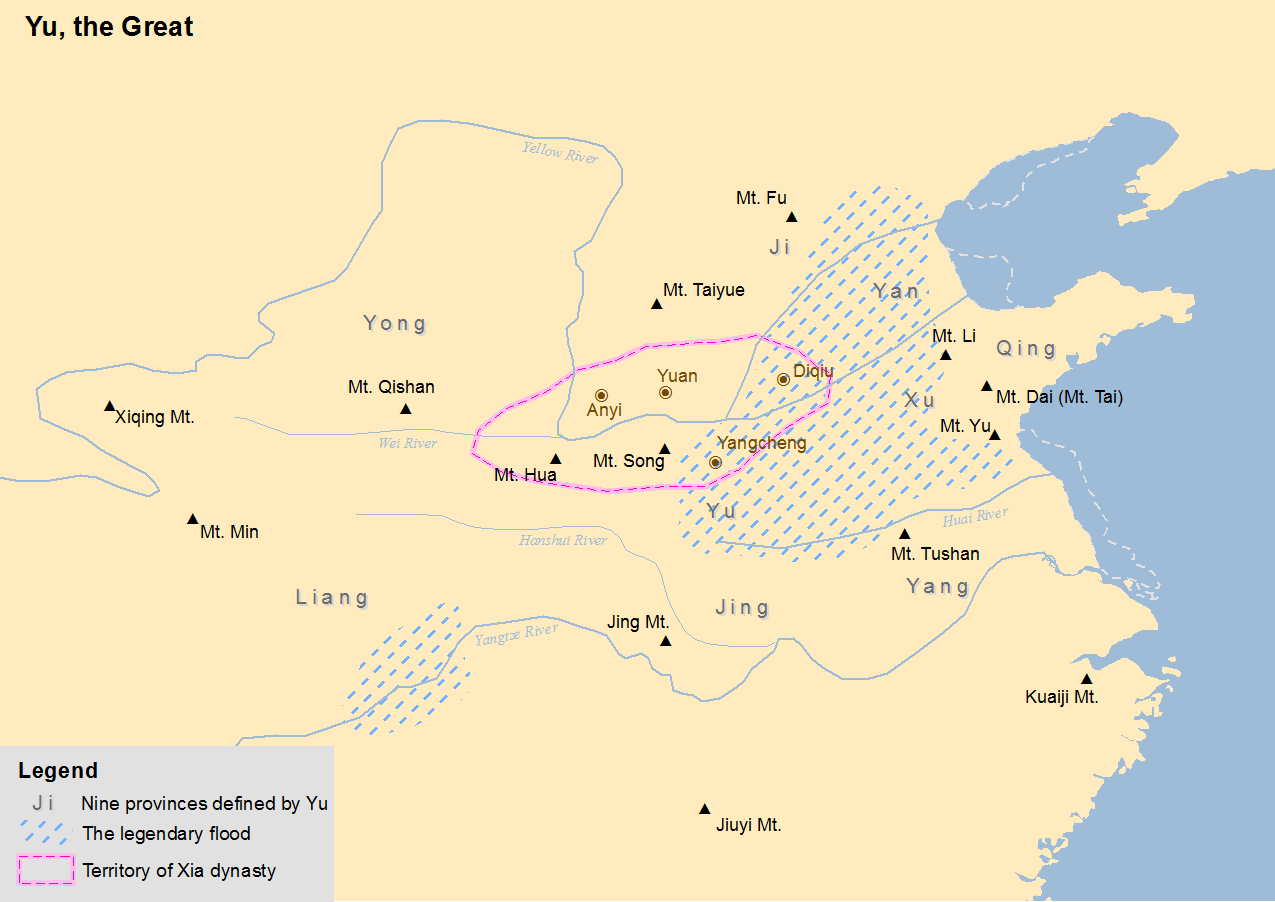
Jing Mountains
The Jingshan or Jing Mountains () are a chain of mountains in the western part of Nanzhang County, Hubei Province, People’s Republic of China. Stretching for around 150 kilometers, their peaks range in height from 1200 to about 1800 meters above sea level with the highest peak, Mount Julong (), reaching an elevation of 1852 meters. The Jingshan Mountains can be thought of as the easternmost extension of the Daba Mountains, separating the basin of the Han River (a tributary of the Yangtze) in the north from the rest of the Yangtze basin (in the south). The River Ju () and River Zhang (), both tributaries of the Yangtze River as well as the Han River tributary the River Man () have their source in the Jingshan Mountains. In ancient times, the Jingshan Mountains were at the heart of the Zhou Dynasty (1046-256 BCE) vassal State of Chu.Sima Qian, ''Records of the Grand Historian'' See also * Shennongjia Massif - to the west * Wudang Mountains The Wudang Mountains () consist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dan River (China)
The Dan River (), formerly known as the Dan Shui (丹水) or 800 ''Li'' Black River (八百里黑江), is a river located in Shaanxi province in the People's Republic of China. The longest tributary of the Han River, the Dan rises at Heilongkou (黑龙口) in the Qin Mountains of Shaanxi province then flows south east through Shangluo City, Danfeng County, Shangnan County and Xichuan County, Henan province before joining the Han River at Danjiangkou, Hubei province. Origin of the name There are three different theories as to how the Dan River got its name: *When the Black River (黑水) flooded in ancient times, Yu the Great assigned Dan Zhu the task of bringing it under control. Dan Zhu died during the work so the local people renamed the Black River in his honor. *Following the Battle of Changping between the States of Qi and Zhao during the Warring States period (771–426 BCE), 400,000 bodies were dumped in the river causing its waters to turn red. Since in Chinese "丹 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xia Dynasty
The Xia dynasty () is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, the Xia dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great, after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In traditional historiography, the Xia was later succeeded by the Shang dynasty. There are no contemporaneous records of the Xia, who are not mentioned in the oldest Chinese texts, since the earliest oracle bone inscriptions date from the late Shang period (13th century BC). The earliest mentions occur in the oldest chapters of the '' Book of Documents'', which report speeches from the early Western Zhou period and are accepted by most scholars as dating from that time. The speeches justify the Zhou conquest of the Shang as the passing of the Mandate of Heaven and liken it to the succession of the Xia by the Shang. That political philosophy was promoted by the Confucian school in the Eastern Zhou period. The succession of dynasties was incorporat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north into hillier areas in the south and east, it shares a border with Anhui to the north, Zhejiang to the northeast, Fujian to the east, Guangdong to the south, Hunan to the west, and Hubei to the northwest. The name "Jiangxi" is derived from the circuit administrated under the Tang dynasty in 733, Jiangnanxidao (; Gan: Kongnomsitau). The abbreviation for Jiangxi is "" (; Gan: Gōm), for the Gan River which runs across from the south to the north and flows into the Yangtze River. Jiangxi is also alternately called ''Ganpo Dadi'' () which literally means the "Great Land of Gan and Po". After the fall of the Qing dynasty, Jiangxi became one of the earliest bases for the Communists and many peasants were recruited to join the growing people's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wucheng Culture
The Wucheng culture (吳城文化) was a Bronze Age archaeological culture in Jiangxi, China. The initial site, spread out over , was discovered at Wucheng Township, Jiangxi. Located on the Gan River, the site was first excavated in 1973. The Wucheng culture probably developed in response to cultural contacts with the expanding Erligang culture, melding Erligang influences with local traditions. The Wucheng culture was a distinct contemporary of Sanxingdui and Yinxu (Anyang). The site at Wucheng was a regional protoporcelain production center; the culture is known for its distinctive geometric pottery. The Wucheng culture is also known for its bronze bells, the clapperless ''nao''. The Wucheng site at Xingan (archaeological site), Xingan contained a rich cache of localized bronze vessels. The bronze axes were similar to those of the Dong Dau culture in the Red River (Asia), Red River valley. The earliest period, around 1600 BCE, contemporaneous with late Erligang, yielded pottery s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oracle Bone
Oracle bones () are pieces of ox scapula and turtle plastron, which were used for pyromancy – a form of divination – in ancient China, mainly during the late Shang dynasty. ''Scapulimancy'' is the correct term if ox scapulae were used for the divination, ''plastromancy'' if turtle plastrons were used. Diviners would submit questions to deities regarding future weather, crop planting, the fortunes of members of the royal family, military endeavors, and other similar topics. These questions were carved onto the bone or shell in oracle bone script using a sharp tool. Intense heat was then applied with a metal rod until the bone or shell cracked due to thermal expansion. The diviner would then interpret the pattern of cracks and write the prognostication upon the piece as well. Pyromancy with bones continued in China into the Zhou dynasty, but the questions and prognostications were increasingly written with brushes and cinnabar ink, which degraded over time. The oracle bones be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yueyang
Yueyang, formerly known as Yuezhou or Yochow, is a prefecture-level city on the eastern shores of Dongting Lake and Yangtze in the northeastern corner of Hunan Province in the People's Republic of China. Yueyang has an administrative area of and the city proper, . The population was 5,051,922 at the 2020 Chinese census whom 1,134,058 lived in the built-up (or metro) area made up of Yueyanglou District and Yunxi District, Junshan District not being conurbated. Yueyang is the only international trade port city in Hunan and a famous port city in China, at the same time, Yueyang's comprehensive economic strength ranks of Hunan second only to Changsha, the provincial capital. The city's most famous attractions are the Yueyang Tower and Dongting Lake. The most famous food is Dongting lake silver fish (). In 2021, the city's permanent resident population was 5,051,922, a decrease of 424,162 from the end of last year. Administration The Yueyang prefecture is made up of six outlyin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huangshi
Huangshi (), alternatively romanized as Hwangshih, is a prefecture-level city in southeastern Hubei province, People's Republic of China. Its population was 2,469,079 inhabitants at the 2020 census; 1,567,108 of whom lived in the built-up (''or metro'') area made up of 4 urban districts plus the city of Daye, now being part of the agglomeration. History In 845 BC Marquis Wen () Huang Meng (), or Huang Zhang () moved the capital of the State of Huang from Yicheng to Huangchuan (present-day Huangchuan, Henan). Huang Xi's descendants ruled State of Huang until 648 BC when it was destroyed by the State of Chu. The Marquis of Huang, Marquis Mu () Huang Qisheng (), fled to the state of Qi. The people of Huang were forced to relocate to Chu. They settled in the region of present-day Hubei province, in a region known as the Jiangxia Prefecture () during the Han dynasty (206 BC-AD 220). On 9 March 1944, 18 CACW B-25s escorted by 24 P-40s bombed a foundry and floating docks at Huangsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panlongcheng
Panlongcheng () or Panlong City is an archaeological site associated with the Erligang culture () during the Shang dynasty period (). The site is located just north of the Yangtze river, on the bank of the Panlong lake, and is surrounded by the Fushui river in Huangpi, Wuhan, Hubei, China. Panlongcheng is the largest excavated Erligang site ( at its greatest), showing the southernmost reach of the Erligang culture at its peak. It was discovered in 1954, and excavated in 1974 and 1976. The site at Panlongcheng was sparsely inhabited during the Erlitou period (), consisting mainly of several small settlements and occupying an area of around . During the early Erligang period, the site suddenly grew rapidly, reaching an area of around . The central town was surrounded by a ''hangtu'', or rammed earth, wall. Inside the walls two palaces occupying were discovered. Panlongcheng may have been an Erligang outpost used to control regional resources, such as copper mine Copper extr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shang Dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou dynasty. The classic account of the Shang comes from texts such as the '' Book of Documents'', '' Bamboo Annals'' and '' Records of the Grand Historian''. According to the traditional chronology based on calculations made approximately 2,000 years ago by Liu Xin, the Shang ruled from 1766 to 1122 BC, but according to the chronology based upon the "current text" of ''Bamboo Annals'', they ruled from 1556 to 1046 BC. Comparing the same text with dates of five-planet conjunctions, David Pankenier, supported by David Nivison, proposed dates of the establishment of the dynasty to 1554 BC. The Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project dated the establishment to c. 1600 BC based on the carbon-14 dates of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)