|
Zhili Province
Zhili, alternately romanized as Chihli, was a northern administrative region of China since the 14th-century that lasted through the Ming dynasty and Qing dynasty until 1911, when the region was dissolved, converted to a province, and renamed Hebei in 1928. History The name ''Zhili'' means "directly ruled" and indicates regions directly ruled by the imperial government of China. Zhili province was first constituted during the Ming dynasty when the capital of China was located at Nanjing along the Yangtze River. In 1403, the Ming Yongle Emperor relocated the capital to Beiping, which was subsequently renamed Beijing.Susan Naquin, ''Peking: Temples and City Life, 1400-1900'', p xxxiii The region known as North Zhili was composed of parts of the modern provinces of Hebei, Henan, Shandong, including the provincial-level municipalities of Beijing and Tianjin. There was another region located around the "reserve capital" Nanjing known as South Zhili that included parts of what are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beiping
"Beijing" is from pinyin ''Běijīng,'' which is romanized from , the Chinese name for this city. The pinyin system of transliteration was approved by the Chinese government in 1958, but little used until 1979. It was gradually adopted by various news organizations, governments, and international agencies over the next decade. Etymology The Chinese characters ("north") and ("capital") together mean the "Northern Capital". The name was first used during the reign of the Ming dynasty's Yongle Emperor, who made his northern fief a second capital, along with Nanjing (, the "Southern Capital"), in 1403 after successfully dethroning his nephew during the Jingnan Campaign. The name was restored in 1949 at the founding of the People's Republic of China. Peking Portugal was the first European country to contact China in modern times. In Portuguese, the city is called ''Pequim.'' This name appeared in the letters of Francis Xavier in 1552. It transferred to English as "Pekin" and to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiangsu
Jiangsu (; ; pinyin: Jiāngsū, Postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Kiangsu or Chiangsu) is an Eastern China, eastern coastal Provinces of the People's Republic of China, province of the China, People's Republic of China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its capital in Nanjing. Jiangsu is the List of Chinese administrative divisions by area, third smallest, but the List of Chinese administrative divisions by population, fifth most populous and the List of Chinese administrative divisions by population density, most densely populated of the 23 provinces of the People's Republic of China. Jiangsu has the highest GDP per capita of Chinese provinces and second-highest GDP of Chinese provinces, after Guangdong. Jiangsu borders Shandong in the north, Anhui to the west, and Zhejiang and Shanghai to the south. Jiangsu has a coastline of over along the Yellow Sea, and the Yangtze River passes through the southern part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Empire
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaking ethnic group who unified other Jurchen tribes to form a new "Manchu" ethnic identity. The dynasty was officially proclaimed in 1636 in Manchuria (modern-day Northeast China and Outer Manchuria). It seized control of Beijing in 1644, then later expanded its rule over the whole of China proper and Taiwan, and finally expanded into Inner Asia. The dynasty lasted until 1912 when it was overthrown in the Xinhai Revolution. In orthodox Chinese historiography, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China. The multiethnic Qing dynasty lasted for almost three centuries and assembled the territorial base for modern China. It was the largest imperial dynasty in the history of China and in 1790 the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Baptiste Bourguignon D'Anville
Jean-Baptiste Bourguignon d'Anville (; born in Paris 11 July 169728 January 1782) was a French geographer and cartographer who greatly improved the standards of map-making. D'Anville became cartographer to the king, who purchased his cartographic materials, the largest collection in France. He made more than 200 maps during his lifetime, which are characterized by a careful, accurate work largely based on original research. In particular, D'Anville left unknown areas of continents blank and noted doubtful information as such, contrary to the lavish maps of his predecessors. His maps remained the reference point in cartography throughout the 19th century and were used by numerous explorers and travellers. Biography Jean-Baptiste Bourguignon d'Anville was born in Paris on 11 July 1697, in the Kingdom of France. His passion for geographical research displayed itself from early years: at age of twelve he was already amusing himself by drawing maps for Latin authors. Later, his f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manzi (geography)
The names of China include the many contemporary and historical appellations given in various languages for the East Asian country known as ''Zhōngguó'' (/, "middle country") in its national language, Standard Mandarin. China, the name in English for the country, was derived from Portuguese in the 16th century, and became common usage in the West in the subsequent centuries. It is believed to be a borrowing from Middle Persian, and some have traced it further back to Sanskrit. It is also thought that the ultimate source of the name China is the Chinese word "Qin" (), the name of the Qin dynasty, dynasty that unified China but also existed as a Qin (state), state for many centuries prior. There are, however, other alternative suggestions for the origin of the word. Chinese names for China, aside from ''Zhongguo'', include ''Zhonghua minzu, Zhōnghuá'' (/, "central beauty"), ''Huaxia, Huáxià'' (/, "beautiful grandness"), ''Shénzhōu'' (, "divine state") and ''Jiǔzhōu'' (, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
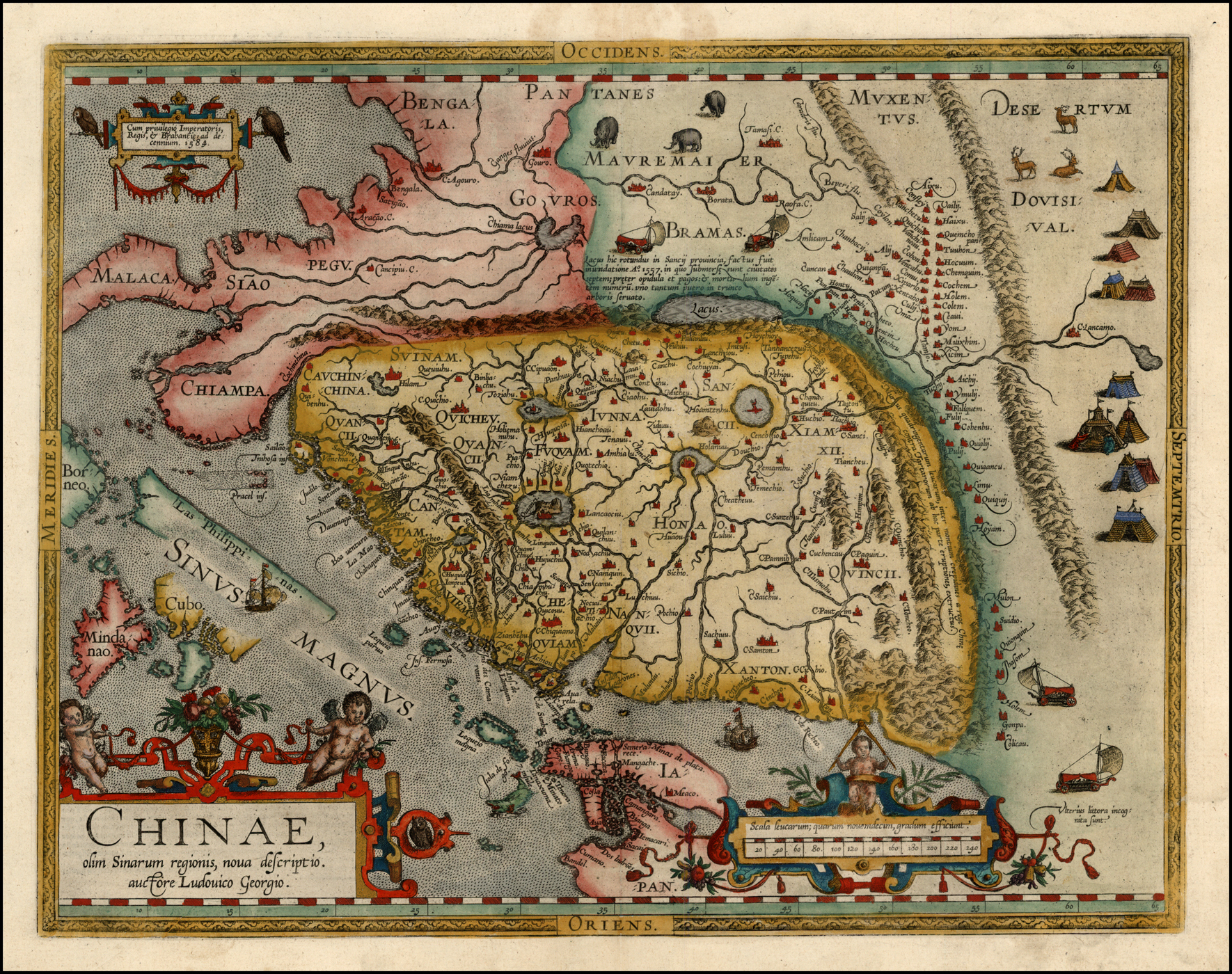
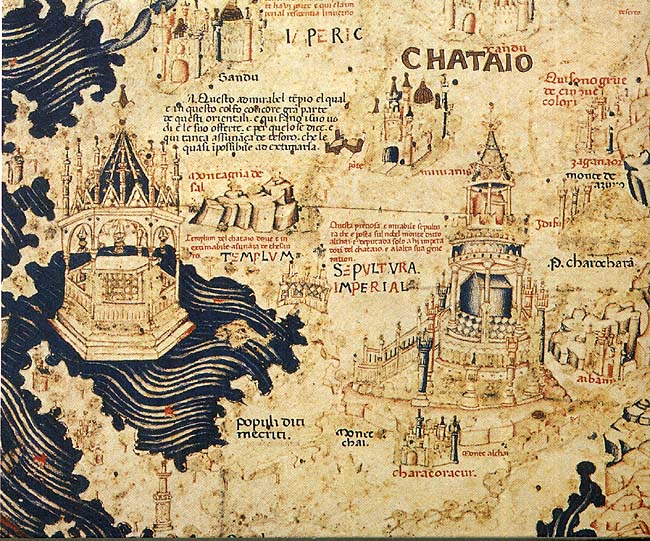
Cathay
Cathay (; ) is a historical name for China that was used in Europe. During the early modern period, the term ''Cathay'' initially evolved as a term referring to what is now Northern China, completely separate and distinct from China, which was a reference to southern China. As knowledge of East Asia increased, Cathay came to be seen as the same polity as China as a whole. The term ''Cathay'' became a poetic name for China. The name ''Cathay'' originates from the word '' Khitan'', a name of a para-Mongolic nomadic people who ruled the Liao dynasty in northern China from 916 to 1125, and who later migrated west after they were overthrown by the Jin dynasty to form the Qara Khitai (Western Liao dynasty) for another century thereafter. Originally, this name was the name applied by Central and Western Asians and Europeans to northern China; the name was also used in Marco Polo's book on his travels in Yuan dynasty China (he referred to southern China as '' Mangi''). Odoric of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of China (1912–1949)
The Republic of China (ROC), between 1912 and 1949, was a sovereign state recognised as the official designation of China when it was based on Mainland China, prior to the Retreat of the government of the Republic of China to Taiwan, relocation of Government of the Republic of China, its central government to Taiwan as a result of the Chinese Civil War. At a Population history of China, population of 541 million in 1949, it was the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's most populous country. Covering , it consisted of 35 provinces of China, provinces, 1 Special administrative regions of China#ROC special administrative regions, special administrative region, 2 regions, 12 special municipality (Republic of China), special municipalities, 14 leagues, and 4 special banners. The China, People's Republic of China (PRC), which rules mainland China today, considers ROC as a country that ceased to exist since 1949; thus, the history of ROC before 1949 is often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhongshu Sheng
