|
Zhang Ji (Han Dynasty)
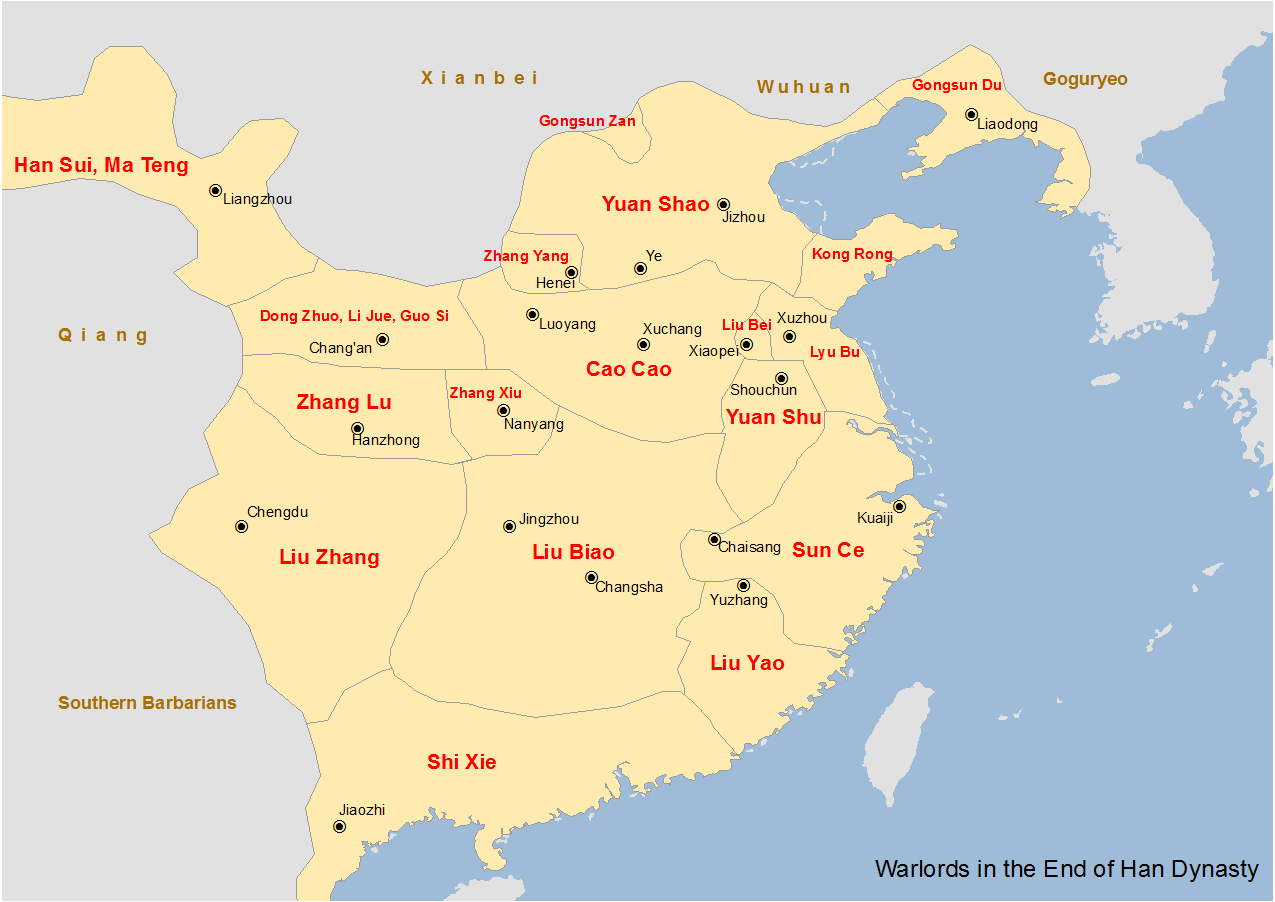
Zhang Ji (died 196) was a military general serving under the warlord Dong Zhuo during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. Life Zhang Ji was from Zuli County (), Wuwei Commandery (), which is in present-day Jingyuan County, Gansu. He started his career as a subordinate of Niu Fu, a son-in-law of the warlord Dong Zhuo, who controlled the Han central government and the figurehead Emperor Xian from 189 to 192. In 192, Niu Fu ordered Zhang Ji to join Li Jue and Guo Si in leading troops to attack the general Zhu Jun at Zhongmu County () and pillage Chenliu () and Yingchuan () commanderies. After Dong Zhuo was assassinated in Chang'an in 192, Li Jue, Guo Si, Zhang Ji and other former followers of Dong Zhuo requested amnesty from Wang Yun, who replaced Dong Zhuo as the new head of the central government. However, Wang Yun refused and wanted to have all of them executed. Heeding Jia Xu's advice, Li Jue, Guo Si, Zhang Ji and Dong Zhuo's former followers led their troops to attack Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Xian Of Han
Emperor Xian of Han (2 April 181 – 21 April 234), personal name Liu Xie (劉協), courtesy name Bohe, was the 14th and last emperor of the Eastern Han dynasty in China. He reigned from 28 September 189 until 11 December 220. Liu Xie was a son of Liu Hong (Emperor Ling) and was a younger half-brother of his predecessor, Liu Bian (Emperor Shao). In 189, at the age of eight, he became emperor after the warlord Dong Zhuo, who had seized control of the Han central government, deposed Emperor Shao and replaced him with Liu Xie. The newly enthroned Liu Xie, historically known as Emperor Xian, was in fact a puppet ruler under Dong Zhuo's control. In 190, when a coalition of regional warlords launched a punitive campaign against Dong Zhuo in the name of freeing Emperor Xian, Dong Zhuo ordered the destruction of the imperial capital, Luoyang, and forcefully relocated the imperial capital along with its residents to Chang'an. After Dong Zhuo's assassination in 192, Emperor Xian fell u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River (Henan), Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyang, Henan, Nanyang to the south, Sanmenxia to the west, Jiyuan to the north, and Jiaozuo to the northeast. As of December 31, 2018, Luoyang had a population of 6,888,500 inhabitants with 2,751,400 people living in the built-up (or metro) area made of the city's five out of six urban districts (except the Jili District not continuously urbanized) and Yanshi District, now being conurbated. Situated on the Central Plain (China), central plain of China, Luoyang is among the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities#East Asia, oldest cities in China and one of the History of China#Ancient China, cradles of Chinese civilization. It is the earliest of the Historical capitals of China, Four Great Ancient Capitals of China. Name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Shou
Chen Shou (; 233–297), courtesy name Chengzuo (), was a Chinese historian, politician, and writer who lived during the Three Kingdoms period and Jin dynasty of China. Chen Shou is most known for his most celebrated work, the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' (''Sanguozhi''), which records the history of the late Eastern Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period. Chen Shou wrote the Sanguozhi primarily in the form of biographies of notable persons of those eras. Today, Chen's ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is part of the ''Twenty-Four Histories'' canon of ancient Chinese history. Historical sources on Chen Shou's life There are two biographies of Chen Shou. The first one is in the ''Chronicles of Huayang'', which was written by Chang Qu in the fourth century during the Eastern Jin dynasty. The second one is in the ''Book of Jin'', which was written by Fang Xuanling and others in the seventh century during the Tang dynasty. Life He started his career as an official in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lists Of People Of The Three Kingdoms
The following are lists of people significant to the Three Kingdoms period (220–280) of Chinese history. Their names in Mandarin pinyin are sorted in alphabetical order. Fictional characters in the 14th-century historical novel ''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' and those found in other cultural references to the Three Kingdoms are listed separately in List of fictional people of the Three Kingdoms. Notes The states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu were officially established in 220, 221, and 229 respectively. Therefore, certain people in the list who died before these years have their respective lords' names, in place of either of the three states, listed in the allegiance column. Take Guan Yu for example — he died before Liu Bei established Shu Han in 221, so his allegiance is listed as "Liu Bei" instead of "Shu Han". See also * List of fictional people of the Three Kingdoms The following is a list of fictional people significant to the Three Kingdoms period (220� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Cao
Cao Cao () (; 155 – 15 March 220), courtesy name Mengde (), was a Chinese statesman, warlord and poet. He was the penultimate Grand chancellor (China), grand chancellor of the Eastern Han dynasty, and he amassed immense power in the End of the Han dynasty, dynasty's final years. As one of the central figures of the Three Kingdoms period, Cao Cao laid the foundations for what became the state of Cao Wei, and he was posthumously honoured as "Emperor Wu of Wei", despite the fact that he never officially proclaimed himself Emperor of China or Son of Heaven. Cao Cao remains a controversial historical figure—he is often portrayed as a cruel and merciless tyrant in literature, but he has also been praised as a brilliant ruler, military genius, and great poet possessing unrivalled charisma, who treated his subordinates like family. During the fall of the Eastern Han dynasty, Cao Cao was able to secure most of northern China—which was at the time the most populated and developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romance Of The Three Kingdoms
''Romance of the Three Kingdoms'' () is a 14th-century historical novel attributed to Luo Guanzhong. It is set in the turbulent years towards the end of the Han dynasty and the Three Kingdoms period in Chinese history, starting in 184 AD and ending with the reunification of the land in 280 by Western Jin. The novel is based primarily on the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' (), written by Chen Shou. The story – part historical and part fictional – romanticises and dramatises the lives of feudal lords and their retainers, who tried to replace the dwindling Han dynasty or restore it. While the novel follows hundreds of characters, the focus is mainly on the three power blocs that emerged from the remnants of the Han dynasty, and would eventually form the three states of Cao Wei, Shu Han, and Eastern Wu. The novel deals with the plots, personal and military battles, intrigues, and struggles of these states to achieve dominance for almost 100 years. ''Romance of the Three Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanyang, Henan
Nanyang is a prefecture-level city in the southwest of Henan province, China. The city with the largest administrative area in Henan, Nanyang borders Xinyang to the southeast, Zhumadian to the east, Pingdingshan to the northeast, Luoyang to the north, Sanmenxia to the northwest, the province of Shaanxi to the west, and the province of Hubei to the south. Dinosaur egg fossils have been discovered in the Nanyang Basin. The 35,000 capacity Nanyang Sports Centre Stadium is the main (football) venue in the city. Names In the name "Nanyang" (), ''Nan'' () means south, and ''Yang'' (/) means sun—the south side of a mountain, or the north side of a river, in Chinese is called ''Yang''. The name came from Nanyang Commandery, a commandery established in the region during the Warring States period. Before the name "Nanyang" became associated with the city itself, it was referred to as "Wan" (). History Nanyang was the capital of the state of Shen in the first millennium BCE. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wancheng District
Wancheng District () is one of two districts of the city of Nanyang, in the southwest of Henan province, People's Republic of China. Administrative divisions As 2012, this district is divided to 6 subdistricts, 4 towns and 6 townships. ;Subdistricts ;Towns ;Townships Education Higher education * Nanyang Institute of Technology() * Henan Polytechnic Institutehttp://www.hnpi.cn/ (Chinese)() See also *Expressways of Henan *China National Highways *Expressways of China *Henan * Wolong District *Nanyang, Henan Nanyang is a prefecture-level city in the southwest of Henan province, China. The city with the largest administrative area in Henan, Nanyang borders Xinyang to the southeast, Zhumadian to the east, Pingdingshan to the northeast, Luoyang to the n ... References Nanyang, Henan County-level divisions of Henan {{Henan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Biao
Liu Biao () () (151 – September 208), courtesy name Jingsheng, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He is best known for serving as the Governor of Jing Province (covering present-day Hubei and Hunan) from 192 until his death in 208. He was also a member of the extended family of the Han emperors through his ancestor Liu Yu, the fifth son of Emperor Jing. Liu Biao was described as a handsome man and was over eight ''chi'' tall (1.86 metres). Life In 166 to 167, when Liu Biao was 17 (by East Asian reckoning), he became a student of Wang Chang (grandfather of Wang Can). At the time, Wang Chang was Administrator of Nanyang (南阳太守). When the Han dynasty was consumed with war following the Yellow Turban Rebellion in 184, Liu Biao held the governorship of Jing Province (covering present-day Hubei and Hunan). Liu Biao later started a war against the warlord Yuan Shu and his minor vassal, Sun Jian. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jing Province
Jingzhou or Jing Province was one of the Nine Provinces of ancient China referenced in Chinese historical texts such as the ''Tribute of Yu'', '' Erya'' and '' Rites of Zhou''. Jingzhou became an administrative division during the reign of Emperor Wu (r. 141–87 BCE) in the Western Han dynasty (206 BCE–9 CE). It usually corresponded with the modern-day provinces of Hubei and Hunan until the Sui dynasty, after which it referred to the city of Jingzhou. History Pre-Qin era In the Warring States period, the Chu state covered most of present-day Hubei and Hunan, the areas that would form Jingzhou in a later era. The Qin state dropped the name "Chu" (楚) (literally "chaste tree") and used its synonym "Jing" (荊) instead to avoid a naming taboo, since the personal name of Qin's King Zhuangxiang (281–247 BCE) was "Zichu" (子楚; lit. "son of Chu") because his adoptive mother, Lady Huayang, was from Chu. Chu was conquered by Qin in 223 BCE in the final stages of the Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanyang Commandery
Nanyang Commandery ( zh, 南陽郡) was a Chinese commandery that existed from the Warring States period to Tang dynasty. It was centered in present-day Nanyang, Henan. History Nanyang Commandery was established by Qin in the 35th year of King Zhao (272 BC). The seat was Wan (), present-day Nanyang, Henan. It consisted of the land north of the Han River previously conquered from Chu. In the Western Han dynasty, the commandery consisted of 36 counties: Wan, Chou (), Duyan (), Zan (), Yuyang (), Boshan (), Nieyang (), Yin (), Duyang (), Zhi (), Shandu (), Caiyang (), Xinye (), Zhuyang (), Jiyang (), Wudang (), Wuyin (), Xi'e (), Rang (), Li (), Anzhong (), Guanjun (), Biyang (), Pingshi (), Sui (), She (), Deng (), Chaoyang (), Luyang (), Chongling (), Xindu (), Huyang (), Hongyang (), Lecheng (), Bowang (), and Fuyang (). The total population in 2 AD was 1,942,051, in 359,116 households. By 140 AD, the population had grown to 2,439,618, in 528,551 households. During the Three K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanzhong
Guanzhong (, formerly romanised as Kwanchung) region, also known as the Guanzhong Basin, Wei River Basin, or uncommonly as the Shaanzhong region, is a historical region of China corresponding to the crescentic graben basin within present-day central Shaanxi, bounded between the Qinling Mountains in the south (known as Guanzhong's "South Mountains"), and the Huanglong Mountain, Meridian Ridge and Long Mountain ranges in the north (collectively known as its "North Mountains"). The central flatland area of the basin, known as the Guanzhong Plain, is made up of alluvial plains along the lower Wei River and its numerous tributaries and thus also called the Wei River Plain. The region is part of the Jin- Shaan Basin Belt, and is separated from its geological sibling — the Yuncheng Basin to its northeast — by the Yellow River section southwest of the Lüliang Mountains and north of the river's bend at the tri-provincial junction among Shaanxi, Shanxi and Henan. The name ''Guanzho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)