|
Zion Hill Mission
The Zion Hill Mission was a Christian mission founded in the area now known as Nundah, Queensland by German Lutheran missionaries. The mission is notable as being the first free European settlement in what is now the state of Queensland. Despite limited success at converting the local Aboriginal Australians to Christianity, many of the missionaries later became pioneers and farmers in the district, shaping the social fabric of the North Brisbane area for decades to come. Foundation The idea of establishing a Christian mission in the Moreton Bay district was the idea of John Dunmore Lang, who had ambitious plans to establish a series of missions along the Australian coast north of Sydney, ostensibly in order to bring Christianity to the Aboriginal peoples, but also to pacify them and prevent attacks on shipwrecked European sailors, as had happened in the case of the '' Stirling Castle'' incident some years prior. Lang justified the placement of the mission far from the main col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zion Hill Mission Sketch By Gerler
Zion ( he, צִיּוֹן ''Ṣīyyōn'', LXX , also variously transliterated ''Sion'', ''Tzion'', ''Tsion'', ''Tsiyyon'') is a placename in the Hebrew Bible used as a synonym for Jerusalem as well as for the Land of Israel as a whole (see Names of Jerusalem). The name is found in 2 Samuel (5:7), one of the books of the Hebrew Bible dated to before or close to the mid-6th century BCE. It originally referred to a specific hill in Jerusalem ( Mount Zion), located to the south of Mount Moriah (the Temple Mount). According to the narrative of 2 Samuel 5, Mount Zion held the Jebusite fortress of the same name that was conquered by David and was renamed the City of David. That specific hill ("mount") is one of the many squat hills that form Jerusalem, which also includes Mount Moriah (the Temple Mount), the Mount of Olives, etc. Over many centuries, until as recently as the Ottoman era, the city walls of Jerusalem were rebuilt many times in new locations, so that the particular hill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typhoid
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. This is commonly accompanied by weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, headaches, and mild vomiting. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases, people may experience confusion. Without treatment, symptoms may last weeks or months. Diarrhea may be severe, but is uncommon. Other people may carry the bacterium without being affected, but they are still able to spread the disease. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever, along with paratyphoid fever. ''S. enterica'' Typhi is believed to infect and replicate only within humans. Typhoid is caused by the bacterium ''Salmonella enterica'' subsp. ''enterica'' serovar Typhi growing in the intestines, peyers patches, mesenteric lymph nodes, spleen, liver, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Downfall Creek
Downfall may refer to: Books * ''The Downfall'' (novel), an 1892 book by Émile Zola * ''Downfall: The End of the Imperial Japanese Empire'', a 1999 book by Richard B. Frank about the last days of World War II * ''Downfall'', a 2001 Dragonlance novel by Jean Rabe * ''Downfall'', a 2007 novel in the LEGO ''Bionicle Legends'' series * ''Downfall'' (book), a 2011 book about the political career of Tommy Sheridan Film and television * ''Downfall'' (1923 film), a 1923 German silent film * ''The Downfall'' (film) ( gr, Kataforos, link=no), a 1961 Greek film * ''Downfall'' (1997 film), a 1997 Korean film starring Shin Eun-gyeong * ''Downfall'' (2004 film) (german: Der Untergang, link=no), a 2004 German film about the last days of Nazi Germany * "Downfall" (''RahXephon'' episode) * ''Downfall'' (game show), an American game show, hosted by Chris Jericho * '' Downfall: The Case Against Boeing'', a 2022 documentary film about two fatal crashes of the Boeing 737 MAX and the subsequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zillmere, Queensland
Zillmere is a suburb in the City of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. In the , Zillmere had a population of 8,967 people. Geography As at 2008, Zillmere was approximately 60% residential and 40% industrial. History The Turrbal people occupied the region north of Brisbane River, including the area covered by Zillmere. With European settlement, the area came to be known as Zillman's Waterholes, named after Johann Leopold Zillmann (1813–1892), a Lutheran missionary who served at the mission station nearby at Nundah. In January 1872, the Brisbane Courier described Zillman's Waterholes as being situated between Cabbage Tree Creek and Downfall Creek. It was settled with twenty-seven small farmers residing on the land. At the time there were "two chapels, a brickyard and pottery". The settlers grew pineapples, pigs and other small crops. St John's Lutheran Church opened at 110 Church Road () in 1875. It was built from timber. It was enlarged in 1932. In 1984, the church was sold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kilcoy, Queensland
Kilcoy is a rural town and locality in the Somerset Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , the locality of Kilcoy had a population of 1,898 people. Geography The township is on the D'Aguilar Highway, north west of the state capital, Brisbane, and just to the north of Lake Somerset. The topography directly north of the town is dominated by the mountains of the Conondale Range and covered by forests, some of which are protected in state forests and the Conondale National Park. Kilcoy is located in the Somerset Region. Climate The Somerset region experiences a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification Cfa) with hot and humid summers and mild to warm winters with cool overnight temperatures. Median monthly rainfall at the Post Office weather Station in Kilcoy since records began in 1890 is . The highest recorded annual rainfall was in 1893, the year of the 1893 Brisbane flood also known as the Black February floods. Records of rainfall for the year of the 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squatting (pastoral)
Squatting is a historical Australian term that referred to someone who occupied a large tract of Crown land in order to graze livestock. Initially often having no legal rights to the land, squatters became recognised by the colonial government as owning the land by being the first (and often the only) European settlers in the area. Eventually, the term "squattocracy", a play on "aristocracy", came into usage to refer to squatters and the social and political power they possessed. Evolution of meaning The term ' squatter' derives from its English usage as a term of contempt for a person who had taken up residence at a place without having legal claim. The use of 'squatter' in the early years of British settlement of Australia had a similar connotation, referring primarily to a person who had 'squatted' on Aboriginal land for pastoral or other purposes. In its early derogatory context the term was often applied to the illegitimate occupation of land by ticket-of-leave convicts or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
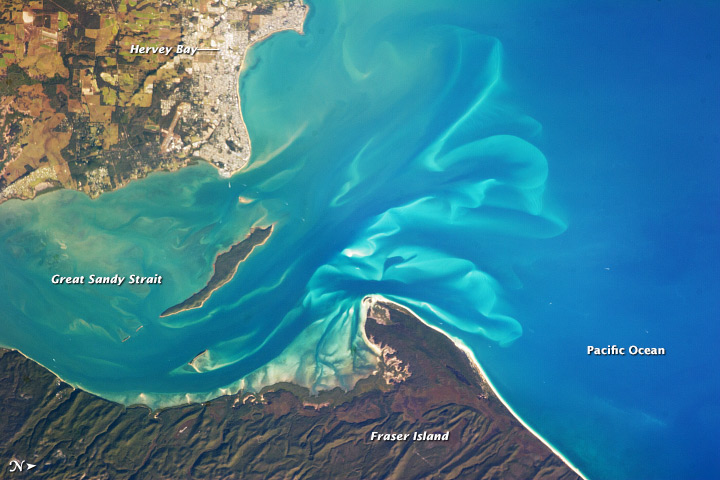
Wide Bay–Burnett
Wide Bay–Burnett is a region of the Australian state of Queensland, located between north of the state capital, Brisbane. The area's population growth has exceeded the state average over the past 20 years, and it is forecast to grow to more than 430,000 by 2031. It is the subject of the ''Draft Wide Bay–Burnett Regional Plan'', which aims to facilitate this growth while protecting over 90% of the region from urban development. Wide Bay was the name given by the early European explorer James Cook to a coastal indentation as he was sailing past Double Island Point. As the Port of Maryborough developed during the 19th century Wide Bay became well known as ships passed through the area before entering the Great Sandy Strait and the port. Geography The coastal parts of the region are centered on the city of Maryborough. The inland is defined by a series of ranges which create the water of the Burnett River. In the southeast of the region is a coastal area known as Cooloola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunya Mountains
The Bunya Mountains are a distinctive set of peaks forming an isolated section of the Great Dividing Range in southern Queensland. The mountain range forms the northern edge of the Darling Downs in the locality also called Bunya Mountains near Bell and Dalby. The mountains are south of Kingaroy and just to the south west of Nanango. The range is the remains of a shield volcano which was built from numerous basalt lava flows about 23-24 million years ago. In 2009 as part of the Q150 celebrations, the Bunya Mountains was announced as one of the Q150 Icons of Queensland for its role as a "Natural attraction". Landforms The range rises to an average elevation of 975 m; however the two tallest mountains on the range, Mount Kiangarow and Mount Mowbullan, rise to over 1,100 m. Slopes facing the north east are part of the Burnett River catchment, those on the south east make up part of the Brisbane River catchment, while those facing the south west belong to the Conda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Gipps
Sir George Gipps (23 December 1790 – 28 February 1847) was the Governor of New South Wales, Governor of the British colony of New South Wales for eight years, between 1838 and 1846. His governorship oversaw a tumultuous period where the rights to land were bitterly contested in a three way struggle between the colonial government, Aboriginal people and wealthy graziers known as Squatting (pastoral), squatters. The management of other major issues such as the end of convict transportation, large immigration programs and the introduction of majority elected representation also featured strongly during his tenure. Gipps is regarded as a man who brought a high moral and intellectual standard to the position of governor, but was ultimately defeated in his aims by the increasing power and avarice of the squatters. Early life Gipps was born in December 1790 at Ringwould, Kent, England, the son of Rev George Gipps and Susannah Bonella Venn. Both his parents were from wealthy families, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor Of New South Wales
The governor of New South Wales is the viceregal representative of the Australian monarch, King Charles III, in the state of New South Wales. In an analogous way to the governor-general of Australia at the national level, the governors of the Australian states perform constitutional and ceremonial functions at the state level. The governor is appointed by the king on the advice of the premier of New South Wales, and serves in office for an unfixed period of time—known as serving ''At His Majesty's pleasure''—though five years is the general standard of office term. The current governor is retired jurist Margaret Beazley, who succeeded David Hurley on 2 May 2019. The office has its origin in the 18th-century colonial governors of New South Wales upon its settlement in 1788, and is the oldest continuous institution in Australia. The present incarnation of the position emerged with the Federation of Australia and the ''New South Wales Constitution Act 1902'', which defined t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |