|
Zarya (non-magnetic Ship)
''Zarya'' (russian: Заря, ''The Sunrise'') was a sailing-motor schooner built in 1952, and since 1953 used by the USSR Academy of Sciences to study Earth's magnetic field. After the Continuation War Finland was ordered by the USSR to provide 50 wooden sailing-motor fishing schooners as reparations. One of them was taken, and in 1952 modified, into a low magnetic research vessel named ''Zarya'' for the Pushkov Institute of Terrestrial Magnetism, Ionosphere and Radiowave Propagation (IZMIRAN). From 1953 the ship was used to measure the magnetic field of the Earth. She participated in the International Geophysical Year in 1957–1958. In 1991 IZMIRAN was transferred to the Russian Academy of Sciences. In 1976 a rupes on planet Mercury was named after the ship, the "Zarya Rupes". See also * Carnegie (yacht), another ship for which a rupes on Mercury is named References External links History of Zarya from one of its crewmen (in russian)Photo of ''Zarya'' at Odessa in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USSR Academy Of Sciences
The Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union was the highest scientific institution of the Soviet Union from 1925 to 1991, uniting the country's leading scientists, subordinated directly to the Council of Ministers of the Soviet Union (until 1946 – to the Council of People's Commissars of the Soviet Union). In 1991, by the decree of the President of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, the Russian Academy of Sciences was established on the basis of the Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union. History Creation of the Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union The Academy of Sciences of the Soviet Union was formed by a resolution of the Central Executive Committee and the Council of People's Commissars of the Soviet Union dated July 27, 1925 on the basis of the Russian Academy of Sciences (before the February Revolution – the Imperial Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences). In the first years of Soviet Russia, the Institute of the Academy of Sciences was perceived ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish War Reparations To The Soviet Union
War reparations of Finland to the Soviet Union were originally worth US$300,000,000 at 1938 prices (equivalent to US$ in ). Finland agreed to pay the reparations in the Moscow Armistice signed on 19 September 1944. The protocol to determine more precisely the war reparations to the Soviet Union was signed in December 1944, by the prime minister Juho Kusti Paasikivi and the chairman of the Allied Control Commission for controlling the Moscow Armistice in Helsinki, Andrei Zhdanov. Finland was originally obliged to pay $300,000,000 in gold to be paid in the form of ships and machinery, over six years. The Soviet Union agreed to prolong the payment period from six to eight years in late 1945. In summer 1948 the sum was cut to $226,500,000 (equivalent to US$ in ). The last dispatched train of the deliveries paying the war reparations crossed the border between Finland and the Soviet Union on 18 September 1952, in Vainikkala railway border station. Approximately 340,000 railroad carload ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Vessels Of The Soviet Union
Research is " creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion on past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Vessels Of Russia
Research is " creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion on past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schooners
A schooner () is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schooner also has a square topsail on the foremast, to which may be added a topgallant. Differing definitions leave uncertain whether the addition of a fore course would make such a vessel a brigantine. Many schooners are gaff-rigged, but other examples include Bermuda rig and the staysail schooner. The origins of schooner rigged vessels is obscure, but there is good evidence of them from the early 17th century in paintings by Dutch marine artists. The name "schooner" first appeared in eastern North America in the early 1700s. The name may be related to a Scots word meaning to skip over water, or to skip stones. The schooner rig was used in vessels with a wide range of purposes. On a fast hull, good ability to windward was useful for priv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life (magazine)
''Life'' was an American magazine published weekly from 1883 to 1972, as an intermittent "special" until 1978, and as a monthly from 1978 until 2000. During its golden age from 1936 to 1972, ''Life'' was a wide-ranging weekly general-interest magazine known for the quality of its photography, and was one of the most popular magazines in the nation, regularly reaching one-quarter of the population. ''Life'' was independently published for its first 53 years until 1936 as a general-interest and light entertainment magazine, heavy on illustrations, jokes, and social commentary. It featured some of the most notable writers, editors, illustrators and cartoonists of its time: Charles Dana Gibson, Norman Rockwell and Jacob Hartman Jr. Gibson became the editor and owner of the magazine after John Ames Mitchell died in 1918. During its later years, the magazine offered brief capsule reviews (similar to those in ''The New Yorker'') of plays and movies currently running in New York City, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
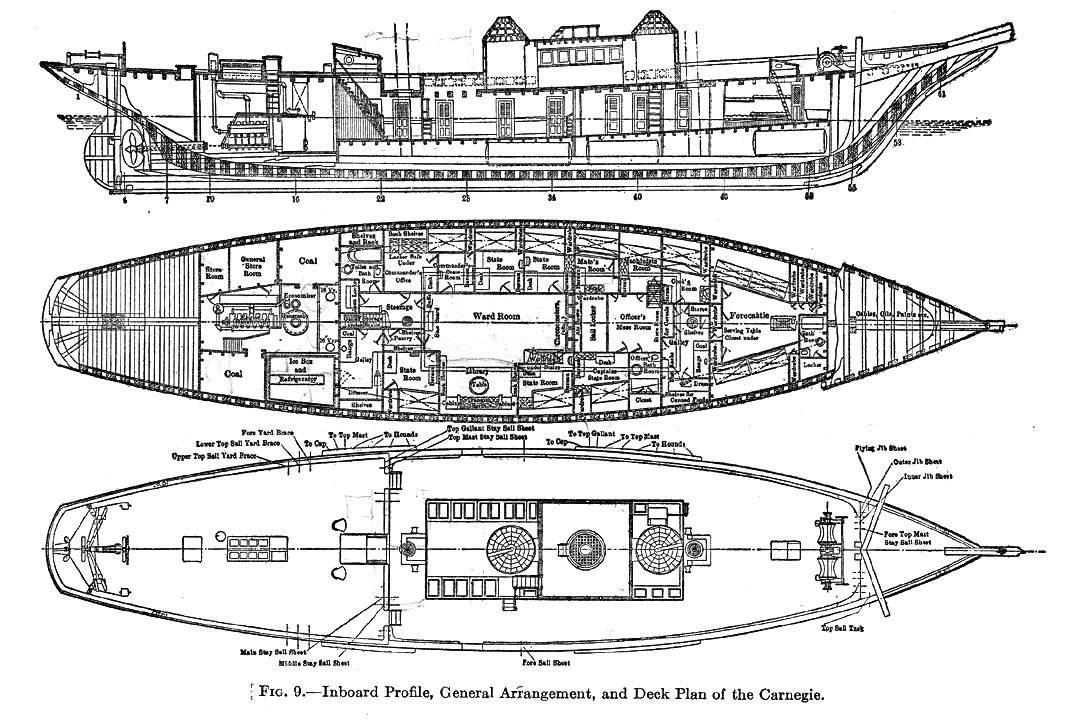
Carnegie (yacht)
''Carnegie'' was a brigantine yacht, equipped as a research vessel, constructed almost entirely from wood and other non-magnetic materials to allow sensitive magnetic measurements to be taken for the Carnegie Institution's Department of Terrestrial Magnetism. She carried out a series of cruises from her launch in 1909 to her destruction by an onboard explosion while in port in 1929. She covered almost in her twenty years at sea. The Carnegie Rupes on the planet Mercury are named after this research vessel. Construction Louis Agricola Bauer, the first director of the Department of Terrestrial Magnetism at the Carnegie Institution, wanted to focus on acquiring oceanic magnetic data to improve the understanding of the Earth's magnetic field. After an experiment in which the brigantine ''Galilee'' was adapted by removing as much magnetic material as possible, it became clear that a new entirely non-magnetic ship was needed. After convincing the institution's board, Bauer set about g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (planet)
Mercury is the smallest planet in the Solar System and the closest to the Sun. Its orbit around the Sun takes 87.97 Earth days, the shortest of all the Sun's planets. It is named after the Roman god ' ( Mercury), god of commerce, messenger of the gods, and mediator between gods and mortals, corresponding to the Greek god Hermes (). Like Venus, Mercury orbits the Sun within Earth's orbit as an inferior planet, and its apparent distance from the Sun as viewed from Earth never exceeds 28°. This proximity to the Sun means the planet can only be seen near the western horizon after sunset or the eastern horizon before sunrise, usually in twilight. At this time, it may appear as a bright star-like object, but is more difficult to observe than Venus. From Earth, the planet telescopically displays the complete range of phases, similar to Venus and the Moon, which recurs over its synodic period of approximately 116 days. The synodic proximity of Mercury to Earth makes Mercury most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rupes
Rupes (plural ) is the Latin word for 'cliff'. It is used in planetary geology to refer to escarpments on other worlds. , the IAU has named 62 such features in the Solar System, on Mercury (17), Venus (7), the Moon (8), Mars (23), the asteroids Vesta (2) and Lutetia (2), and Uranus's satellites Miranda (2) and Titania (1). How rupes formed is, , a matter of speculation. Compressional strain from the cooling of the crust of terrestrial planets and large scale displacement due to impacts are the two dominant theories. See also * Rupes on the Earth's moon * Rupes on Mercury * Rupes on Venus * Rousillon Rupes * Rupes Tenuis * Verona Rupes Verona Rupes is a cliff on Miranda, a moon of Uranus. It was discovered by the ''Voyager 2'' space probe in January 1986. The cliff face, previously thought to be from high, as of 2016 is estimated to be high, which makes it the tallest known ... References Planetary geology Slope landforms * {{Geology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; french: Année géophysique internationale) was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War when scientific interchange between East and West had been seriously interrupted. Sixty-seven countries participated in IGY projects, although one notable exception was the mainland People's Republic of China, which was protesting against the participation of the Republic of China (Taiwan). East and West agreed to nominate the Belgian Marcel Nicolet as secretary general of the associated international organization. The IGY encompassed eleven Earth sciences: aurora and airglow, cosmic rays, geomagnetism, gravity, ionospheric physics, longitude and latitude determinations (precision mapping), meteorology, oceanography, seismology, and solar activity. The timing of the IGY was particularly suited for studying some of these phenomena, since it covered th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IZMIRAN
The Pushkov Institute of Terrestrial Magnetism, Ionosphere and Radiowave Propagation of the Russian Academy of Sciences (IZMIRAN, russian: Институт земного магнетизма, ионосферы и распространения радиоволн им. Н. В. Пушкова Российской Академии наук, ИЗМИРАН) is a scientific institution of the Russian Academy of Sciences. this institute was founded in 1939 by Nikolay Pushkov. Institute owns several space satellites programs: * CORONAS - Complex ORbital Near Earth Solar Activities (experiment ended) * COMPASS (Kompas) - Complex Orbital Magneto-Plasma Autonomous Small Satellite (see 2001 in spaceflight) * Interheliozond * Intercosmos-19 (Cosmos-1809) - research of the Earth ionospheric structure and of the electromagnetic processes in it (experiment ended) * Prognoz - a series of magnetometer A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |