|
Zlatograd Dialect
The Zlatograd dialect is a Bulgarian dialect, member of the Rup or Southeastern Bulgarian dialects. The Zlatograd dialect is spoken in the southwestern part of the Eastern Rhodopes, i.e. in the town of Zlatograd, as well as a number of neighbouring villages and towns, e.g. Nedelino, Kirkovo, etc. The Zlatograd dialect is most closely related to the eastern and western Rup dialects, but also shares a number of phonological and morphological characteristics with the Rhodopean dialects. Thus, it is usually considered to be transitional between the two groups. Phonological and morphological characteristics * The reflex of Old Church Slavonic yat is usually before a hard syllable and broad e () before a soft syllable: ''бял/бли'' instead of formal Bulgarian ''бял/бели'' (white). However, there are also a number of cases where the reflex of yat is even before a soft syllable: ''врме'' vs. formal Bulgarian ''време''. This a feature the Zlatograd dialect shares with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Language
Bulgarian (, ; bg, label=none, български, bălgarski, ) is an Eastern South Slavic language spoken in Southeastern Europe, primarily in Bulgaria. It is the language of the Bulgarians. Along with the closely related Macedonian language (collectively forming the East South Slavic languages), it is a member of the Balkan sprachbund and South Slavic dialect continuum of the Indo-European language family. The two languages have several characteristics that set them apart from all other Slavic languages, including the elimination of case declension, the development of a suffixed definite article, and the lack of a verb infinitive. They retain and have further developed the Proto-Slavic verb system (albeit analytically). One such major development is the innovation of evidential verb forms to encode for the source of information: witnessed, inferred, or reported. It is the official language of Bulgaria, and since 2007 has been among the official languages of the Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
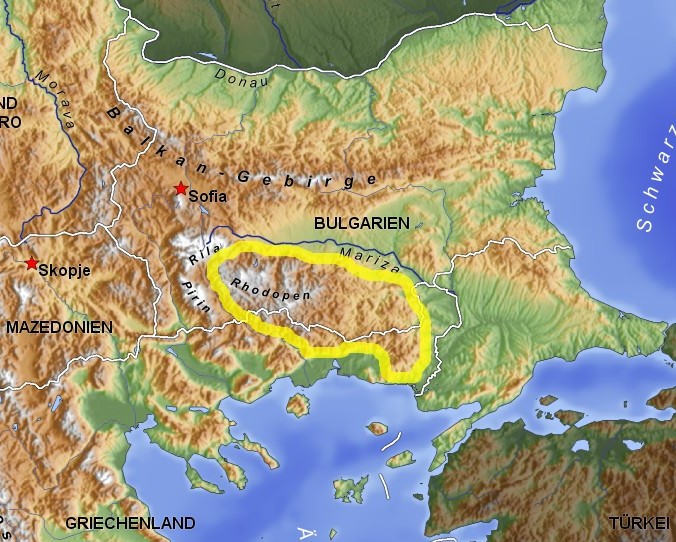
Rup Dialects
The Rup dialects, or the Southeastern dialects, are a group of Bulgarian dialects located east of the yat boundary, thus being part of the Eastern Bulgarian dialects. The range of the Rup dialects includes the southern part of Thrace, i.e. Strandzha, the region of Haskovo, the Rhodopes and the eastern half of Pirin Macedonia. Overview Before the Balkan wars and World War I, the Rup dialects covered a much larger territory, including vast areas of Eastern Thrace, Western Thrace and the eastern part of Greek Macedonia. Following the wars, most of the Bulgarian population in these areas fled or resettled to Bulgaria and nowadays, the Rup dialects outside Bulgaria are spoken only by the Muslim Bulgarians (Pomaks) in Western Thrace in Greece. Unlike the Northwestern or the Balkan dialects, the dialects included in the Rup group are not uniform and have vastly different phonological characteristics. What brings them together is the vast array of reflexes of Old Church Slavonic ѣ ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodopes
The Rhodopes (; bg, Родопи, ; el, Ροδόπη, ''Rodopi''; tr, Rodoplar) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at . The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge. A significant part of Bulgaria's hydropower resources are located in the western areas of the range. There are a number of hydro-cascades and dams used for electricity production, irrigation, and as tourist destinations. In Greece, there are also the hydroelectric power plants of Thisavros and Platanovrysi. The Rhodopes have a rich cultural heritage including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zlatograd
Zlatograd ( bg, Златоград, , ) is a town in Smolyan Province, southern-central Bulgaria. It is the administrative centre of the homonymous Zlatograd Municipality. In December 2009, the town had a population of 7,110.Bulgarian National Statistical Institute - towns in 2009 It is located 60 km from the province centre of . The border is 5 km from the town. The cross-border Zlatograd - Thermes (Greece) road was inaugurated on 15 January 2010. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nedelino
Nedelino ( bg, Неделино ) is a town and municipality in the Rhodope Mountains of the Smolyan Province, southern Bulgaria Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon .... The former name of Nedelino was Uzundere (until 1934), which means "Long Creek". Image:Building of Nedelino Municipality.jpg, Municipality Building in Nedelino Image:Nedelino, panorama 2004.jpg , Nedelino, panorama 2004 References Towns in Bulgaria Cities and towns in the Rhodopes Populated places in Smolyan Province {{Smolyan-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkovo
Kirkovo ( bg, Кирково) is a village in Kardzhali Province, southern Bulgaria, near the Greek Greek may refer to: Greece Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group. *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family. **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ... border. External linksKirkovo municipality Villages in Kardzhali Province {{Kardzhali-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serres-Nevrokop Dialect
The Ser-Drama-Lagadin-Nevrokop dialect is a dialect currently treated both in the contexts of the southeastern group of Bulgarian dialects and the southeastern subgroup of dialects of the Macedonian. Prior to the codification of standard Macedonian in 1945, the dialects of Macedonia were classified as Bulgarian.Mazon, Andre. ''Contes Slaves de la Macédoine Sud-Occidentale: Etude linguistique; textes et traduction''; Notes de Folklore, Paris 1923, p. 4. The dialect is dynamic and is well known for the shortening of the words, and also characterised by the excessive use of for the Proto-Slavic yat even in cases where standard Bulgarian has , a feature which is typical for a number of dialects spoken in southern and southwestern Bulgaria (e.g. the Thracian dialect). The Ser-Drama-Lagadin-Nevrokop dialect is closely related to the neighbouring dialects. It is closer to all Eastern Bulgarian dialects than to all Western. Macedonian shares much less features with the dialect than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thracian Dialect
The Thracian dialect is a dialect of the Bulgarian language, member of the Rup or Southeastern Bulgarian dialects. The present range of the dialect includes the regions of Haskovo, Parvomay, Elhovo, Harmanli, Svilengrad, Topolovgrad and Ivaylovgrad. In the past, the dialect was spoken on a much larger territory and extended far down into Eastern and Western Thrace, now in Turkey and Greece, respectively. Following the Balkan wars, the Bulgarian population there was forced to flee to Bulgaria, settling mostly in the regions of Burgas and Haskovo, Yambol and Plovdiv. Phonological and morphological characteristics * Lack of consonants дж and дз and are pronounced instead: жам vs. джам ('windowpane') * Disappearance of from the consonant group : сесра vs. formal Bulgarian сестра ('sister') * Personal pronouns нега vs. formal Bulgarian него ('him') and хми vs. formal Bulgarian им * Future tense particles жъ, шъ, зъ in the northern subd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Language
Russian (russian: русский язык, russkij jazyk, link=no, ) is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language mainly spoken in Russia. It is the First language, native language of the Russians, and belongs to the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of four living East Slavic languages, and is also a part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages. Besides Russia itself, Russian is an official language in Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, and is used widely as a lingua franca throughout Ukraine, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to some extent in the Baltic states. It was the De facto#National languages, ''de facto'' language of the former Soviet Union,1977 Soviet Constitution, Constitution and Fundamental Law of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, 1977: Section II, Chapter 6, Article 36 and continues to be used in public life with varying proficiency in all of the post-Soviet states. Russian has over 258 million total speakers worldwide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smolyan Dialect
The Smolyan dialect or Central Rhodope dialect is a Bulgarian dialect of the Rhodopean group of the Rup dialects. Its range includes most of the Central Rhodopes, i.e. the region of Smolyan. Its immediate neighbours are the Rhodopean Hvoyna dialect to the north, the Serres-Nevrokop dialect and the Razlog dialect to the west and the Turkish dialects of the Turkish population in the Eastern Rhodopes. To the south, the Smolyan dialect crosses the Greek-Bulgarian border and is spoken by much of the Muslim Bulgarian (Pomak) population in Western Thrace. As a result of the rugged mountainous terrain and the century-long isolation of the region from the rest of the country, the Smolyan dialect is the most idiosyncratic of all Bulgarian dialects (including the Western Central Macedonian dialects) and is not readily understandable even for its immediate neighbours. Phonological and morphological characteristics * The most important phonological characteristic of the Smolyan dialect is the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |