|
Zeta Aurigae
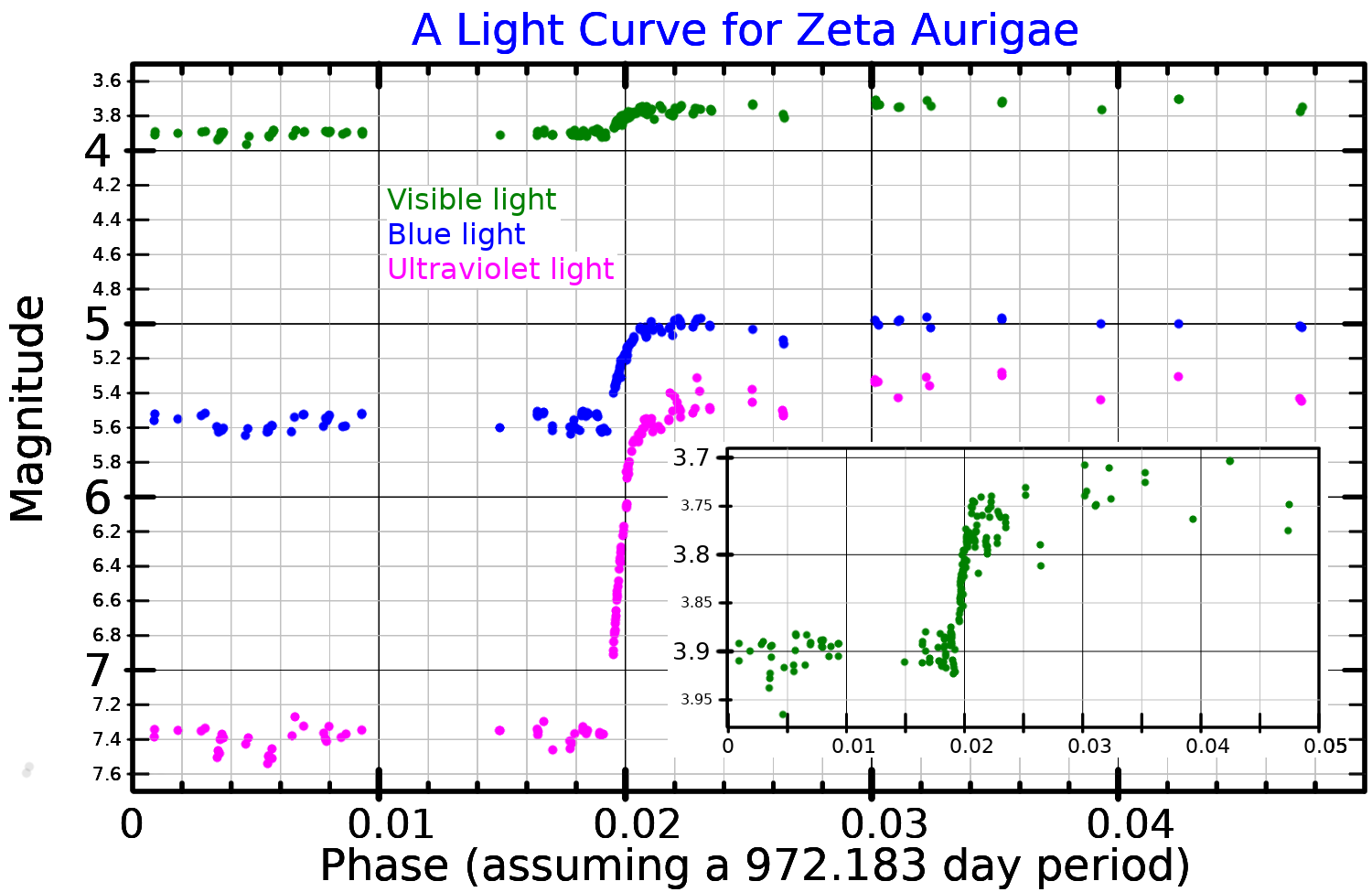
Zeta Aurigae, or ζ Aurigae, is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Auriga. Based upon parallax measurements made during the Hipparcos mission, this system is approximately distant from the sun. It has a combined apparent visual magnitude of 3.75, which is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. The two components are designated Zeta Aurigae A (officially named Saclateni , an old misspelling of "Sadatoni") and B. Nomenclature ''ζ Aurigae'' ( Latinised to ''Zeta Aurigae'') is the system's Bayer designation. The designations of the two components as ''ζ Aurigae A'' and ''B'' derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star systems, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). The system bore the traditional names ''Haedus I'' (also ''Hoedus'') and ''Sadatoni'' (rarely ''Saclateni''). It was one of the two ''haedi'' (Latin: 'kids') of the she-goat Capella, the other being Haedus II, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auriga (constellation)
Auriga is a constellation in the northern celestial hemisphere. It is one of the 88 modern constellations; it was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy. Its name is Latin for '(the) charioteer', associating it with various mythological beings, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the northern Hemisphere, as are five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far south as -34°; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest, Hydra. Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IAU Working Group On Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under Division C – Education, Outreach and Heritage. The IAU states that it is keen to make a distinction between the terms ''name'' and ''designation''. To the IAU, ''name'' refers to the (usually colloquial) term used for a star in everyday conversation, while ''designation'' is solely alphanumerical, and used almost exclusively in official catalogues and for professional astronomy. (The WGSN notes that transliterated Bayer designations (e.g., Tau Ceti) are considered a special historical case and are treated as designations.) Terms of reference The terms of reference for the WGSN for the period 2016–2018 were approved by the IAU Executive Committee at its meeting on 6 May 2016. In summary, these are to: * establish IAU guidelines for the proposal and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hammond Wright
William Hammond Wright (November 4, 1871 – May 16, 1959) was an American astronomer and the director of the Lick Observatory from 1935 until 1942. Wright was born in San Francisco. After graduating in 1893 from the University of California, he became Assistant Astronomer at Lick Observatory. From 1903 to 1906 he worked on establishing the "Manuel Foster Observatory, Southern station" of the observatory at Cerro San Cristobal near Santiago de Chile. It only took him 6 months to start with observations from this new site, and he recorded a large series of radial velocity measurements of stars in the southern sky. In 1908 he was promoted to Astronomer. From 1918 to 1919 he was stationed at Aberdeen Proving Ground working for the United States Army Ordnance Corps, ordnance section of the United States Army. He then returned to the Lick Observatory and worked there until his retirement. He is most famous for his work on radial velocity of stars in our galaxy, and his work with h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Star Names
Chinese star names (Chinese: , ''xīng míng'') are named according to ancient Chinese astronomy and astrology. The sky is divided into star mansions (, ''xīng xiù'', also translated as "lodges") and asterisms (, ''xīng guān''). The system of 283 asterisms under Three Enclosures and Twenty-eight Mansions was established by Chen Zhuo of the Three Kingdoms period, who synthesized ancient constellations and the asterisms created by early astronomers Shi Shen, Gan De and Wuxian. Since the Han and Jin Dynasties, stars have been given reference numbers within their asterisms in a system similar to the Bayer or Flamsteed designations, so that individual stars can be identified. For example, Deneb (α Cyg) is referred to as (''Tiān Jīn Sì'', the Fourth Star of Celestial Ford). In the Qing Dynasty, Chinese knowledge of the sky was improved by the arrival of European star charts. ''Yixiang Kaocheng'', compiled in mid-18th century by then deputy Minister of Rites Ignaz Kögler, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
26 Aurigae
26 Aurigae is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Auriga. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.41. The distance to this system remains poorly constrained. The new Hipparcos reduction gives a parallax of . The original Hipparcos parallax was given as , leading to a distance of being assumed in many texts. A distance of has been derived from fitting the spectrum. 26 Aurigae is a visual binary system, and the two stars orbit each other every 52.735 years with an ellipticity of 0.653 and an angular separation . The system is made of a magnitude 6.29 G-type red giant, and a hotter magnitude 6.21 star that has been classified as an early B-type main-sequence star to an A-type subgiant star. Component A is the cool giant star, the brighter but less massive of the pair. The hotter star is sometimes listed as the primary on the basis of its stronger showing in the blended spectrum. References {{DEFAUL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chi Aurigae
Chi Aurigae, Latinized from χ Aurigae, is the Bayer designation for a binary star system in the northern constellation of Auriga. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.74. The annual parallax shift of this object is much smaller than the measurement error, making distance estimates by that means unreliable. The estimated distance to this star is approximately 3,000 light years. The brightness of the star is diminished by 1.26 in magnitude from extinction caused by intervening gas and dust. Chi Aurigae is a spectroscopic binary with an orbital period of 676.85 d and an eccentricity of 0.12. The primary component of this system is a supergiant star with a stellar classification of B5 Iab. It has a stellar wind that is causing mass loss at the rate of 0.38–0.46 × 10−9 solar mass The solar mass () is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is often used to indicate the masses of other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tau Aurigae
Tau Aurigae, Latinized from τ Aurigae, is a star in the northern constellation Auriga. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.505, and is approximately distant from Earth. Tau Aurigae is an evolved giant star with a stellar classification of G8 III. It has expanded to 11 times the radius of the Sun and shines with 63 times the Sun's luminosity. This energy is radiated into outer space from the outer atmosphere at an effective temperature of 4,887. This heat gives it the yellow-hued glow of a G-type star. References External links HR 1995CCDM J05492+3911Image Tau Aurigae {{DEFAULTSORT:Tau Aurigae 038656 001995 Aurigae, Tau Auriga (constellation) G-type giants Aurigae, 29 1995 File:1995 Events Collage V2.png, From left, clockwise: O.J. Simpson is O. J. Simpson murder case, acquitted of the murders of Nicole Brown Simpson and Ronald Goldman from the 1994, year prior in "The Trial of the Century" in the United States; The .. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nu Aurigae
Nu Aurigae, Latinised from ν Aurigae, is the Bayer designation for a star in the northern constellation of Auriga. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.96 and is approximately distant from the Earth. This is an evolved giant star with a stellar classification of G9.5 III. It is a red clump star, which indicates that it is generating energy through the fusion of helium at its core. The outer envelope has expanded to 19 times the radius of the Sun and cooled to , giving it the characteristic yellow-hued glow of a G-type star. It shines with 135 times the luminosity of the Sun. This is an astrometric binary with a suspected white dwarf companion. A 10th-magnitude star 54.6 arcseconds away is an optical companion. References External links HR 2012CCDM J05515+3909Image Nu Aurigae {{DEFAULTSORT:Nu Aurigae G-type giants Horizontal-branch stars Astrometric binaries Auriga (constellation) Aurigae, Nu Durchmusterung objects Aurig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upsilon Aurigae
Upsilon Aurigae, Latinised from υ Aurigae, is the Bayer designation for a single star in the northern constellation of Auriga. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.74, which means it is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements, this star is approximately distant from the Earth. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +38 km/s. This is an evolved red giant star with a stellar classification of M0 III. It is a suspected variable star and is currently on the asymptotic giant branch, which means it is generating energy through the fusion of helium along a shell surrounding a small, inert core of carbon and oxygen. The star is two billion years old with 1.64 times the mass of the Sun and has expanded to 61 times the Sun's radius. It is radiating 1,165 times the Sun's luminosity from its photosphere at an effective temperature of . References External links HR 2011Image Upsilon Aurigae {{DEFAULTSORT:Upsil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Aurigae
Epsilon Aurigae (ε Aurigae, abbreviated Epsilon Aur, ε Aur) is a multiple star system in the northern constellation of Auriga, the charioteer. It is an unusual eclipsing binary system comprising an F0 supergiant (officially named Almaaz , the traditional name for the system) and a companion which is generally accepted to be a huge dark disk orbiting an unknown object, possibly a binary system of two small B-type stars. The distance to the system is still a subject of debate, but data from the Gaia spacecraft puts its distance at around light years from Earth. Epsilon Aurigae was first suspected to be a variable star when German astronomer Johann Heinrich Fritsch observed it in 1821. Later observations by Eduard Heis and Friedrich Wilhelm Argelander reinforced Fritsch's initial suspicions and attracted attention to the star. Hans Ludendorff, however, was the first to study it in great detail. His work revealed that the system was an eclipsing binary variable, a star t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterism (astronomy)
An asterism is an observed pattern or group of stars in the sky. Asterisms can be any identified pattern or group of stars, and therefore are a more general concept than the formally defined 88 constellations. Constellations are based on asterisms, but unlike asterisms, constellations outline and today completely divide the sky and all its celestial objects into regions around their central asterisms. For example, the asterism known as the Big Dipper comprises the seven brightest stars in the constellation Ursa Major. Another is the asterism of the Southern Cross, within the constellation of Crux. Asterisms range from simple shapes of just a few stars to more complex collections of many stars covering large portions of the sky. The stars themselves may be bright naked-eye objects or fainter, even telescopic, but they are generally all of a similar brightness to each other. The larger brighter asterisms are useful for people who are familiarizing themselves with the night sky. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |