|
Zhong Hui
Zhong Hui (225 – 3 March 264), courtesy name Shiji, was a Chinese calligrapher, essayist, military general, and politician of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He was the younger son of Zhang Changpu with Zhong Yao, who served as the Grand Tutor in the Wei imperial court. He was already known for being insightful, intelligent and knowledgeable since he was young. Zhong Hui rose to prominence in the 250s when he became a close aide to Sima Zhao, the regent and ''de facto'' ruler of Wei. He advised Sima Zhao on how to deal with the Third Rebellion in Shouchun from 257–258 and was highly regarded by the latter. With Sima Zhao's help, Zhong Hui steadily moved up the ranks and became one of the key figures in the Wei government. In 263, the Wei imperial court ordered Zhong Hui, Deng Ai and Zhuge Xu to lead separate armies to attack and conquer Wei's rival state, Shu Han. During and after the campaign against Shu, Zhong Hui framed Zhuge Xu and Deng A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
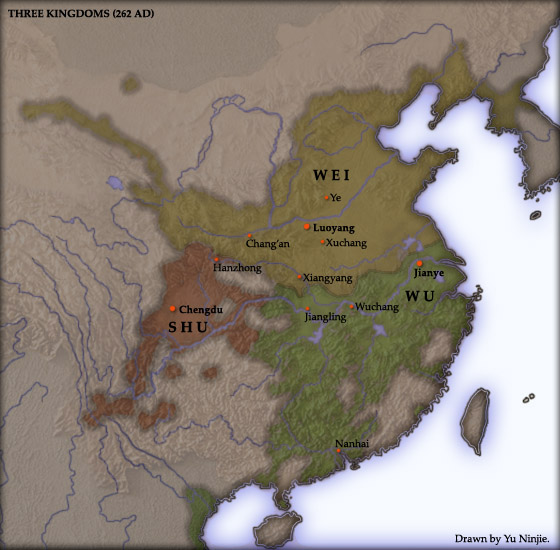
Cao Wei
Wei ( Hanzi: 魏; pinyin: ''Wèi'' < : *''ŋjweiC'' < : *''ŋuiC'') (220–266), known as Cao Wei or Former Wei in historiography, was one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over China in the period (220–280). With its capital initially located at , and thereafter |
Yingchuan Commandery
Yingchuan Commandery ( zh, 潁川郡) was a Chinese commandery from the Warring States period to Tang dynasty, located in modern central Henan province. The name referred to the Ying River, which flowed through its territory. The commandery was established by the state of Qin after it conquered Hán. The seat was Yangdi (陽翟, modern Yuzhou, Henan), which, according to legend, was the capital of Yu the Great, and was the capital of the Warring States era State of Han. After the establishment of Hàn dynasty, it originally became Xin, King of Hán's fief. However, Xin was soon moved to Taiyuan, and the commandery was restored. In 2 AD, it administered 20 counties: Yangdi, Kunyang (昆陽), Yingyang (潁陽), Dingling (定陵), Changshe (長社), Xinji (新汲), Xiangcheng (襄城), Yan (郾), Jia (郟), Wuyang (舞陽), Yingyin (潁陰), Chonggao (崇高), Xu (許), Yanling (傿陵), Linying (臨潁), Fucheng (父城), Cheng'an (成安), Zhouchengxiu (周承休), Yangche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancestral Home (Chinese)
In Chinese culture, hometown or ancestral home () is the place of origin of one's extended family. It may or may not be the place where one is born. For instance, two people may both be born in Shanghai, but the hometowns of their ancestors may be different. Definition A subjective concept, a person's ancestral home could be the birthplace of ''any'' of their patriline ancestors. Su Shi limited it to five generations, i.e. it refers to the home of one's great-great-grandfather. Even more broadly, an ancestral home can refer to the first locality where a surname came to be established or prominent. Commonly, a person usually defines their hometown as what their father considers to be his ancestral home. In practice, most people would define their ancestral homes as the birthplace of their patriline ancestors from the early 20th century, around the time when government authorities began to collect such information from individuals. Moreover, a person's ancestral home can be defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhong Hui's Rebellion
Zhong Hui's Rebellion was a rebellion in March 264 led by Zhong Hui, a general of the state of Cao Wei, against the Wei regent, Sima Zhao. Zhong Hui had support from Jiang Wei, a general from the former state of Shu Han, which was conquered by Wei forces just before the rebellion started. Zhong Hui, as one of the Wei commanders in the Conquest of Shu by Wei, had considered himself capable enough to overcome the Wei regime and establish his own kingdom in the newly conquered Shu territory.Alan Kam-Leung Chan, National University of Singapore. http://www.iep.utm.edu/zhonghui/#H1 The rebellion ended when some Wei officers and soldiers, who were unwilling to join Zhong Hui, started a mutiny against him and killed him and Jiang Wei. Background Initially, when Sima Zhao wanted to put Zhong Hui in charge of leading the Wei army to conquer Shu, Shao Ti warned him that Zhong Hui might rebel against Wei because he was in command of an army of thousands, was single, and had no family to wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiang Wei
Jiang Wei (202 – 3 March 264), courtesy name Boyue, was a military general of the state of Shu during the Three Kingdoms period of China. Born in Ji County (present-day Gangu County, Gansu), Jiang Wei started his career as a military officer in his native Tianshui Commandery, which was a territory of Wei. In 228, when Wei's rival state Shu launched an invasion led by Zhuge Liang, Jiang Wei was distrusted by Ma Zun, then administrator of Tianshui Commandery. As such, Jiang Wei had to defect to Shu. Zhuge Liang, the Imperial Chancellor and regent of Shu, highly regarded Jiang Wei and appointed him as a general in Shu. After Zhuge Liang's death in 234, Jiang Wei continued serving as a military commander during the regencies Jiang Wan and Fei Yi, eventually rising to the highest military rank of General-In-Chief (大將軍) after Fei Yi’s death in 253. Between 240 and 262, he continued Zhuge Liang's legacy of waging war against Wei by leading another 11 military campaigns. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shu Han
Han (; 221–263), known in historiography as Shu Han ( ) or Ji Han ( "Junior Han"), or often shortened to Shu (; pinyin: ''shŭ'' < : *''źjowk'' < : *''dźok''), was one of the three major states that competed for supremacy over China in the period (220–280). The state was based in the area around present-day , , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conquest Of Shu By Wei
The Conquest of Shu by Wei was a military campaign launched by the dynastic state of Cao Wei against its rival Shu Han in late 263 during the Three Kingdoms period of China. The campaign culminated in the fall of Shu Han and the tripartite equilibrium maintained in China proper for over 40 years since the end of the Eastern Han dynasty in 220. The conquest laid the foundation for an eventual reunified China proper under the Western Jin dynasty in 280. Background Following the end of the Eastern Han dynasty in 220, three contending states emerged in China and fought for control over the territories of the former Han Empire. Among the three, Wei was the most powerful one in terms of military prowess, economic resources, manpower and geographical size. The other two, Shu and Wu, reestablished their alliance against Wei in 223. Between 228 and 234, the Shu regent Zhuge Liang, who advocated an aggressive foreign policy towards Wei, launched a series of five military campaign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhuge Xu
Zhuge Xu ( 255–260s) was a Chinese general and politician of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. Life Zhuge Xu was from Yangdu County (), Langya Commandery (), which is in present-day Yinan County, Shandong. He was probably a distant relative of other famous Zhuges in the Three Kingdoms period, such as Zhuge Jin, Zhuge Liang and Zhuge Dan, since he shared the same ancestral home as them. He served in the state of Cao Wei in the Three Kingdoms period. In 255, when the Wei generals Guanqiu Jian and Wen Qin started a rebellion in Shouchun (壽春; present-day Shou County, Anhui), Zhuge Xu was then serving as the Administrator () of Taishan Commandery (泰山郡; around present-day Tai'an, Shandong). He led troops from Taishan Commandery to assist other Wei imperial forces led by the regent Sima Shi to suppress the rebellion. Zhuge Xu was later promoted to the position of Inspector () of Yong Province in an unknown year. In 263, he participated in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deng Ai
Deng Ai (197 – late March 264Vol.04 of ''Sanguozhi'' and vol.02 of ''Jin Shu'' both indicated that Deng Ai was arrested in the 1st month of the 1st year of the ''Xianxi'' era. The month corresponds to 15 Feb to 14 Mar 264 in the Julian calendar. Volume 78 of ''Zizhi Tongjian'' dated Deng Ai's arrest to the ''renchen'' day of that month, but there is no ''renchen'' day in that month. The next ''renchen'' day is in the 2nd month, and corresponds to 16 Mar 264 in the Julian calendar. All sources agree that Deng Ai died after Zhong Hui, who died on 3 Mar 264.), courtesy name Shizai, was a Chinese military general and politician of the state of Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He is best known for his pivotal role in the Wei conquest of its rival state, Shu, in 263. He was described as a very loyal subject who made great contributions to Wei, but was also noted for his arrogance and audacity, which led to his downfall and death. Born in a peasant family, Deng Ai star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Rebellion In Shouchun
Zhuge Dan's Rebellion, or the Third Rebellion in Shouchun, was a revolt led by Zhuge Dan, a general from the state of Cao Wei, against the regent Sima Zhao. Zhuge Dan received some support from Eastern Wu, Cao Wei's rival state. It was the third and final of a series of three rebellions that took place in Shouchun (壽春; present-day Shou County, Anhui) in the 250s during the Three Kingdoms period of China. Background Following the events of the previous rebellions in Shouchun and the Incident at Gaoping Tombs, the regency and almost complete control of Wei was in the hands of Sima Zhao and his clan. After the second uprising, Sima Shi died, giving control to his second brother, Sima Zhao. The Wei emperor was Cao Mao, and since Wen Qin fled to Eastern Wu, Shouchun's affairs were given to the Wei general Zhuge Dan. Zhuge Dan had witnessed the rise and fall of both Wang Ling, and Guanqiu Jian, and also playing an enormous role in the second revolt in Shouchun. However, as Xiah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by law"), which refers to things that happen according to official law, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. History In jurisprudence, it mainly means "practiced, but not necessarily defined by law" or "practiced or is valid, but not officially established". Basically, this expression is opposed to the concept of "de jure" (which means "as defined by law") when it comes to law, management or technology (such as standards) in the case of creation, development or application of "without" or "against" instructions, but in accordance with "with practice". When legal situations are discussed, "de jure" means "expressed by law", while "de facto" means action or what is practiced. Similar expressions: "essentially", "unofficial", "in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)