|
Z280
The Zilog Z280 is a 16-bit microprocessor, an enhancement of the Zilog Z80 architecture, introduced in July 1987. It is basically the Z800, renamed, with slight improvements such as being fabricated in CMOS. It was a commercial failure. Zilog added a memory management unit (MMU) to expand the addressing range to 16 MB, features for multitasking and multiprocessor and coprocessor configurations, and 256 bytes of on-chip static RAM, configurable as either a cache for instructions and/or data, or as part of the ordinary address space. It has a huge number of new instructions and addressing modes giving a total of over 2000 combinations. It is capable of efficiently handling 32-bit data operations including hardware multiply, divide, and sign extension. It offers Supervisor and User operating modes, and optionally separate address spaces for instructions and data in both modes (four total possible address spaces). Its internal clock signal can be configured to run at 1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
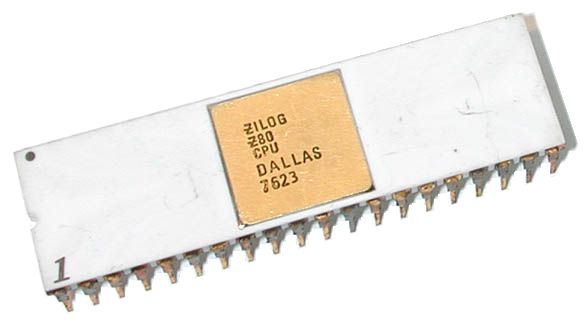
Zilog Z80
The Z80 is an 8-bit microprocessor introduced by Zilog as the startup company's first product. The Z80 was conceived by Federico Faggin in late 1974 and developed by him and his 11 employees starting in early 1975. The first working samples were delivered in March 1976, and it was officially introduced on the market in July 1976. With the revenue from the Z80, the company built its own chip factories and grew to over a thousand employees over the following two years. The Zilog Z80 is a software-compatible extension and enhancement of the Intel 8080 and, like it, was mainly aimed at embedded systems. Although used in that role, the Z80 also became one of the most widely used CPUs in desktop computers and home computers from the 1970s to the mid-1980s. It was also common in military applications, musical equipment such as synthesizers (like the Roland Jupiter-8), and coin-operated arcade games of the late 1970s and early 1980s, including '' Pac-Man''. Zilog licensed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STEbus Z280 CPU On 100x160mm Eurocard
The STEbus (also called the IEEE-1000 bus) is a non-proprietary, processor-independent, computer bus with 8 data lines and 20 address lines. It was popular for industrial control systems in the late 1980s and early 1990s before the ubiquitous IBM PC dominated this market. STE stands for STandard Eurocard. Although no longer competitive in its original market, it is valid choice for hobbyists wishing to make 'home brew' computer systems. The Z80 and probably the CMOS 65C02 are possible processors to use. The standardized bus allows hobbyists to interface to each other's designs. Origins In the early 1980s, there were many proprietary bus systems, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Most had grown in an ad-hoc manner, typically around a particular microprocessor. The S-100 bus is based on Intel 8080 signals, the STD Bus around Z80 signals, the SS-50 bus around the Motorola 6800, and the G64 bus around 6809 signals. This made it harder to interface other processors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zilog Z800
The Zilog Z800 was a 16-bit microprocessor designed by Zilog and meant to be released in 1985. It was instruction compatible with their existing Z80, and differed primarily in having on-chip cache and a memory management unit (MMU) to provide a 16 MB address range. It also added a huge number of new more orthogonal instructions and addressing modes. Zilog essentially ignored the Z800 in favor of their 32-bit Z80000 and the Z800 never entered mass production. After more than five years had elapsed since it was originally introduced, the effort was redubbed the Z280 in 1986.EDN November 27, 1986, p133 An actual product, the Z280 would ship in 1987 with almost the same design as the Z800, but this time implemented in CMOS. The Z800 contrasts with Zilog's first 16-bit effort, the Zilog Z8000, in that the Z800 was intended to be Z80 compatible, while the Z8000 was only Z80-like and did not offer any direct compatibility. Short description There was no expansion of the register set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zilog EZ80
The Zilog eZ80 is an 8-bit microprocessor from Zilog, introduced in 2001. eZ80 is an updated version of the company's first product, the Z80 microprocessor. Design The eZ80 (like the Z380) is binary compatible with the Z80 and Z180, but almost three times as fast as the original Z80 chip at the same clock frequency. The eZ80 has a three-stage pipeline. Available at up to 50 MHz (2004), the performance is comparable to a Z80 clocked at 150 MHz if fast memory is used (i.e. no wait states for opcode fetches, for data, or for I/O) or even higher in some applications (a 16-bit addition is 11 times as fast as in the original). The eZ80 also supports direct continuous addressing of 16 MB of memory without a memory management unit, by extending most registers (HL, BC, DE, IX, IY, SP, and PC) from 16 to 24 bits. In order to do so, the CPU has a full 24-bit address mode called ADL mode. Z80 register pairs are extended to 24 bits and renamed with U e.g. HL is now HL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zilog
Zilog, Inc. is an American manufacturer of microprocessors and 8-bit and 16-bit microcontrollers. It is also a supplier of application-specific embedded system-on-chip (SoC) products. Its most famous product is the Z80 series of 8-bit microprocessors that were compatible with the Intel 8080 but significantly cheaper. The Z80 was widely used during the 1980s in many popular home computers such as the TRS-80, MSX, Amstrad CPC and the ZX Spectrum, as well as arcade games such as '' Pac-Man''. The company also made 16- and 32-bit processors, but these did not see widespread use. From the 1990s, the company focused primarily on the microcontroller market. The name (pronunciation varies) is an acronym of ''Z integrated logic'', also thought of as "Z for the last word of Integrated Logic". In the oral history interview video which Federico Faggin (co-founder of Zilog) recorded for the Computer History Museum, he pronounced Zilog with a long "i" () consistently. History Zilog was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instruction Pipelining
In computer engineering, instruction pipelining or ILP is a technique for implementing instruction-level parallelism within a single processor. Pipelining attempts to keep every part of the processor busy with some instruction by dividing incoming instructions into a series of sequential steps (the eponymous "pipeline") performed by different processor units with different parts of instructions processed in parallel. Concept and motivation In a pipelined computer, instructions flow through the central processing unit (CPU) in stages. For example, it might have one stage for each step of the von Neumann cycle: Fetch the instruction, fetch the operands, do the instruction, write the results. A pipelined computer usually has "pipeline registers" after each stage. These store information from the instruction and calculations so that the logic gates of the next stage can do the next step. This arrangement lets the CPU complete an instruction on each clock cycle. It is common for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Management Unit
A memory management unit (MMU), sometimes called paged memory management unit (PMMU), is a computer hardware unit having all memory references passed through itself, primarily performing the translation of virtual memory addresses to physical addresses. An MMU effectively performs virtual memory management, handling at the same time memory protection, cache control, bus arbitration and, in simpler computer architectures (especially 8-bit systems), bank switching. Overview Modern MMUs typically divide the virtual address space (the range of addresses used by the processor) into pages, each having a size which is a power of 2, usually a few kilobytes, but they may be much larger. The bottom bits of the address (the offset within a page) are left unchanged. The upper address bits are the virtual page numbers. Page table entries Most MMUs use an in-memory table of items called a "page table", containing one "page table entry" (PTE) per page, to map virtual page numbers to ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Memory Allocation
Memory management is a form of resource management applied to computer memory. The essential requirement of memory management is to provide ways to dynamically allocate portions of memory to programs at their request, and free it for reuse when no longer needed. This is critical to any advanced computer system where more than a single process might be underway at any time. Several methods have been devised that increase the effectiveness of memory management. Virtual memory systems separate the memory addresses used by a process from actual physical addresses, allowing separation of processes and increasing the size of the virtual address space beyond the available amount of RAM using paging or swapping to secondary storage. The quality of the virtual memory manager can have an extensive effect on overall system performance. In some operating systems, e.g. OS/360 and successors, memory is managed by the operating system. In other operating systems, e.g. Unix-like operating sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Jose, California
San Jose, officially San José (; ; ), is a major city in the U.S. state of California that is the cultural, financial, and political center of Silicon Valley and largest city in Northern California by both population and area. With a 2020 population of 1,013,240, it is the most populous city in both the Bay Area and the San Jose–San Francisco–Oakland, CA Combined Statistical Area, San Jose-San Francisco-Oakland Combined Statistical Area, which contain 7.7 million and 9.7 million people respectively, the List of largest California cities by population, third-most populous city in California (after Los Angeles and San Diego and ahead of San Francisco), and the List of United States cities by population, tenth-most populous in the United States. Located in the center of the Santa Clara Valley on the southern shore of San Francisco Bay, San Jose covers an area of . San Jose is the county seat of Santa Clara County, California, Santa Clara County and the main component of the San ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Protection
Memory protection is a way to control memory access rights on a computer, and is a part of most modern instruction set architectures and operating systems. The main purpose of memory protection is to prevent a process from accessing memory that has not been allocated to it. This prevents a bug or malware within a process from affecting other processes, or the operating system itself. Protection may encompass all accesses to a specified area of memory, write accesses, or attempts to execute the contents of the area. An attempt to access unauthorized memory results in a hardware fault, e.g., a segmentation fault, storage violation exception, generally causing abnormal termination of the offending process. Memory protection for computer security includes additional techniques such as address space layout randomization and executable space protection. Methods Segmentation Segmentation refers to dividing a computer's memory into segments. A reference to a memory location incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z280 PLCC 1987
Z (or z) is the 26th and last letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its usual names in English are ''zed'' () and ''zee'' (), with an occasional archaic variant ''izzard'' ()."Z", ''Oxford English Dictionary,'' 2nd edition (1989); ''Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged'' (1993); "zee", ''op. cit''. Name and pronunciation In most English-speaking countries, including Australia, Canada, India, Ireland, New Zealand and the United Kingdom, the letter's name is ''zed'' , reflecting its derivation from the Greek ''zeta'' (this dates to Latin, which borrowed Y and Z from Greek), but in American English its name is ''zee'' , analogous to the names for B, C, D, etc., and deriving from a late 17th-century English dialectal form. Another English dialectal form is ''izzard'' . This dates from the mid-18th century and probably derives fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trap (computing)
In digital computers, an interrupt (sometimes referred to as a trap) is a request for the processor to ''interrupt'' currently executing code (when permitted), so that the event can be processed in a timely manner. If the request is accepted, the processor will suspend its current activities, save its state, and execute a function called an ''interrupt handler'' (or an ''interrupt service routine'', ISR) to deal with the event. This interruption is often temporary, allowing the software to resume normal activities after the interrupt handler finishes, although the interrupt could instead indicate a fatal error. Interrupts are commonly used by hardware devices to indicate electronic or physical state changes that require time-sensitive attention. Interrupts are also commonly used to implement computer multitasking, especially in real-time computing. Systems that use interrupts in these ways are said to be interrupt-driven. Types Interrupt signals may be issued in response to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |