Zeta Aurigae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Zeta Aurigae, or ζ Aurigae, is a
 Zeta Aurigae was first recognized as a spectroscopic binary by
Zeta Aurigae was first recognized as a spectroscopic binary by
HR 1612
Image Zeta Aurigae
{{DEFAULTSORT:Zeta Aurigae K-type bright giants B-type main-sequence stars Eclipsing binaries Algol variables Auriga (constellation) Aurigae, Zeta Durchmusterung objects Aurigae, 08 032068 023453
binary star
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in wh ...
system in the northern constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
of Auriga
AURIGA (''Antenna Ultracriogenica Risonante per l'Indagine Gravitazionale Astronomica'') is an ultracryogenic resonant bar gravitational wave detector in Italy. It is at the Laboratori Nazionali di Legnaro of the Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nuclea ...
. Based upon parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby objects ...
measurements made during the Hipparcos
''Hipparcos'' was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial obj ...
mission, this system is approximately distant from the sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared radi ...
. It has a combined apparent visual magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's lig ...
of 3.75, which is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye.
The two components are designated Zeta Aurigae A (officially named Saclateni , an old misspelling of "Sadatoni") and B.
Nomenclature
''ζ Aurigae'' ( Latinised to ''Zeta Aurigae'') is the system'sBayer designation
A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek or Latin letter followed by the genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer designations contained 1,564 stars. ...
. The designations of the two components as ''ζ Aurigae A'' and ''B'' derive from the convention used by the Washington Multiplicity Catalog (WMC) for multiple star system
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a '' star cluster'' or '' galaxy'', although, broadly speaki ...
s, and adopted by the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreac ...
(IAU).
The system bore the traditional names ''Haedus I'' (also ''Hoedus'') and ''Sadatoni'' (rarely ''Saclateni''). It was one of the two ''haedi'' (Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
: 'kids') of the she-goat Capella
Capella is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Auriga. It has the Bayer designation α Aurigae, which is Latinised to Alpha Aurigae and abbreviated Alpha Aur or α Aur. Capella is the sixth-brightest star i ...
, the other being Haedus II, Eta Aurigae. The name Sadatoni is from the Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
الساعد الثاني ''as-sācid aθ-θānī'' "the second arm (of the charioteer)". The rare traditional name ''Azaleh'' is shared (in the form ''Hassaleh'') with Iota Aurigae
Iota Aurigae (ι Aurigae, abbreviated Iota Aur, ι Aur), officially named Hassaleh , is a star in the northern constellation of Auriga (constellation), Auriga. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 2.7, which is bright enough to be Bortle ...
. In 2016, the IAU organized a Working Group on Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under Division C – Education ...
(WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN decided to attribute proper names to individual stars rather than entire multiple systems. It approved the names ''Saclateni'' for the component Zeta Aurigae A and ''Haedus'' for Eta Aurigae on 30 June 2017 and they are both now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names.
In Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
, (), meaning ''Pillars
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression (physical), compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column i ...
'', refers to an asterism consisting of Zeta Aurigae, Epsilon Aurigae
Epsilon Aurigae (ε Aurigae, abbreviated Epsilon Aur, ε Aur) is a multiple star system in the northern constellation of Auriga, the charioteer. It is an unusual eclipsing binary system comprising an F0 supergiant (officially named Alma ...
, Eta Aurigae, Upsilon Aurigae
Upsilon Aurigae, Latinised from υ Aurigae, is the Bayer designation for a single star in the northern constellation of Auriga. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.74, which means it is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. B ...
, Nu Aurigae, Tau Aurigae, Chi Aurigae
Chi Aurigae, Latinized from χ Aurigae, is the Bayer designation for a binary star system in the northern constellation of Auriga. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.74. The annual parallax shi ...
and 26 Aurigae. Consequently, the Chinese name
Chinese names or Chinese personal names are names used by individuals from Greater China and other parts of the Chinese-speaking world throughout East and Southeast Asia (ESEA). In addition, many names used in Japan, Korea and Vietnam are often a ...
for Zeta Aurigae itself is (, en, the Second Star of Pillars.)
Properties
 Zeta Aurigae was first recognized as a spectroscopic binary by
Zeta Aurigae was first recognized as a spectroscopic binary by William Hammond Wright
William Hammond Wright (November 4, 1871 – May 16, 1959) was an American astronomer and the director of the Lick Observatory from 1935 until 1942.
Wright was born in San Francisco. After graduating in 1893 from the University of California ...
while analyzing photographic plate
Photographic plates preceded photographic film as a capture medium in photography, and were still used in some communities up until the late 20th century. The light-sensitive emulsion of silver salts was coated on a glass plate, typically thinn ...
s taken at Lick Observatory
The Lick Observatory is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by the University of California. It is on the summit of Mount Hamilton, in the Diablo Range just east of San Jose, California, United States. The observatory is managed by th ...
between 1898 and 1908. This star is among those earlier described by Antonia Maury
Antonia Caetana de Paiva Pereira Maury (March 21, 1866 – January 8, 1952) was an American astronomer who was the first to detect and calculate the orbit of a spectroscopic binary. She published an important early catalog of stellar spectra us ...
as having a composite spectrum. The first orbit was determined in 1924 by William Edmund Harper using measurements taken at Dominion Observatory
The Dominion Observatory was an astronomical observatory in Ottawa, Ontario that operated from 1902 to 1970. The Observatory was also an institution within the Canadian Federal Government. The observatory grew out of the Department of the Int ...
, his orbital elements are very similar to the most recent determinations. Harper also noticed that the composite nature of the spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors i ...
had disappeared on the one plate when the K type primary was nearest the sun indicating a possible eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three ce ...
. In 1932 the eclipsing binary
A binary star is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved using a telescope as separate stars, in wh ...
nature of the system was confirmed by Paul Guthnick
Paul Guthnick (January 12, 1879 – September 6, 1947) was a German astronomer.
Born in Hitdorf am Rhein, he studied at the University of Bonn receiving his doctorate in 1901 under Friedrich Küstner. He worked from 1901 at the Royal Observat ...
, Heribert Schneller and independently Josef Hopmann
Josef Hopmann (22 December 1890 – 11 October 1975) was a German astronomer.
He was born in Berlin and received his education at universities in Bonn and Berlin, then became an assistant at Bonn Observatory in 1914. In 1930 he became a full profe ...
.
The orbital plane
The orbital plane of a revolving body is the geometric plane in which its orbit lies. Three non-collinear points in space suffice to determine an orbital plane. A common example would be the positions of the centers of a massive body (host) an ...
of this eclipsing system is oriented close to the line of sight from the Earth, with an inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a Plane of reference, reference plane and the orbital plane or Axis of rotation, axis of direction of the orbiting object ...
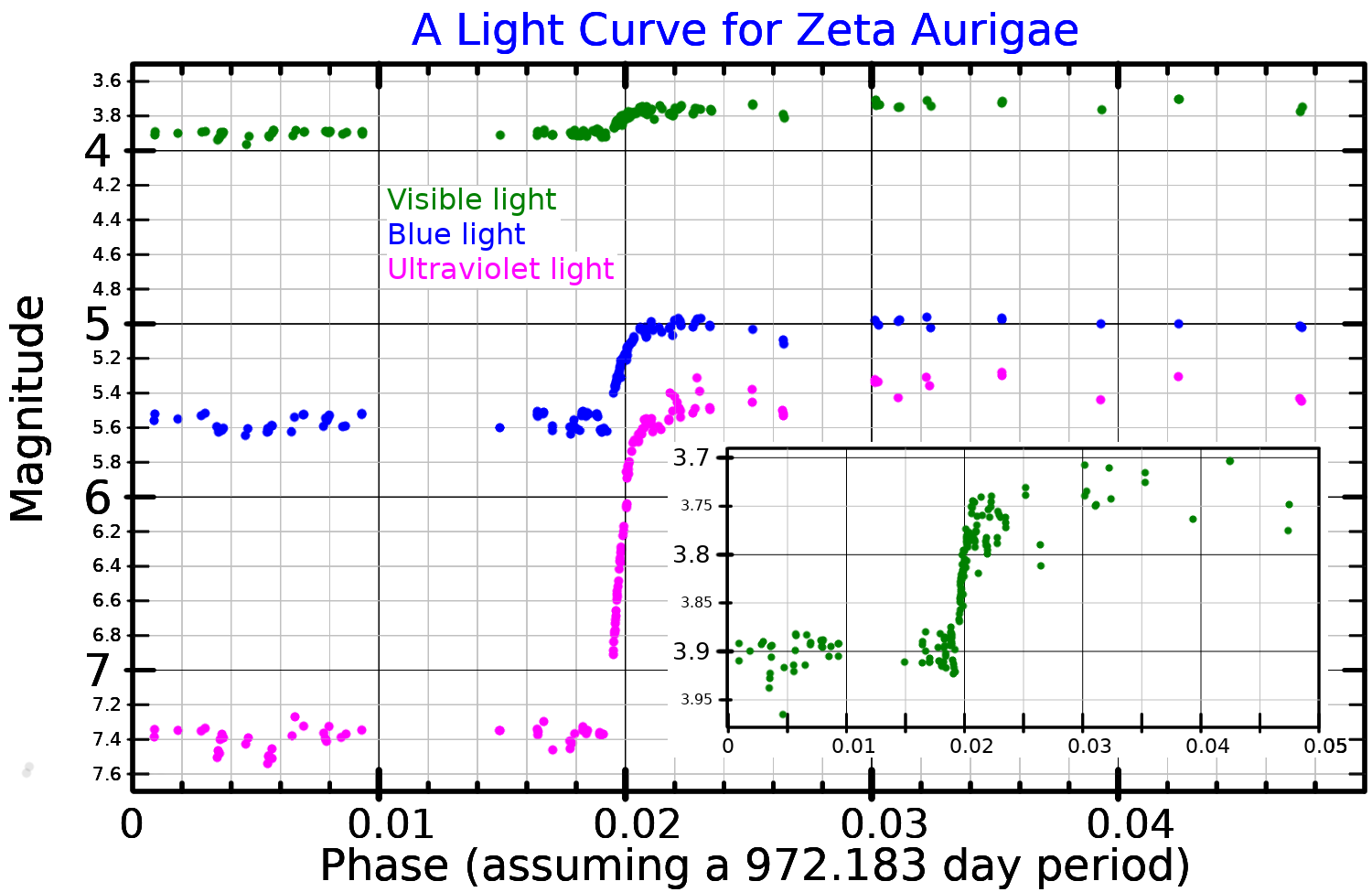
estimated as 87.0°. As a result, an eclipse of one star by the other occurs during each orbit, causing the net magnitude to decrease to +3.99. The pair have an orbital period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets ...
of and an eccentricity
Eccentricity or eccentric may refer to:
* Eccentricity (behavior), odd behavior on the part of a person, as opposed to being "normal"
Mathematics, science and technology Mathematics
* Off-center, in geometry
* Eccentricity (graph theory) of a v ...
(ovalness) of 0.4. The primary, component A, has been categorized as a K-type bright giant
A giant star is a star with substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main-sequence (or ''dwarf'') star of the same surface temperature.Giant star, entry in ''Astronomy Encyclopedia'', ed. Patrick Moore, New York: Oxford University Press ...
or supergiant star
Supergiants are among the most massive and most luminous stars. Supergiant stars occupy the top region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram with absolute visual magnitudes between about −3 and −8. The temperature range of supergiant stars ...
. Its companion, component B, is a B-type main-sequence star
A B-type main-sequence star (B V) is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type B and luminosity class V. These stars have from 2 to 16 times the mass of the Sun and surface temperatures between 10,000 and 30,000 K. B-type stars ...
with a stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction grati ...
B5 V or B7 V. Because component B has a much hotter photosphere than component A, component B produces most of the system's ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than ...
light. This causes the brightness change seen during the eclipses (when B is obscured) to be much greater in ultraviolet light than it is in visible light.
References
External links
HR 1612
Image Zeta Aurigae
{{DEFAULTSORT:Zeta Aurigae K-type bright giants B-type main-sequence stars Eclipsing binaries Algol variables Auriga (constellation) Aurigae, Zeta Durchmusterung objects Aurigae, 08 032068 023453
1612
Events
January–June
* January 6 – Axel Oxenstierna becomes Lord High Chancellor of Sweden. He persuades the Riksdag of the Estates to grant the Swedish nobility the right and privilege to hold all higher offices of governme ...
Sadatoni