|
Zhang Haipeng
Zhang Haipeng (, Hepburn: ''Chō Kaihō''; 1867–1949), was a Chinese Northeastern Army general, who went over to the Japanese during the Invasion of Manchuria and became a general in the Manchukuo Imperial Army of the State of Manchuria. Biography Zhang was a member of the Honghuzi irregular cavalry forces of the Manchurian warlord Feng Delin during the First Sino-Japanese War. These forces were recruited as mercenaries by the Japanese during the Russo-Japanese War from 1904 to 1905. He subsequently studied at the Northeast Military Academy built by Gen. Zhao Erxun. Following the Xinhai Revolution, he was assigned command of an infantry regiment under the Republic of China; however, he supported Zhang Xun's abortive attempt to restore the Qing dynasty in 1917. He afterwards joined forces with Manchurian warlord Zhang Zuolin. In 1923 he was appointed a commissioner of the Chinese Eastern Railway and participated in the First Zhili–Fengtian War. in early 1931 his forces wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang (surname)
Zhang () is the third most common surname in China and Taiwan (commonly spelled as "Chang" in Taiwan), and it is one of the most common surnames in the world. Zhang is the pinyin romanization of the very common Chinese surname written in simplified characters and in traditional characters. It is spoken in the first tone: ''Zhāng''. It is a surname that exists in many languages and cultures, corresponding to the surname 'Archer' in English for example. In the Wade-Giles system of romanization, it is romanized as "Chang", which is commonly used in Taiwan; "Cheung" is commonly used in Hong Kong as romanization. It is also the pinyin romanization of the less-common surnames (''Zhāng''), which is the 40th name on the ''Hundred Family Surnames'' poem. There is the even-less common (''Zhǎng''). was listed 24th in the famous Song-era ''Hundred Family Surnames'', contained in the verse 何呂施張 (He Lü Shi Zhang). Today, it is one of the most common surnames in the world a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of Manchuria
Manchukuo, officially the State of Manchuria prior to 1934 and the Empire of (Great) Manchuria after 1934, was a puppet state of the Empire of Japan in Manchuria from 1932 until 1945. It was founded as a republic in 1932 after the Japanese invasion of Manchuria, and in 1934 it became a constitutional monarchy under the ''de facto'' control of Japan. It had limited international recognition. The area was the homeland of the Manchu people, Manchus, including the emperors of the Qing dynasty. In 1931, Japanese invasion of Manchuria, Japan seized the region following the Mukden Incident. A pro-Japanese government was installed one year later with Puyi, the List of emperors of the Qing dynasty, last Qing emperor, as the nominal regent and later emperor. Manchukuo's government was dissolved in 1945 after the Surrender of Japan, surrender of Imperial Japan at the End of World War II in Asia, end of World War II. The territories claimed by Manchukuo were first seized in the Soviet inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gada Meiren
Gada Meiren ( Mongolian: ''ɣada meyiren'', Гаадаа мэйрэн, , 1892 - April 5, 1931) was the Mongol leader of a struggle and, eventually, an uprising against the sale of the Khorchin grasslands (in what is now Tongliao City of Inner Mongolia) to Han settlers in 1929. Family Gada Meiren was born in a village named ''jam-un tokhui'' in Khorchin Left Wing Middle Banner (commonly called Darkhan Banner), Jirim League, Qing China. Gada Meiren was a nickname. His given name was Nadmid and he belonged to the Mültütü clan. He also had a Chinese name Meng Qingshan (孟青山). As he was the last son of a family, he was always called ''lou ɣada'' (youngest son). Meiren was a loan word from Manchu and referred to a military officer. As Jirim League was close to China proper, it was subjected to an enormous population pressure from the Chinese heartland. Han immigrants came under the administration of Chinese counties, and the Mongol banner quickly shrunk. His family origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Zhili–Fengtian War
The First Zhili–Fengtian War (First Chihli-Fengtien War; ) was a 1922 conflict in the Republic of China's Warlord Era between the Zhili and Fengtian cliques for control of Beijing. The war led to the defeat of the Fengtian clique and the fall of its leader, Zhang Zuolin, from the coalition Zhili-Fengtian government in Beijing. Wu Peifu was credited as the strategist behind Zhili's victory. Prelude Having jointly seized Beijing in 1920, the Fengtian and Zhili cliques controlled the nominal government of China. Tensions soon began building between the two cliques in their uneasy coalition government. In 1922 the Fengtian clique replaced Premier Jin Yunpeng with Liang Shiyi without getting prior consent of their partner, the Zhili clique. While the Zhili had the backing of the British and Americans, the Fengtian leader was backed by Japan. The Japanese government had once supported their enemy, the Anhui clique, but had switched sides soon after the change of power. On 25 December ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Eastern Railway
The Chinese Eastern Railway or CER (, russian: Китайско-Восточная железная дорога, or , ''Kitaysko-Vostochnaya Zheleznaya Doroga'' or ''KVZhD''), is the historical name for a railway system in Northeast China (also known as Manchuria). The Russian Empire constructed the line from 1897 to 1902 using a concession from the Qing dynasty government of Imperial China. The system linked Chita with Vladivostok in the Russian Far East and with Port Arthur, then an Imperial Russian leased ice-free port. The T-shaped line consisted of three branches: * the western branch, now the Harbin–Manzhouli Railway * the eastern branch, now the Harbin–Suifenhe Railway * the southern branch, now part of the Beijing–Harbin Railway which intersected in Harbin. Saint Petersburg administered the railway and the concession, known as the Chinese Eastern Railway Zone, from the city of Harbin, which grew into a major rail-hub. The southern branch of the CER, kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Zuolin
Zhang Zuolin (; March 19, 1875 June 4, 1928), courtesy name Yuting (雨亭), nicknamed Zhang Laogang (張老疙瘩), was an influential Chinese bandit, soldier, and warlord during the Warlord Era in China. The warlord of Manchuria from 1916 to 1928, and the military dictator of the Republic of China in 1927 and 1928, he rose from banditry to power and influence. Backed by Japan, Zhang successfully influenced politics in the Republic of China during the early 1920s. In the fall of 1924, during the Second Zhili–Fengtian War, he invaded and gained control of Peking, including the internationally recognized government, in April 1926. His appointment as grand marshal of the Republic of China in June 1927 represented the height of his success, but was quickly followed by defeat: the economy of Manchuria, the basis of his power, was overtaxed by his adventurism and collapsed in the winter of 1927; and he was defeated by the National Revolutionary Army of the Kuomintang under Gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhang Xun (Qing Loyalist)
Zhang Xun (; September 16, 1854 – September 11, 1923), courtesy name Shaoxuan (), art name Songshoulaoren (), nickname Bianshuai (, ), was a Chinese general and Qing loyalist who attempted to restore the abdicated emperor Puyi in the Manchu Restoration of 1917. He also supported Yuan Shikai during his time as president. Biography He was born on September 16, 1854, in Chitian village, Fengxin county, Jiangxi. Zhang served as a military escort for Empress Dowager Cixi during the Boxer Uprising. He later served as a subordinate of General Yuan Shikai in the Beiyang Army. He fought for the Qing at Nanjing in 1911, and then after the fall of the Qing, he remained loyal to Yuan Shikai. Despite serving as a general in the new Republic, he refused to cut his queue, as a symbol of his loyalty to the Qing. He was called the "Queue General". He seized Nanjing from the KMT in 1913, defeating the Second Revolution. Despite allowing his troops to savagely loot the city, Zhang was named ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of China (1912–1949)
The Republic of China (ROC), between 1912 and 1949, was a sovereign state recognised as the official designation of China when it was based on Mainland China, prior to the Retreat of the government of the Republic of China to Taiwan, relocation of Government of the Republic of China, its central government to Taiwan as a result of the Chinese Civil War. At a Population history of China, population of 541 million in 1949, it was the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's most populous country. Covering , it consisted of 35 provinces of China, provinces, 1 Special administrative regions of China#ROC special administrative regions, special administrative region, 2 regions, 12 special municipality (Republic of China), special municipalities, 14 leagues, and 4 special banners. The China, People's Republic of China (PRC), which rules mainland China today, considers ROC as a country that ceased to exist since 1949; thus, the history of ROC before 1949 is often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xinhai Revolution
The 1911 Revolution, also known as the Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Manchu-led Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China. The revolution was the culmination of a decade of agitation, revolts, and uprisings. Its success marked the collapse of the Chinese monarchy, the end of 2,132 years of imperial rule in China and 276 years of the Qing dynasty, and the beginning of China's early republican era.Li, Xiaobing. 007(2007). ''A History of the Modern Chinese Army''. University Press of Kentucky. , . pp. 13, 26–27. The Qing dynasty had struggled for a long time to reform the government and resist foreign aggression, but the program of reforms after 1900 was opposed by conservatives in the Qing court as too radical and by reformers as too slow. Several factions, including underground anti-Qing groups, revolutionaries in exile, reformers who wanted to save the monarchy by modernizing it, and activists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhao Erxun
Zhao Erxun (23 May 1844 – 3 September 1927), courtesy name Cishan, art name Wubu, was a Chinese political and military officeholder who lived in the late Qing dynasty. He served in numerous high-ranking positions under the Qing government, including Viceroy of Sichuan, Viceroy of Huguang, and Viceroy of the Three Northeast Provinces. After the fall of the Qing dynasty, he became a historian and was the lead editor of the ''Draft History of Qing'' (''Qing Shi Gao''). Life Early career Zhao's ancestral roots were in Tieling, Fengtian Province (present-day Liaoning Province). His family was under the Plain Blue Banner of the Han Chinese Eight Banners. He sat for the provincial-level imperial examination in 1867 and obtained the position of a ''juren''. In 1874, he sat for the palace-level examination and emerged as a ''jinshi'', after which he was admitted to the Hanlin Academy as a ''bianxiu'' (編修; compiler and editor). The first position Zhao held was an assistant exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
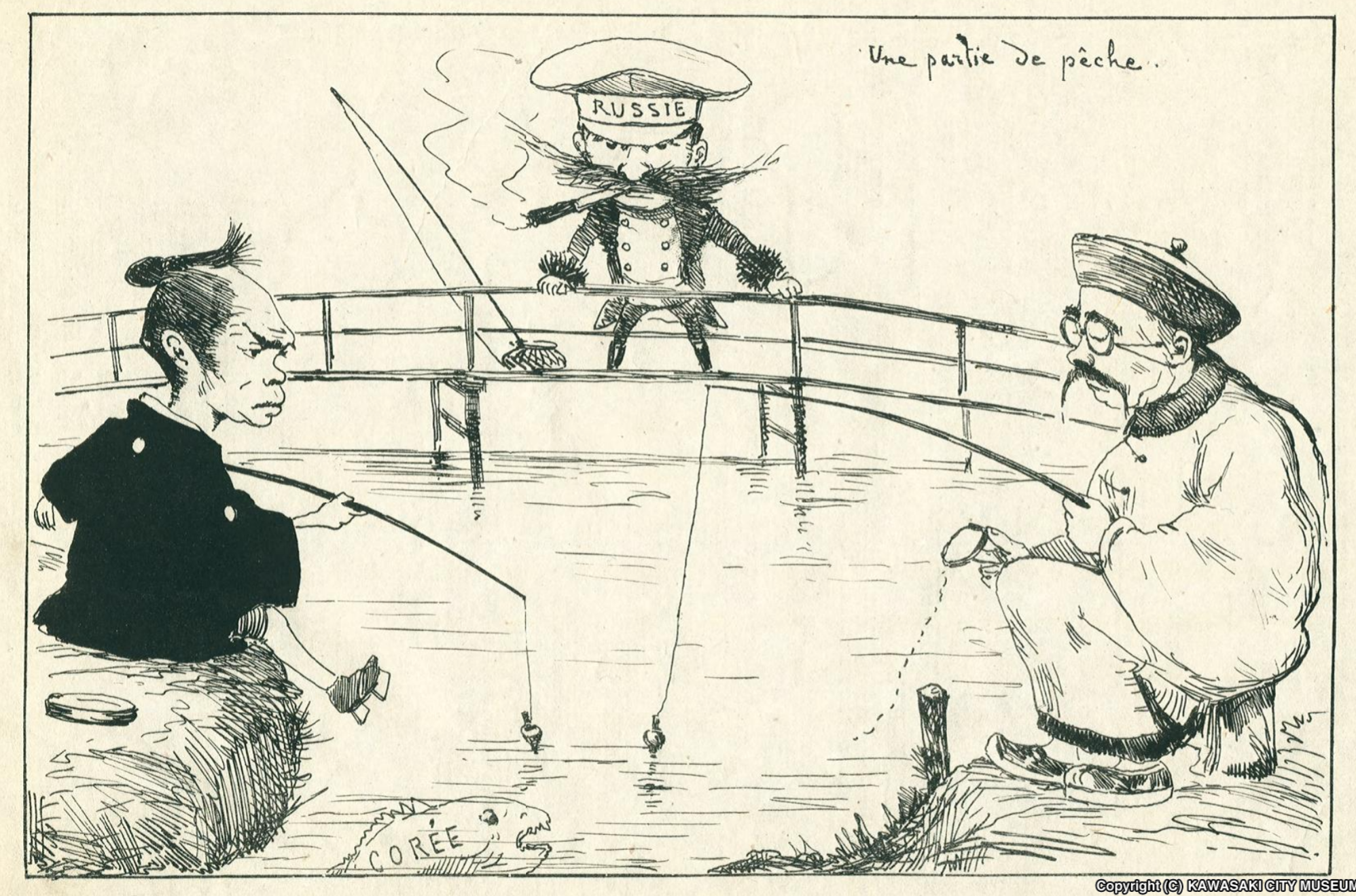
Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1905 over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major theatres of military operations were located in Liaodong Peninsula and Mukden in Southern Manchuria, and the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. Russia sought a warm-water port on the Pacific Ocean both for its navy and for maritime trade. Vladivostok remained ice-free and operational only during the summer; Port Arthur, a naval base in Liaodong Province leased to Russia by the Qing dynasty of China from 1897, was operational year round. Russia had pursued an expansionist policy east of the Urals, in Siberia and the Far East, since the reign of Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century. Since the end of the First Sino-Japanese War in 1895, Japan had feared Russian en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 1894 – 17 April 1895) was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the port of Weihaiwei, the Qing government sued for peace in February 1895. The war demonstrated the failure of the Qing dynasty's attempts to modernize its military and fend off threats to its sovereignty, especially when compared with Japan's successful Meiji Restoration. For the first time, regional dominance in East Asia shifted from China to Japan; the prestige of the Qing dynasty, along with the classical tradition in China, suffered a major blow. The humiliating loss of Korea as a tributary state sparked an unprecedented public outcry. Within China, the defeat was a catalyst for a series of political upheavals led by Sun Yat-sen and Kang Youwei, culminating in the 1911 Xinhai Revolution. The war is commonly known in China as the War of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |