|
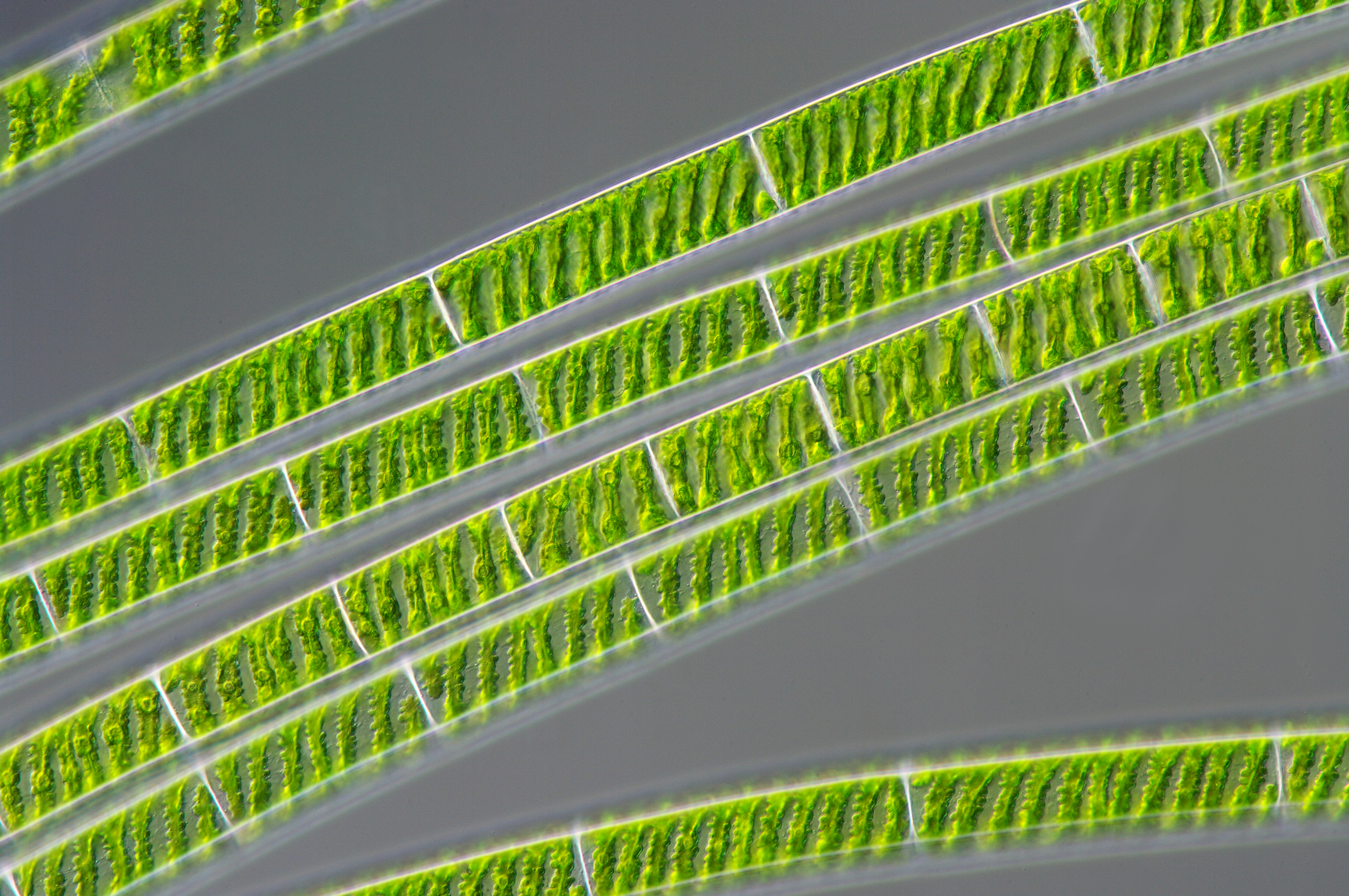
Zygnematales
The Zygnematales ( el, ζυγός (''zygós'') and νῆμα (''nḗma'') ( nom.), νήματος (''nḗmatos'') (gen.)), also called the Conjugatales, are an order of green algae, comprising several thousand different species in two families. The larger family Zygnemataceae, with well-known genera such as ''Zygnema'' and ''Spirogyra'', includes members that grow as unbranched filaments, which grow longer through normal cell division. This group includes the desmids. Most members of both families live in freshwater, and form an important component of the algal scum that grows on or near plants, rocks, and various debris. Systematically they fall within the division Charophyta/Streptophyta, in which the land plants (Embryophyta) emerged. Sexual reproduction in Zygnematales takes place through a process called ''conjugation''. Here filaments of opposite gender line up, and tubes form between corresponding cells. The male cells then become amoeboid and crawl across, or sometimes b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygnematales
The Zygnematales ( el, ζυγός (''zygós'') and νῆμα (''nḗma'') ( nom.), νήματος (''nḗmatos'') (gen.)), also called the Conjugatales, are an order of green algae, comprising several thousand different species in two families. The larger family Zygnemataceae, with well-known genera such as ''Zygnema'' and ''Spirogyra'', includes members that grow as unbranched filaments, which grow longer through normal cell division. This group includes the desmids. Most members of both families live in freshwater, and form an important component of the algal scum that grows on or near plants, rocks, and various debris. Systematically they fall within the division Charophyta/Streptophyta, in which the land plants (Embryophyta) emerged. Sexual reproduction in Zygnematales takes place through a process called ''conjugation''. Here filaments of opposite gender line up, and tubes form between corresponding cells. The male cells then become amoeboid and crawl across, or sometimes b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmids
Desmidiales, commonly called desmids (''Gr.'' ''desmos'', bond or chain), are an order in the Charophyta, a division of green algae in which the land plants (Embryophyta) emerged. Or in other words, Desmid, (order Desmidiales), order of single-celled (sometimes filamentous or colonial) microscopic green algae. Desmids are sometimes treated as a family (Desmidiaceae) of the order Zygnematales. The desmids belong to the class Zygnematophyceae. Although they are sometimes grouped together as a single family Desmidiaceae, most classifications recognize three to five families, either within the order Zygnematales or as their own order Desmidiales. The Desmidiales comprise around 40 genera and 5,000 to 6,000 species, found mostly but not exclusively in fresh water. Many species may be found in the fissures between patches of sphagnum moss in marshes. With a pH level of approximately 4.0, sphagnum peat provides the ideal environment for this flora. Morphology The structure of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmidiales
Desmidiales, commonly called desmids (''Gr.'' ''desmos'', bond or chain), are an order in the Charophyta, a division of green algae in which the land plants (Embryophyta) emerged. Or in other words, Desmid, (order Desmidiales), order of single-celled (sometimes filamentous or colonial) microscopic green algae. Desmids are sometimes treated as a family (Desmidiaceae) of the order Zygnematales. The desmids belong to the class Zygnematophyceae. Although they are sometimes grouped together as a single family Desmidiaceae, most classifications recognize three to five families, either within the order Zygnematales or as their own order Desmidiales. The Desmidiales comprise around 40 genera and 5,000 to 6,000 species, found mostly but not exclusively in fresh water. Many species may be found in the fissures between patches of sphagnum moss in marshes. With a pH level of approximately 4.0, sphagnum peat provides the ideal environment for this flora. Morphology The structure of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryophyte
The Embryophyta (), or land plants, are the most familiar group of green plants that comprise vegetation on Earth. Embryophytes () have a common ancestor with green algae, having emerged within the Phragmoplastophyta clade of green algae as sister of the Zygnematophyceae. The Embryophyta consist of the bryophytes plus the polysporangiophytes. Living embryophytes therefore include hornworts, liverworts, mosses, lycophytes, ferns, gymnosperms and flowering plants. The land plants have diplobiontic life cycles and it is accepted now that they emerged from freshwater, multi-celled algae. The embryophytes are informally called land plants because they live primarily in terrestrial habitats (with exceptional members who evolved to live once again in aquatic habitats), while the related green algae are primarily aquatic. Embryophytes are complex multicellular eukaryotes with specialized reproductive organs. The name derives from their innovative characteristic of nurturing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptophyta
Streptophyta (), informally the streptophytes (, from the Greek ''strepto'' 'twisted', for the morphology of the sperm of some members), is a clade of plants. The composition of the clade varies considerably between authors, but the definition employed here includes land plants and all green algae except the Chlorophyta and the more basal Prasinodermophyta. Classifications The composition of Streptophyta and similar groups (Streptophytina, Charophyta) varies in each classification. Some authors are more restrictive, including only the Charales and Embryophyta (e.g., Streptophyta Jeffrey 1967; Adl et al. 2012, Streptophytina Lewis & McCourt 2004), others include more groups (e.g., Charophyta Lewis & McCourt 2004; Karol et al. 2009; Adl et al. 2012, Streptophyta Bremer, 1985; de Reviers 2002; Leliaert et al. 2012, Streptobionta Kenrick & Crane 1997; some authors use this broader definition, but exclude the Embryophyta, e.g., Charophyta Cavalier-Smith 1993; Leliaert et al. 2012, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Alga
The green algae (singular: green alga) are a group consisting of the Prasinodermophyta and its unnamed sister which contains the Chlorophyta and Charophyta/Streptophyta. The land plants (Embryophytes) have emerged deep in the Charophyte alga as sister of the Zygnematophyceae. Since the realization that the Embryophytes emerged within the green algae, some authors are starting to properly include them. The completed clade that includes both green algae and embryophytes is monophyletic and is referred to as the clade Viridiplantae and as the kingdom Plantae. The green algae include unicellular and colonial flagellates, most with two flagella per cell, as well as various colonial, coccoid and filamentous forms, and macroscopic, multicellular seaweeds. There are about 22,000 species of green algae. Many species live most of their lives as single cells, while other species form coenobia (colonies), long filaments, or highly differentiated macroscopic seaweeds. A few other organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesotaeniaceae
The Mesotaeniaceae are a small family of unicellular green algae known as the "saccoderm desmids". The Mesotaeniaceae appear to be sister or ancestral to the Zygnemataceae. The desmids are a deep branching group of Zygnemataceae. ''Spirotaenia'' was found to be a basal green alga. Genera The Mesotaeniaceae includes the following genera: * ''Ancylonema'' Berggren, 1872 * ''Cylindrocystis'' Meneghini ex De Bary, 1858 * '' Geniculus'' Prescott, 1967 * ''Mesotaenium'' Nägeli, 1849 * ''Netrium'' (Nägeli) Itzigsohn & Rothe, 1856 * '' Nucleotaenium'' Gontcharov & Melkonian, 2010 * '' Planotaenium'' (Ohtani) Petlovany & Palamar-Mordvintseva, 2009 * '' Roya'' West & G.S.West, 1896 * ''Spirotaenia'' Brébisson, 1848 * '' Tortitaenia'' A.J.Brook, 1998 Synonyms: * ''Endospira'' Brébisson, nom. inval., is a synonym of Spirotaenia * ''Entospira'' Kuntze, 1898 is a synonym of ''Spirotaenia'' * ''Polytaenia'' A.J.Brook, 1997, nom. illeg. ''Nomen illegitimum'' (Latin for illegitimate na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netrium
''Netrium'' is a genus of algae belonging to the family Mesotaeniaceae The Mesotaeniaceae are a small family of unicellular green algae known as the "saccoderm desmids". The Mesotaeniaceae appear to be sister or ancestral to the Zygnemataceae. The desmids are a deep branching group of Zygnemataceae. ''Spirotaeni .... The species of this genus are found in Europe, America and Australia. Species: *'' Netrium digitus'' *'' Netrium interruptum'' *'' Netrium lamellosum'' *'' Netrium naegelii'' *'' Netrium obesus'' *'' Netrium oblongum'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q1231838 Zygnematales Charophyta genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirogyra
''Spirogyra'' (common names include water silk, mermaid's tresses, and blanket weed) is a genus of filamentous charophyte green algae of the order Zygnematales, named for the helical or spiral arrangement of the chloroplasts that is characteristic of the genus. ''Spirogyra'' species, of which there are more than 400, are commonly found in freshwater habitats. ''Spirogyra'' measures approximately 10 to 100 μm in width and may grow to several centimetres in length. It is often observed as green slimy patches on the ground near ponds and other water bodies having stagnant water. General characteristics ''Spirogyra'' is very common in relatively clear eutrophic water, developing slimy filamentous green masses. In spring ''Spirogyra'' grows under water, but when there is enough sunlight and warmth they produce large amounts of oxygen, adhering as bubbles between the tangled filaments. The filamentous masses come to the surface and become visible as slimy green mats. ''Spirogyr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order ( la, wikt:ordo#Latin, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between Family_(biology), family and Class_(biology), class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include non- salty mineral-rich waters such as chalybeate springs. Fresh water may encompass frozen and meltwater in ice sheets, ice caps, glaciers, snowfields and icebergs, natural precipitations such as rainfall, snowfall, hail/ sleet and graupel, and surface runoffs that form inland bodies of water such as wetlands, ponds, lakes, rivers, streams, as well as groundwater contained in aquifers, subterranean rivers and lakes. Fresh water is the water resource that is of the most and immediate use to humans. Water is critical to the survival of all living organisms. Many organisms can thrive on salt water, but the great majority of higher plants and most insects, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds need fresh water to survive. Fresh wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charophyta
Charophyta () is a group of freshwater green algae, called charophytes (), sometimes treated as a division, yet also as a superdivision or an unranked clade. The terrestrial plants, the Embryophyta emerged within Charophyta, possibly from terrestrial unicellular charophytes, with the class Zygnematophyceae as a sister group. The clade Streptophyta may be formed by placing Embryophyta within the Charophyta. The Embryophyta may already be included in the Charophyta, in which case it is a synonym of the Streptophyta. The sister group of the charophytes are the Chlorophyta. In some charophyte groups, such as the Zygnematophyceae or conjugating green algae, flagella are absent and sexual reproduction does not involve free-swimming flagellate sperm. Flagellate sperm, however, are found in stoneworts ( Charales) and Coleochaetales, orders of parenchymatous charophytes that are the closest relatives of the land plants, where flagellate sperm are also present in all except the coni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |