|
Zalman Shazar Junior High School
Zalman Tech Co. (usually simplified as ZALMAN) is a South Korean company that develops and provides aftermarket desktop computer products with primary focus on cooling enhancement. Zalman has done considerable product development since its founding in January 1999, and now holds several patents focusing on both cooling and fan noise-reduction. Personal computer systems can generate significant heat and noise, the management of which is important for those modifying or assembling computer systems. Zalman's product range includes specialized heat sink and fan solutions for CPUs, as well as quiet power supplies, computer water cooling systems, motherboard chipset coolers, graphics card heat sink and fan combos, laptop coolers, cases, and hard disk cases that lower temperature and reduce noise. Zalman's primary competitors include Antec, Thermaltake, Spire, Cooler Master and Arctic. Zalman has also developed a completely fanless case. It uses a fin based design to dissipate h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia, constituting the southern part of the Korean Peninsula and sharing a land border with North Korea. Its western border is formed by the Yellow Sea, while its eastern border is defined by the Sea of Japan. South Korea claims to be the sole legitimate government of the entire peninsula and adjacent islands. It has a population of 51.75 million, of which roughly half live in the Seoul Capital Area, the fourth most populous metropolitan area in the world. Other major cities include Incheon, Busan, and Daegu. The Korean Peninsula was inhabited as early as the Lower Paleolithic period. Its first kingdom was noted in Chinese records in the early 7th century BCE. Following the unification of the Three Kingdoms of Korea into Silla and Balhae in the late 7th century, Korea was ruled by the Goryeo dynasty (918–1392) and the Joseon dynasty (1392–1897). The succeeding Korean Empire (1897–1910) was an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small rectangular box. Introduced by IBM in 1956, HDDs were the dominant secondary storage device for general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern era of servers and personal computers, though personal computing devices produced in large volume, like cell phones and tablets, rely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Korean Won
The Korean Republic won, unofficially the South Korean won ( Symbol: ₩; Code: KRW; Korean: 대한민국 원) is the official currency of South Korea. A single won is divided into 100 jeon, the monetary subunit. The jeon is no longer used for everyday transactions, and it appears only in foreign exchange rates. The currency is issued by the Bank of Korea, based in the capital city of Seoul. Etymology The old "won" was a cognate of the Chinese yuan and Japanese yen, which were both derived from the Spanish-American silver dollar. It is derived from the hanja (, ''won''), meaning "round", which describes the shape of the silver dollar. The won was subdivided into 100 ''jeon'' (), itself a cognate of the Chinese unit of weight mace and synonymous with money in general. The current won (1962 to present) is written in hangul only and does not officially have any hanja associated with it. First South Korean won History The Korean won, Chinese yuan and Japanese yen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pivot Display