The Zhongshu Sheng (), also known as the Palace Secretariat or Central Secretariat, was one of the departments of the Three Departments and Six Ministries government structure in imperial China from Cao Wei (220–266) until the early Ming dynasty. As one of the Three Departments, the Zhongshu Sheng was primarily a policy-formulating agency responsible for proposing and drafting all imperial decrees, but its actual function varied at different times. The department traces its origins back to the Han dynasty. History Origins: Han dynasty and Cao Wei The Central Secretariat originated during the reign of Emperor Wu of Han (r. 141-87 BC) to handle documents. The chief steward for writing (''shangshu'' 尚書), aided by eunuch secretary-receptionists (''zhongshu yezhe'' 中書謁者)), forwarded documents to the inner palace. This organization was headed by a Secretariat Director (''zhongshu ling'' 中書令) assisted by a Vice Director (''zhongshu puye'' 中書仆射). These two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sili Province
Sili Province or Silizhou (司隸州), in the 5th century reconstituted as Si Province or Sizhou (司州), also known as the ''capital province'' or the ''imperial province'', was a province of ancient China. It encompassed the two Han dynasty capitals of Chang'ande Crespigny, p. 26. and Luoyang, and was bordered in the west by Liang Province. Sili Province was governed by the Director of Retainers (司隸 ''Sī Lì'').de Crespigny, p. 46. The province consisted of the commanderies of Henan (around Luoyang), Hedong, Henei, Hongnong, Jingzhao, Youfufeng and Zuopingyi (around Chang'an). In the early 5th century, the former Sili Province was reconstituted as Si Province or Sizhou by Liu Yu, the future founder of the Liu Song dynasty. See also * Zhili Zhili, alternately romanized as Chihli, was a northern administrative region of China since the 14th-century that lasted through the Ming dynasty and Qing dynasty until 1911, when the region was dissolved, converted to a provin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a small section of China's border with Russia (Zabaykalsky Krai). Its capital is Hohhot; other major cities include Baotou, Chifeng, Tongliao, and Ordos. The autonomous region was established in 1947, incorporating the areas of the former Republic of China provinces of Suiyuan, Chahar, Rehe, Liaobei, and Xing'an, along with the northern parts of Gansu and Ningxia. Its area makes it the third largest Chinese administrative subdivision, constituting approximately and 12% of China's total land area. Due to its long span from east to west, Inner Mongolia is geographically divided into eastern and western divisions. The eastern division is often included in Northeastern China (Dongbei) with major cities including Tongliao, Chifeng, Hai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liaoning
Liaoning () is a coastal province in Northeast China that is the smallest, southernmost, and most populous province in the region. With its capital at Shenyang, it is located on the northern shore of the Yellow Sea, and is the northernmost coastal province of the People's Republic of China. Historically a gateway between China proper and Manchuria, the modern Liaoning province was established in 1907 as Fengtian or Fengtien province and was renamed Liaoning in 1929. It was also known at that time as Mukden Province for the Manchu name of ''Shengjing'', the former name of Shenyang. Under the Japanese-puppet Manchukuo regime, the province reverted to its 1907 name, but the name Liaoning was restored for a brief time in 1945 and then again in 1954. Liaoning borders the Yellow Sea ( Korea Bay) and Bohai Sea in the south, North Korea's North Pyongan and Chagang provinces in the southeast, Jilin to the northeast, Hebei to the southwest, and Inner Mongolia to the northwest. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpeg/1200px-Siège_de_Beijing_(1213-1214).jpeg)
