|
Zhizhi
Zhizhi or Chi-Chi (, from Old Chinese (58 BCE): *''tśit-kie'' < *''tit-ke'';Schuessler 2014, p. 277 died 36 BCE), also known as Jzh-jzh, was a of the at the time of the first Xiongnu , who held the north and west in contention with his younger brother who held the south. His original name in Chinese transcription was Luandi Hutuwusi (), i.e. one of the |
Battle Of Zhizhi
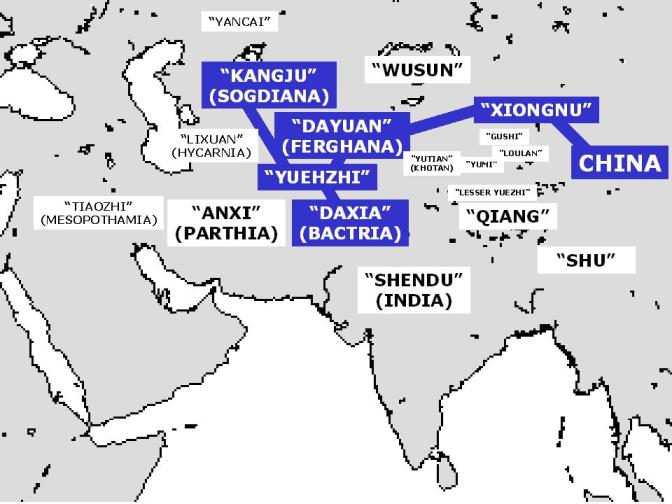
The Battle of Zhizhi (郅支之戰) was fought in 36 BC between the Han Dynasty and the Xiongnu chieftain Zhizhi Chanyu. Zhizhi was defeated and killed. The battle was probably fought near Taraz on the Talas River in eastern Kazakhstan, which makes it one of the westernmost points reached by a Chinese army. The Battle of Talas in 751 AD was fought in the same area. Background In 56 BC Zhizhi revolted against his brother. As his brother grew more powerful, Zhizhi retreated westward. About 44 BC he made a close alliance with the Kangju near Lake Balkhash. Later he quarrelled with the Kangju, killed several hundred of them and forced them to build him a fortress. The fort required 500 men and two years to build. It was probably located near Taraz. Battle Assembly and march of Han forces At approximately 36 BC, the governor of the Western Regions was Gan Yanshou. His deputy commander, Chen Tang, claimed that Zhizhi was planning to build up a great empire and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Yuan Of Han
Emperor Yuan of Han (Liu Shi 劉奭; 75 BC – 8 July 33 BC) was an emperor of the Chinese Han dynasty. He reigned from 48 BC to 33 BC. Emperor Yuan promoted Confucianism as the official creed of the Chinese government. He appointed Confucius adherents to important government posts. However, at the same time that he was solidifying Confucianism's position as the official ideology, the empire's condition slowly deteriorated due to his indecisiveness, his inability to stop factional infighting between officials in his administration, and the trust he held in certain corrupt officials. Family background When Emperor Yuan was born as Liu Shi in 75 BC, his parents Liu Bingyi and Xu Pingjun were commoners without titles. Bingyi was the great-grandson of Emperor Wu, and his grandfather Liu Ju was Emperor Wu's crown prince, until he was forced by Emperor Wu's paranoia into a failed rebellion in 91 BC while Bingyi was still just an infant. The aftermath of the failed rebellion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC, founded the Xiongnu Empire. After their previous rivals, the Yuezhi, migrated west into Central Asia during the 2nd century BC, the Xiongnu became a dominant power on the steppes of East Asia, centred on the Mongolian Plateau. The Xiongnu were also active in areas now part of Siberia, Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Xinjiang. Their relations with adjacent Chinese dynasties to the south-east were complex—alternating between various periods of peace, war, and subjugation. Ultimately, the Xiongnu were defeated by the Han dynasty in a centuries-long conflict, which led to the confederation splitting in two, and forcible resettlement of large numbers of Xiongnu within Han borders. During the Sixteen Kingdoms era, as one of the "Five B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Tang
Chen Tang (), born in Jining, Shandong, was a Han dynasty Chinese general famous for his battle against Zhizhi in 36 BC during the Han–Xiongnu War. Battle of Zhizhi At approximately 36 BC, the governor of the Western Regions was Gan Yanshou. His deputy commander, Chen Tang claimed that Zhizhi was planning to build up a great empire and proposed a pre-emptive attack. Gan Yanshou objected; but he soon fell ill, and while he was incapacitated Chen Tang forged an edict in Yanshou's name and mobilized the army. Gan Yanshou was forced to yield. All this was done without the Emperor's permission. An army of 40,000 Han and Hu troops (' 'Hu" here is a loose term for non-Chinese) assembled. It marched west on both sides of the Tarim Basin, reunited near Kashgar and moved across Kangju territory reaching the western shore of Lake Balkhash. At this point a party of several thousand Kangju cavalrymen, returning from a raid on Wusun, stumbled onto the rear of the Chinese army, attack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiongnu Empire
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC, founded the Xiongnu Empire. After their previous rivals, the Yuezhi, migrated west into Central Asia during the 2nd century BC, the Xiongnu became a dominant power on the steppes of East Asia, centred on the Mongolian Plateau. The Xiongnu were also active in areas now part of Siberia, Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Xinjiang. Their relations with adjacent Chinese dynasties to the south-east were complex—alternating between various periods of peace, war, and subjugation. Ultimately, the Xiongnu were defeated by the Han dynasty in a centuries-long conflict, which led to the confederation splitting in two, and forcible resettlement of large numbers of Xiongnu within Han borders. During the Sixteen Kingdoms era, as one of the "Five Bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huhanye
Huhanye (), born Jihoushan (), was a Chanyu of the Xiongnu Empire, the son of Xulüquanqu Chanyu. He rebelled in 59 BC with the aid of Wushanmu and Woyanqudi Chanyu soon committed suicide, leaving the Xiongnu torn apart by factional strife. By 55 BC, only Huhanye and his brother Zhizhi Chanyu were left. Family Parents: *Father: Xulüquanqu Chanyu *Mother: Unknown *Brother: Woyanqudi Chanyu Wives *Lady Da Yanzhi (大阏氏) ** Fuzhulei Ruodi Chanyu (复株絫若鞮单于; r 31–20 BC) **Souxie Chanyu (搜谐单于; r. 20–12 BC) ** Wulei Chanyu (乌累若鞮单于; r.13–18 AD) **Prince Xian of Zuo (左贤王) *Lady Zhuanqu Yanzhi (颛渠阏氏) **Juya Chanyu (车牙单于; r.12–8 B.C) ** Wuzhuliu Chanyu (乌珠留单; r.8 BC–13 AD) *Lady Tuqi Yanzhi (屠耆阏氏) **Prince Xian of You (右贤王) *Lady Diwu Yanzhi (第五阏氏) **Huduershidaogao Chanyu (呼都而尸道皋若鞮单于) *Lady Wang Zhaojun (王昭君) **Prince Yituzhiyashi (伊屠智牙師) ** Another Prin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taraz
Taraz ( kz, Тараз, تاراز, translit=Taraz ; known to Europeans as Talas) is a city and the administrative center of Jambyl Region in Kazakhstan, located on the Talas (river), Talas (Taraz) River in the south of the country near the border with Kyrgyzstan. It had a population of 330,100 as of the 1999 census, up 9% from 1989, making it one of the fastest-growing cities in the country, after Astana and Turkistan (city), Turkistan. One of the oldest cities in Kazakhstan and in Transoxania, built and populated by the ancient Sogdians, Taraz celebrated its official 2,000th anniversary (recognized by UNESCO) in 2001, dating from a fortress built in the area by a Xiongnu Chanyu named Zhizhi, and was a site of the Battle of Zhizhi in 36 BCE. The city was first recorded under the name "Talas" in 568 CE by Menander Protector. The medieval city of Talas was a major trade centre along the Silk Road. Talas was later described by Buddhist monk and traveller Xuanzang, who passed Talas i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanyu
Chanyu () or Shanyu (), short for Chengli Gutu Chanyu (), was the title used by the supreme rulers of Inner Asian nomads for eight centuries until superseded by the title "''Khagan''" in 402 CE. The title was most famously used by the ruling Luandi clan of the Xiongnu during the Qin dynasty (221–206 BCE) and Han dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE). It was later also used infrequently by the Chinese as a reference to Gokturk leaders. Etymology According to the ''Book of Han'', "the Xiongnu called the Tian, Heaven (天) ''Tengri, Chēnglí'' (撐犁) and they called a child (子) ''gūtú'' (孤塗). As for ''Chányú'' (單于), it is a "vast [and] great appearance" (廣大之貌).". L. Rogers and Edwin G. Pulleyblank argue that the title ''chanyu'' may be equivalent to the later attested title ''tarkhan'', suggesting that the Chinese pronunciation was originally ''dān-ĥwāĥ'', an approximation for ''*darxan''.Universität Bonn. Seminar für Sprach- und Kulturwissenschaft Zentra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangju
Kangju (; Eastern Han Chinese: ''kʰɑŋ-kɨɑ'' < *''khâŋ-ka'' (c. 140 BCE)) was the Chinese name of a kingdom in during the first half of the CE. The name ''Kangju'' is now generally regarded as a variant or mutated form of the name . According to contemporaneous Chinese sources, Kangju was the second most powerful state in , after the . [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanyu
Chanyu () or Shanyu (), short for Chengli Gutu Chanyu (), was the title used by the supreme rulers of Inner Asian nomads for eight centuries until superseded by the title "''Khagan''" in 402 CE. The title was most famously used by the ruling Luandi clan of the Xiongnu during the Qin dynasty (221–206 BCE) and Han dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE). It was later also used infrequently by the Chinese as a reference to Gokturk leaders. Etymology According to the ''Book of Han'', "the Xiongnu called the Tian, Heaven (天) ''Tengri, Chēnglí'' (撐犁) and they called a child (子) ''gūtú'' (孤塗). As for ''Chányú'' (單于), it is a "vast [and] great appearance" (廣大之貌).". L. Rogers and Edwin G. Pulleyblank argue that the title ''chanyu'' may be equivalent to the later attested title ''tarkhan'', suggesting that the Chinese pronunciation was originally ''dān-ĥwāĥ'', an approximation for ''*darxan''.Universität Bonn. Seminar für Sprach- und Kulturwissenschaft Zentra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–207 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the ChuHan contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD) and the Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a golden age in Chinese history, and it has influenced the identity of the Chinese civilization ever since. Modern China's majority ethnic group refers to themselves as the "Han people", the Sinitic language is known as "Han language", and the written Chinese is referred to as "Han characters". The emperor was at the pinnacle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woyanqudi .
Woyanqudi (), born Tuqitang (屠耆堂), was a Chanyu of the Xiongnu Empire. The successor to Xulüquanqu Chanyu, he reigned from 60 to 58 BC. Woyanqudi was a tyrannical ruler. He killed his predecessor's supporters and dismissed his own kinsfolk. He killed himself in 58 BC and the Xiongnu split into several warring factions. By 55 BC, the two dominant factions were his sons: Huhanye Chanyu and Zhizhi Chanyu Zhizhi or Chi-Chi (, from Old Chinese (58 BCE): *''tśit-kie'' < *''tit-ke'';Schuessler 2014, p. 277 died 36 BCE), also known as Jzh-jzh, was a Footnotes References *Bichurin N.Ya., ''"Collection of information on peoples in Central Asia in ancient times"'', vol. 1, Sankt Petersburg, 1851, reprint Moscow-Leningrad, 1950 * * * * *Taskin B.S., ''"Materials on Sünnu history"'', Science, Moscow, 1968, p. 31 ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)





.jpg)