Page orientation is the way in which a rectangular page is oriented for normal viewing. The two most common types of orientation are ''portrait'' and ''landscape''. The term "portrait orientation" comes from visual art terminology and describes the dimensions used to capture a person's face and upper body in a picture; in such images, the height of the display area is greater than the width. The term "landscape orientation" also reflects visual art terminology, where pictures with more width than height are needed to fully capture the horizon within an artist's view. Besides describing the way documents can be viewed and edited, the concepts of "portrait" and "landscape" orientation can also be used to describe video and photography display options (where the concept of " aspect ratio" replaces that of "page orientation"). Many types of visual media use landscape mode, especially the 4:3 aspect ratio used for classic TV formatting, which is 4 units or pixels wide and 3 units t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
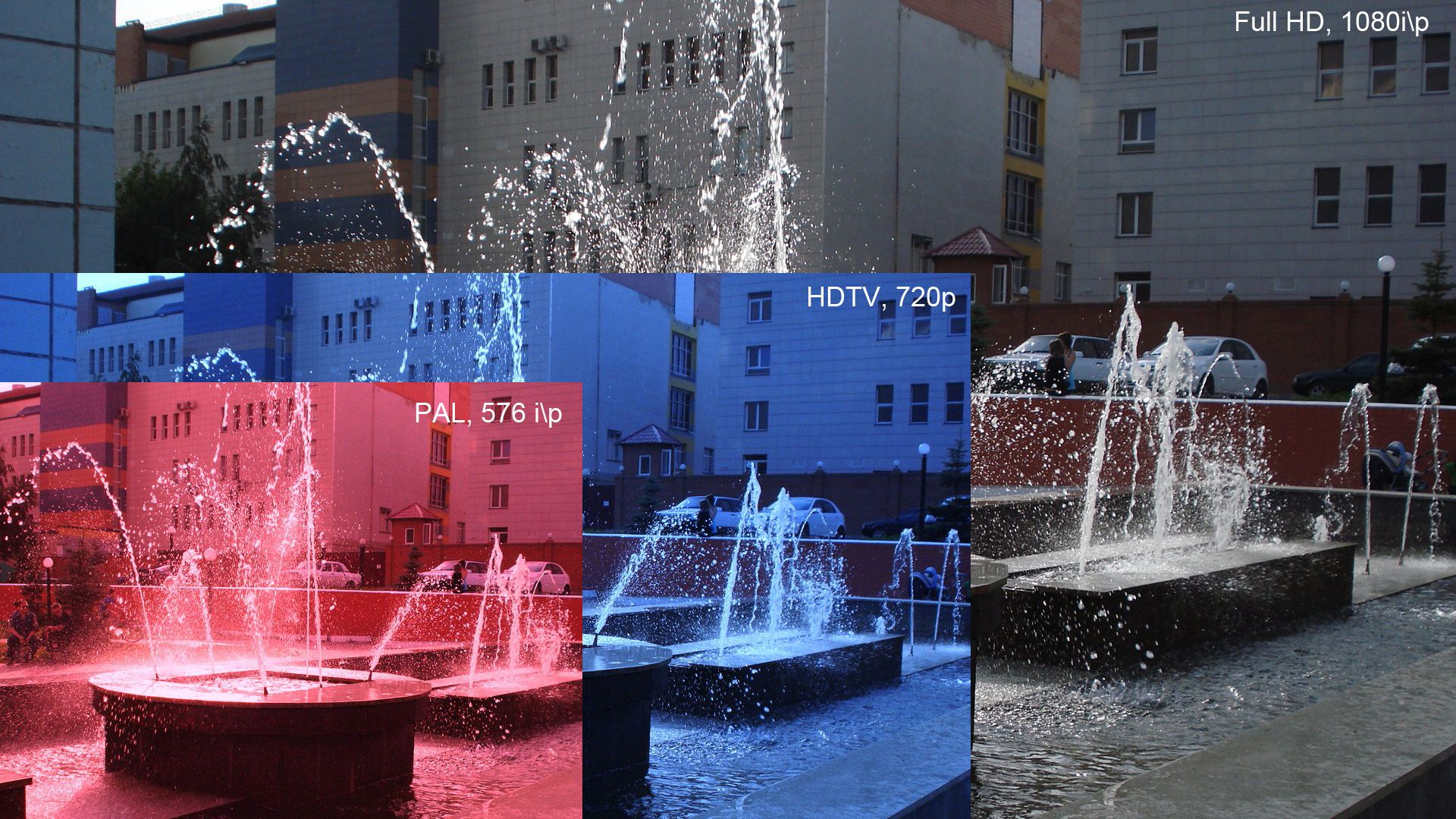
Full HD
1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the ''p'' stands for progressive scan, ''i.e.'' non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes informally referred to as 2K, these terms reflect two distinct technical standards, with differences including resolution and aspect ratio. 1080p video signals are supported by ATSC standards in the United States and DVB standards in Europe. Applications of the 1080p standard include television broadcasts, Blu-ray Discs, smartphones, Internet content such as YouTube videos and Netflix TV shows and movies, consumer-grade televisions and projecto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarized 3D Glasses
A polarized 3D system uses polarization glasses to create the illusion of three-dimensional images by restricting the light that reaches each eye (an example of stereoscopy). To present stereoscopic images and films, two images are projected superimposed onto the same screen or display through different polarizing filters. The viewer wears low-cost eyeglasses with a polarizing filter for each eye. The left and right filters have different polarizations, so each eye receives only the image with the matching polarization. This is used to produce a three-dimensional effect by projecting the same scene into both eyes, but depicted from slightly different perspectives with different polarizations. Multiple people can view the stereoscopic images at the same time. Polarized 3D systems, and stereoscopy systems in general, commonly exhibit the Vergence-Accommodation Conflict. Types of polarised glasses Linearly polarised glasses To present a stereoscopic motion picture, two ima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereoscopic
Stereoscopy (also called stereoscopics, or stereo imaging) is a technique for creating or enhancing the illusion of depth in an image by means of stereopsis for binocular vision. The word ''stereoscopy'' derives . Any stereoscopic image is called a stereogram. Originally, stereogram referred to a pair of stereo images which could be viewed using a stereoscope. Most stereoscopic methods present a pair of two-dimensional images to the viewer. The left image is presented to the left eye and the right image is presented to the right eye. When viewed, the human brain perceives the images as a single 3D view, giving the viewer the perception of 3D depth. However, the 3D effect lacks proper focal depth, which gives rise to the Vergence-Accommodation Conflict. Stereoscopy is distinguished from other types of 3D displays that display an image in three full dimensions, allowing the observer to increase information about the 3-dimensional objects being displayed by head and eye mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
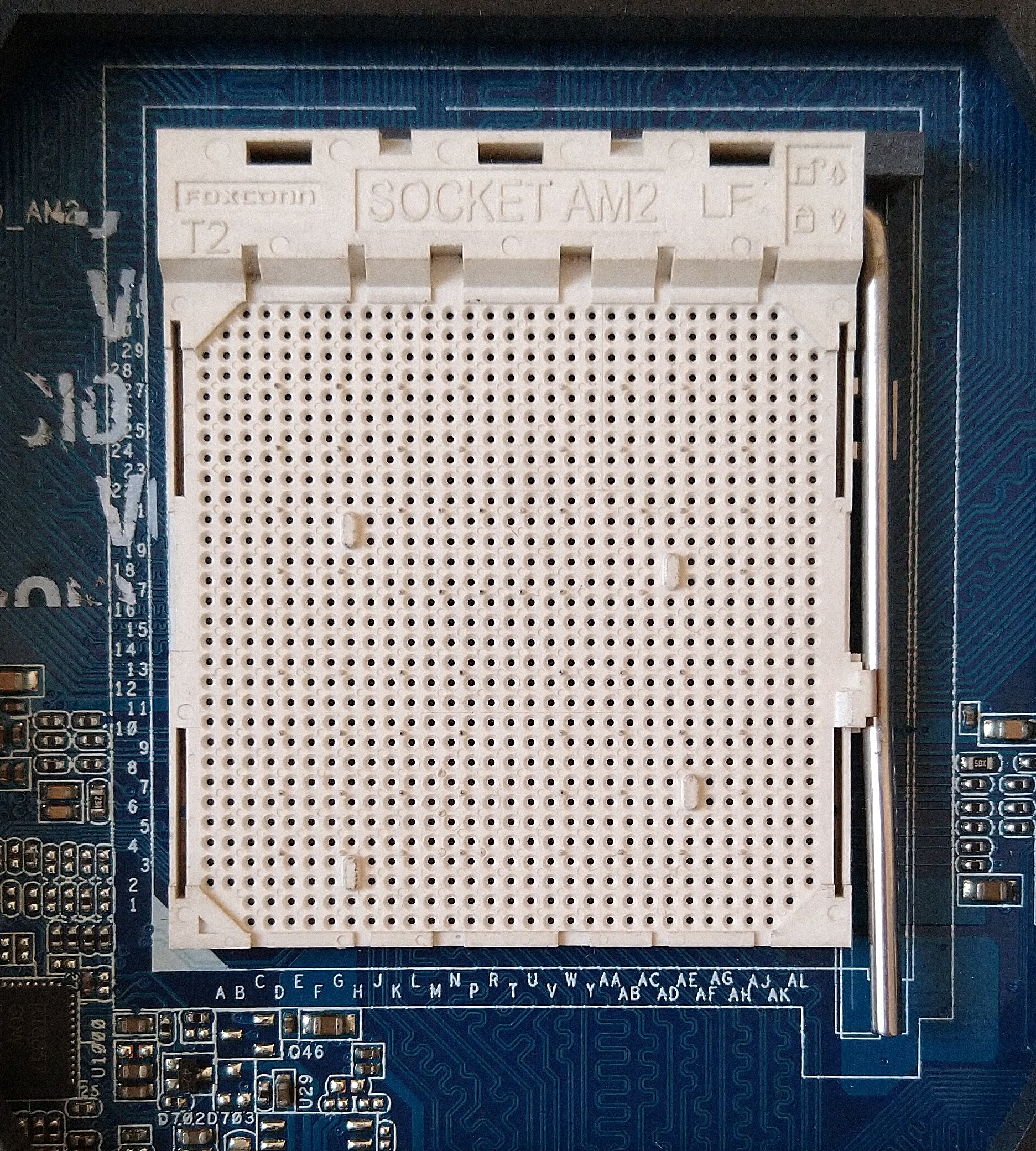
Socket AM2
The Socket AM2, renamed from Socket M2 (to prevent using the same name as Cyrix MII processors), is a CPU socket designed by AMD for desktop processors, including the performance, mainstream and value segments. It was released on May 23, 2006, as a replacement for Socket 939. Technical specifications AM2 processors are incompatible with 939 motherboards and vice versa, and although it has 940 pins, it is incompatible with Socket 940. Socket AM2 supports DDR2 SDRAM memory but not DDR memory, which the previous Socket 939 supported. ''AnandTech'' reported that Socket AM2 system performance was only about 7% faster than Socket 939 equivalents, with most applications about 2% faster, despite having over 30% greater memory bandwidth due to DDR2 support. The first processor cores to support socket AM2 were the single-core Orleans (Athlon 64) and Manila ( Sempron), and the dual-core Windsor (Athlon 64 X2 and Athlon 64 FX). Most processors on Socket AM2 include SSE3 instructions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
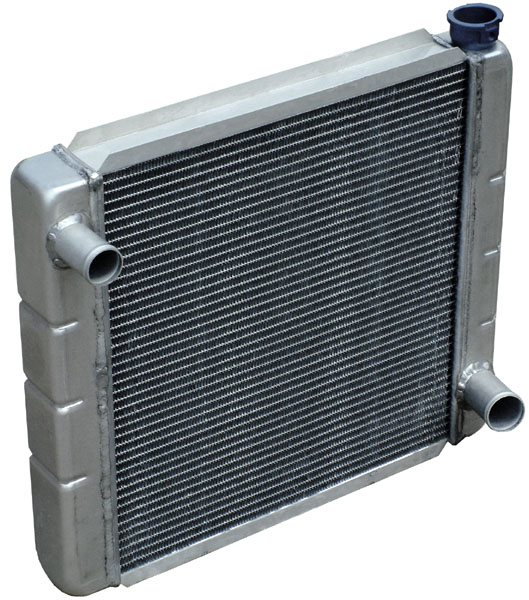
Radiator
Radiators are heat exchangers used to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another for the purpose of cooling and heating. The majority of radiators are constructed to function in cars, buildings, and electronics. A radiator is always a source of heat to its environment, although this may be for either the purpose of heating this environment, or for cooling the fluid or coolant supplied to it, as for automotive engine cooling and HVAC dry cooling towers. Despite the name, most radiators transfer the bulk of their heat via convection instead of thermal radiation. History The Roman hypocaust is an early example of a type of radiator for building space heating. Franz San Galli, a Prussian-born Russian businessman living in St. Petersburg, is credited with inventing the heating radiator around 1855, having received a radiator patent in 1857, but American Joseph Nason developed a primitive radiator in 1841 and received a number of U.S. patents for hot water and steam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Pipe
A heat pipe is a heat-transfer device that employs phase transition to transfer heat between two solid interfaces. At the hot interface of a heat pipe, a volatile liquid in contact with a thermally conductive solid surface turns into a vapor by absorbing heat from that surface. The vapor then travels along the heat pipe to the cold interface and condenses back into a liquid, releasing the latent heat. The liquid then returns to the hot interface through either capillary action, centrifugal force, or gravity and the cycle repeats. Due to the very high heat transfer coefficients for boiling and condensation, heat pipes are highly effective thermal conductors. The effective thermal conductivity varies with heat pipe length, and can approach for long heat pipes, in comparison with approximately for copper. Structure, design and construction A typical heat pipe consists of a sealed pipe or tube made of a material that is compatible with the working fluid such as copper fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic (company)
Arctic GmbH, formerly known as Arctic Cooling, is a German, Swiss-founded manufacturer of computer cooling components, mainly CPU and graphics card coolers, case fans and thermal compound. Since 2010, Arctic expanded its business by starting a range of products to cater other consumer demands beyond that of computer cooling hardware. Nowadays, Arctic also offers various consumer products—spanning audio, home entertainment and computer peripherals. In 2012, Arctic was nominated as one of the finalists in the annual PCR Awards. Founded in 2001, Arctic has offices in Germany, Hong Kong and the United States and cooperates with different production facilities in China. Arctic products are distributed worldwide through distributors, dealers and retailers. The United States, United Kingdom and Germany are Arctic's major markets. The company has also collaborated with leading graphics card brands such as HIS, Inno3D, PowerColor, VTX3D, and Sapphire in the development of OEM cooling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cooler Master
Cooler Master Technology Inc. is a computer hardware manufacturer based in Taiwan. Founded in 1992, the company produces computer cases, power supplies, air and liquid CPU coolers, laptop cooling pads, and computer peripherals. Alongside its retail business, Cooler Master also is an original equipment manufacturer of cooling devices for other manufacturers including NVIDIA (VGA coolers), AMD (CPU and VGA coolers), and EVGA (motherboard heatsinks). The company has sponsored major eSports events. Some of Cooler Master's products have won awards including the iF product design award. History Facilities The company headquarters of Cooler Master is located in Neihu District, Taipei City, Taiwan and has a manufacturing facility in Huizhou, China. To support international operations, the company also has branch offices in various continents, including United States (Fremont, California and Chino, California), the Netherlands (Eindhoven), Italy (Milano), France (Paris), Germany ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |