|
Z Ursae Minoris
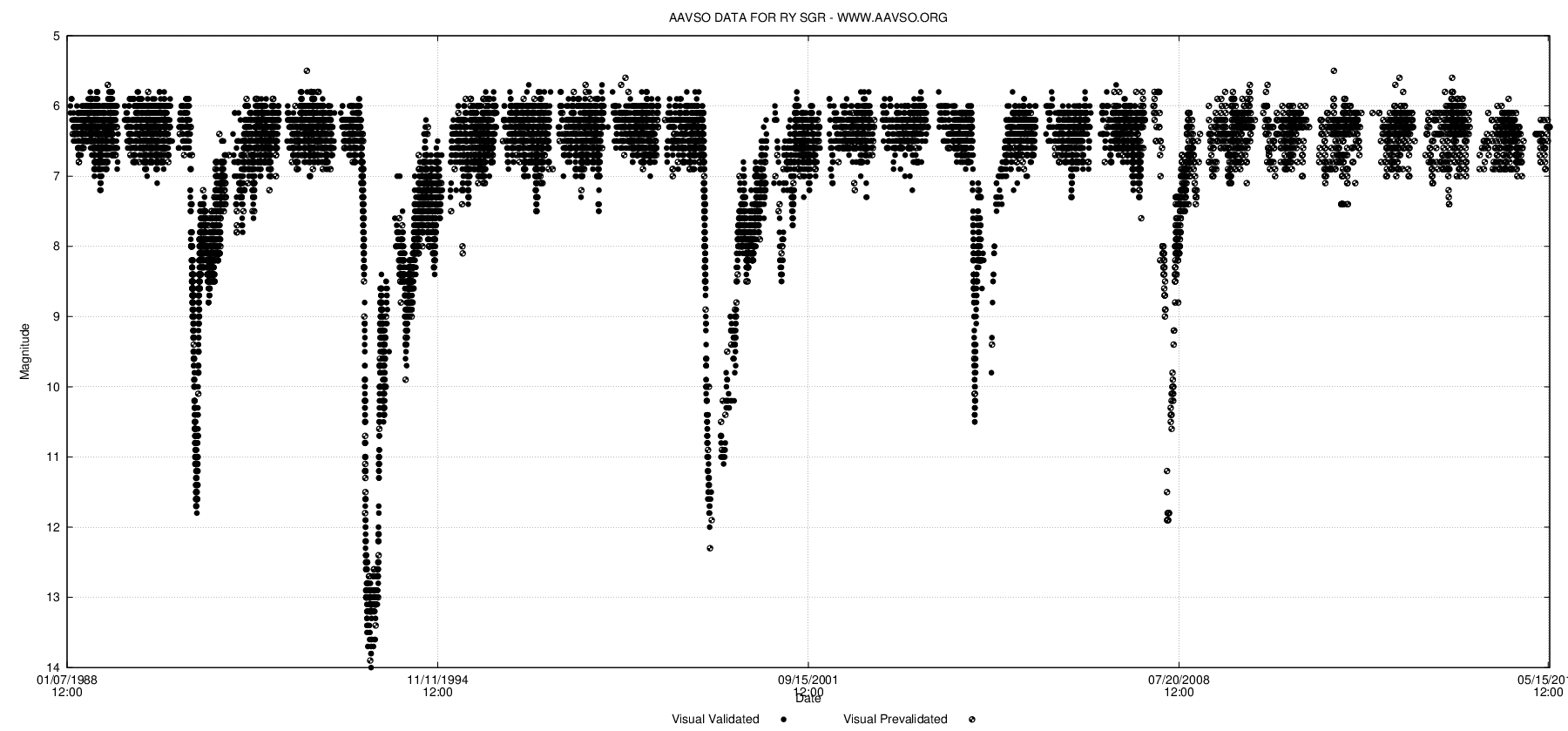
Z Ursae Minoris (Z UMi) is a carbon star and R Coronae Borealis variable in the constellation A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the e ... Ursa Minor. Z Ursae Minoris was discovered to be a variable star in 1934. It was catalogued as a probable Mira variable, due to its red colour and variations over several hundred days. It was discovered to be a carbon star in a survey published in 1985, and subsequently found also to be hydrogen-deficient. After fading by almost six magnitudes in 1992, it was classified as an R Coronae Borealis variable. It was confirmed as an R Coronae Borealis variable, one of the coolest in the class, after its spectrum was analysed in 2006. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Z Ursae Minoris Ursa Minor R Coronae Borealis variables Ursae Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photometric System
In astronomy, a photometric system is a set of well-defined passbands (or optical filters), with a known sensitivity to incident radiation. The sensitivity usually depends on the optical system, detectors and filters used. For each photometric system a set of primary standard stars is provided. A commonly adopted standardized photometric system is the Johnson-Morgan or UBV photometric system (1953). At present, there are more than 200 photometric systems. Photometric systems are usually characterized according to the widths of their passbands: * broadband (passbands wider than 30 nm, of which the most widely used is Johnson-Morgan UBV system) * intermediate band (passbands between 10 and 30 nm wide) * narrow band (passbands less than 10 nm wide) Photometric letters Each letter designates a section of light of the electromagnetic spectrum; these cover well the consecutive major groups, near-ultraviolet (NUV), visible light (centered on the V band), near-infrared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Curve
In astronomy, a light curve is a graph of light intensity of a celestial object or region as a function of time, typically with the magnitude of light received on the y axis and with time on the x axis. The light is usually in a particular frequency interval or band. Light curves can be periodic, as in the case of eclipsing binaries, Cepheid variables, other periodic variables, and transiting extrasolar planets, or aperiodic, like the light curve of a nova, a cataclysmic variable star, a supernova or a microlensing event or binary as observed during occultation events. The study of the light curve, together with other observations, can yield considerable information about the physical process that produces it or constrain the physical theories about it. Variable stars Graphs of the apparent magnitude of a variable star over time are commonly used to visualise and analyse their behaviour. Although the categorisation of variable star types is increasingly done from their s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursa Minor
Ursa Minor (Latin: 'Lesser Bear', contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation located in the far northern sky. As with the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the North American name, Little Dipper: seven stars with four in its bowl like its partner the Big Dipper. Ursa Minor was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, because of Polaris being the north pole star. Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging in apparent magnitude from 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R Coronae Borealis Variable
An R Coronae Borealis variable (abbreviated RCB, R CrB) is an eruptive variable star that varies in luminosity in two modes, one low amplitude pulsation (a few tenths of a magnitude), and one irregular, unpredictably-sudden fading by 1 to 9 magnitudes. The prototype star R Coronae Borealis was discovered by the English amateur astronomer Edward Pigott in 1795, who first observed the enigmatic fadings of the star. Only about 150 RCB stars are currently known in our Galaxy while up to 1000 were expected, making this class a very rare kind of star. It is increasingly suspected that R Coronae Borealis (RCB) stars – rare hydrogen-deficient and carbon-rich supergiant stars – are the product of mergers of white-dwarfs in the intermediary mass regime (total mass between 0.6 and 1.2 ). The fading is caused by condensation of carbon to soot, making the star fade in visible light while measurements in infrared light exhibit no real luminosity decrease. R Coronae Borealis variables ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Star
A carbon star (C-type star) is typically an asymptotic giant branch star, a luminous red giant, whose atmosphere contains more carbon than oxygen. The two elements combine in the upper layers of the star, forming carbon monoxide, which consumes most of the oxygen in the atmosphere, leaving carbon atoms free to form other carbon compounds, giving the star a "sooty" atmosphere and a strikingly ruby red appearance. There are also some dwarf and supergiant carbon stars, with the more common giant stars sometimes being called classical carbon stars to distinguish them. In most stars (such as the Sun), the atmosphere is richer in oxygen than carbon. Ordinary stars not exhibiting the characteristics of carbon stars but cool enough to form carbon monoxide are therefore called oxygen-rich stars. Carbon stars have quite distinctive spectral characteristics, and they were first recognized by their spectra by Angelo Secchi in the 1860s, a pioneering time in astronomical spectroscopy. Spectra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the earliest constellations likely go back to prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation myth, creation, or mythology. Different cultures and countries adopted their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. The 48 traditional Western constellations are Greek. They are given in Aratus' work ''Phenomena'' and Ptolemy's ''Almagest'', though their origin probably predates these works by several centuries. Constellation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursa Minor (constellation)
Ursa Minor (Latin: 'Lesser Bear', contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation located in the far northern sky. As with the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the North American name, Little Dipper: seven stars with four in its bowl like its partner the Big Dipper. Ursa Minor was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, because of Polaris being the north pole star. Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging in apparent magnitude from 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variable Star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are classified as either: * Intrinsic variables, whose luminosity actually changes; for example, because the star periodically swells and shrinks. * Extrinsic variables, whose apparent changes in brightness are due to changes in the amount of their light that can reach Earth; for example, because the star has an orbiting companion that sometimes eclipses it. Many, possibly most, stars have at least some variation in luminosity: the energy output of the Sun, for example, varies by about 0.1% over an 11-year solar cycle. Discovery An ancient Egyptian calendar of lucky and unlucky days composed some 3,200 years ago may be the oldest preserved historical document of the discovery of a variable star, the eclipsing binary Algol. Of the modern astronomers, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mira Variable
Mira variables (named for the prototype star Mira) are a class of pulsating stars characterized by very red colours, pulsation periods longer than 100 days, and amplitudes greater than one magnitude in infrared and 2.5 magnitude at visual wavelengths. They are red giants in the very late stages of stellar evolution, on the asymptotic giant branch (AGB), that will expel their outer envelopes as planetary nebulae and become white dwarfs within a few million years. Mira variables are stars massive enough that they have undergone helium fusion in their cores but are less than two solar masses, stars that have already lost about half their initial mass. However, they can be thousands of times more luminous than the Sun due to their very large distended envelopes. They are pulsating due to the entire star expanding and contracting. This produces a change in temperature along with radius, both of which factors cause the variation in luminosity. The pulsation depends on the mass and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Astronomy
''Open Astronomy'' (formerly ''Baltic Astronomy'') is a peer-reviewed fully open access scientific journal, and currently published by De Gruyter Open. The journal was established in 1992 by the Institute of Theoretical Physics and Astronomy (Vilnius University, Lithuania) as ''Baltic Astronomy'', obtaining its current title in 2017 when it converted to open access. The journal is devoted to publishing research, reviews and news spanning all aspects of astronomy and astrophysics. The editor in chief is Prof. Beatriz Barbuy (IAG, University of São Paulo). History Open Astronomy is the continuation of publishing in the open access model of ''Baltic Astronomy'', which was published by the Institute of Theoretical Physics and Astronomy in Vilnius for astronomical institutions of the Baltic states. The political liberation in the then Soviet Union during the later part of the 1980s enabled increased international contacts. For greater international visibility, a modern jour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Astronomical Journal
''The Astronomical Journal'' (often abbreviated ''AJ'' in scientific papers and references) is a peer-reviewed monthly scientific journal owned by the American Astronomical Society (AAS) and currently published by IOP Publishing. It is one of the premier journals for astronomy in the world. Until 2008, the journal was published by the University of Chicago Press on behalf of the AAS. The reasons for the change to the IOP were given by the society as the desire of the University of Chicago Press to revise its financial arrangement and their plans to change from the particular software that had been developed in-house. The other two publications of the society, the ''Astrophysical Journal'' and its supplement series, followed in January 2009. The journal was established in 1849 by Benjamin A. Gould. It ceased publication in 1861 due to the American Civil War, but resumed in 1885. Between 1909 and 1941 the journal was edited in Albany, New York. In 1941, editor Benjamin Boss arrange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |