|
Zone Rouge (First World War)
The ''Zone Rouge'' (English: Red Zone) is a chain of non-contiguous areas throughout northeastern France that the French government isolated after the First World War. The land, which originally covered more than , was deemed too physically and environmentally damaged by conflict for human habitation. Rather than attempt to immediately clean up the former battlefields, the land was allowed to return to nature. Restrictions within the ''Zone Rouge'' still exist today, although the control areas have been greatly reduced. The ''Zone Rouge'' was defined just after the war as "Completely devastated. Damage to properties: 100%. Damage to Agriculture: 100%. Impossible to clean. Human life impossible". Under French law, activities such as housing, farming, or forestry were temporarily or permanently forbidden in the ''Zone Rouge'', because of the vast amounts of human and animal remains, and millions of items of unexploded ordnance contaminating the land. Some towns and villages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Zone Map-fr
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a secondary color (made from magenta and yellow) in the CMYK color model, and is the complementary color of cyan. Reds range from the brilliant yellow-tinged scarlet and vermillion to bluish-red crimson, and vary in shade from the pale red pink to the dark red burgundy. Red pigment made from ochre was one of the first colors used in prehistoric art. The Ancient Egyptians and Mayans colored their faces red in ceremonies; Roman generals had their bodies colored red to celebrate victories. It was also an important color in China, where it was used to color early pottery and later the gates and walls of palaces. In the Renaissance, the brilliant red costumes for the nobility and wealthy were dyed with kermes and cochineal. The 19th century brought the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
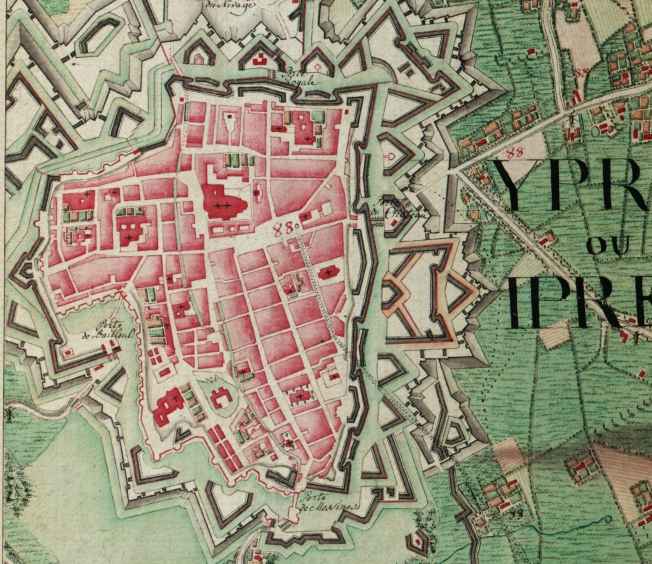
Ypres
Ypres ( , ; nl, Ieper ; vls, Yper; german: Ypern ) is a Belgian city and municipality in the province of West Flanders. Though the Dutch name is the official one, the city's French name is most commonly used in English. The municipality comprises the city of Ypres/Ieper and the villages of Boezinge, Brielen, Dikkebus, Elverdinge, Hollebeke, Sint-Jan, Vlamertinge, Voormezele, Zillebeke, and Zuidschote. Together, they are home to about 34,900 inhabitants. During the First World War, Ypres (or "Wipers" as it was commonly known by the British troops) was the centre of the Battles of Ypres between German and Allied forces. History Origins before First World War Ypres is an ancient town, known to have been raided by the Romans in the first century BC. It is first mentioned by name in 1066 and is probably named after the river Ieperlee on the banks of which it was founded. During the Middle Ages, Ypres was a prosperous Flemish city with a population of 40,000 in 1200 AD, renow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Somme (department)
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France Geography Articles Needing Translation From French Wikipedia
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin. Its eighteen integral regions (five of which are overseas) span a combined area of and contain close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Disasters In Europe
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale from microscopic to global in extent. It can also be subdivided according to its attributes. Examples include the marine environment, the atmospheric environment and the terrestrial environment. The number of biophysical environments is countless, given that each living organism has its own environment. The term ''environment'' can refer to a singular global environment in relation to humanity, or a local biophysical environment, e.g. the UK's Environment Agency. Life-environment interaction All life that has survived must have adapted to the conditions of its environment. Temperature, light, humidity, soil nutrients, etc., all influence the species within an environment. However, life in turn modifies, in various forms, its conditions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environment Of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecotoxicology
Ecotoxicology is the study of the effects of toxic chemicals on biological organisms, especially at the population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecotoxicology is a multidisciplinary field, which integrates toxicology and ecology. The ultimate goal of ecotoxicology is to reveal and predict the effects of pollution within the context of all other environmental factors. Based on this knowledge the most efficient and effective action to prevent or remediate any detrimental effect can be identified. In those ecosystems that are already affected by pollution, ecotoxicological studies can inform the choice of action to restore ecosystem services, structures, and functions efficiently and effectively. Ecotoxicology differs from environmental toxicology in that it integrates the effects of stressors across all levels of biological organisation from the molecular to whole communities and ecosystems, whereas environmental toxicology includes toxicity to humans and often focus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Somme
The Battle of the Somme ( French: Bataille de la Somme), also known as the Somme offensive, was a battle of the First World War fought by the armies of the British Empire and French Third Republic against the German Empire. It took place between 1 July and 18 November 1916 on both sides of the upper reaches of the Somme, a river in France. The battle was intended to hasten a victory for the Allies. More than three million men fought in the battle of whom one million were wounded or killed, making it one of the deadliest battles in human history. The French and British had committed themselves to an offensive on the Somme during the Chantilly Conference in December 1915. The Allies agreed upon a strategy of combined offensives against the Central Powers in 1916 by the French, Russian, British and Italian armies, with the Somme offensive as the Franco-British contribution. Initial plans called for the French army to undertake the main part of the Somme offensive, supported on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Of The Total Environment
''Science of the Total Environment'' is a weekly international peer-reviewed scientific journal covering environmental science. It was established in 1972 and is published by Elsevier. The editors-in-chief are Damià Barceló (Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas), Jay Gan (University of California, Riverside) and Philip Hopke (University of Rochester). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 10.753. Controversies The October 2020 article suggesting that amulets may prevent COVID-19 has been met with skepticism even among the listed coauthors. As of November 2020, the article was under "temporary removal". It was later withdrawn at the request of the authors. References Ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
No Man's Land
No man's land is waste or unowned land or an uninhabited or desolate area that may be under dispute between parties who leave it unoccupied out of fear or uncertainty. The term was originally used to define a contested territory or a dumping ground for refuse between fiefdoms. In modern times, it is commonly associated with World War I to describe the area of land between two enemy trench systems, not controlled by either side. Coleman p. 268 The term is also used metaphorically, to refer to an ambiguous, anomalous, or indefinite area, in regards to an application, situation, or jurisdiction. It has sometimes been used to name a specific place. Origin According to Alasdair Pinkerton, an expert in human geography at Royal Holloway, University of London, the term is first mentioned in Domesday Book (1086), to describe parcels of land that were just beyond the London city walls. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' contains a reference to the term dating back to 1320, spell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Harvest
The iron harvest () is the annual collection of unexploded ordnance, barbed wire, shrapnel, bullets and congruent trench supports collected by Belgian and French farmers after ploughing their fields. The harvest generally consists of material from the First World War, which is still found in large quantities across the former Western Front. Unexploded munitions During World War I, an estimated one tonne of explosives was fired for every square metre of territory on the Western front. As many as one in every three shells fired did not detonate. In the Ypres Salient, an estimated 300 million projectiles that the British and the German forces fired at each other during World War I were duds, and most of them have not been recovered. According to its website, DOVO, the demining unit of the Belgian armed forces defused more than 200 tons of ammunition in 2019. Unexploded weapons—in the form of shells, bullets, and grenades—buried themselves on impact or were otherwise quic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |